Hydrocarbons
| Hydrocarbons |
 methane |
 Ethane |
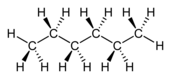 n -hexane |
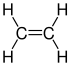 Ethene |
 Propene |
|
Ethine |
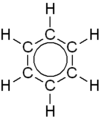 benzene |

The hydrocarbons are a group of chemical compounds that only consist of carbon and hydrogen . This group of substances is diverse, as hydrocarbons can contain carbon chains , rings or combinations thereof. There are several subgroups such as alkanes , alkenes , alkynes and aromatics (arenes). The hydrocarbons have achieved great technical importance primarily through their use as fossil fuels and in organic synthesis .
Occurrence
Hydrocarbons are naturally found in very large quantities, especially in crude oil and natural gas , which is why these two mineral resources are also summarized under the umbrella term fossil hydrocarbons . They are also common in many plants such. B. as terpenes , carotenoids and rubber , and so they are fossilized in coal . Simple hydrocarbons, especially methane , are metabolic products of some microorganisms. In space , hydrocarbons, mostly in the form of methane and ethane , have been found on comets, planets and moons as well as in interstellar matter.
Systematics
Hydrocarbons can be divided into aromatic and aliphatic hydrocarbons, in which unsaturated and saturated compounds are distinguished.
At saturated hydrocarbons, there are chemical compounds which exclusively C-C single bonds contained. They are divided into chain-shaped and ring-shaped connections. Chains are systematically referred to as alkanes . The simplest and best-known alkanes are methane (CH 4 ), ethane (C 2 H 6 ), and propane (C 3 H 8 ). In general, the empirical formula for the homologous series of chain-like alkanes is C n H 2n + 2 . Ring-shaped alkanes are called cycloalkanes . Their general empirical formula for the homologous series is C n H 2n .
Unsaturated hydrocarbons can be divided into alkenes and alkynes . The alkenes are compounds that contain C = C double bonds . The simplest representative of this group of substances is ethene , also called ethylene (C 2 H 4 ). The simplest n -alkenes with only one double bond generally have the empirical formula C n H 2n . Compounds with at least two C =C double bonds, such as 1,3-butadiene , are referred to as polyenes . Cycloalkenes are cyclic hydrocarbons such as cyclopentadiene . Here there are CC double bonds within a carbon ring. Alkynes are hydrocarbons that contain one or more CC triple bonds . The best-known representative is ethyne (acetylene) with the empirical formula C 2 H 2 . Accordingly, alkynes with a triple bond generally have the empirical formula for the homologous series C n H 2n-2 . Saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons are collected under the name of aliphatic hydrocarbons , especially in the petrochemical industry .
The third important group of hydrocarbons are the aromatic hydrocarbons . These are hydrocarbons that are aromatic and usually have C 6 rings (arenes). The best-known representative is benzene (C 6 H 6 ). The polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are a subgroup of aromatics . They are compounds that consist of several benzene rings attached to one another. A well-known representative is naphthalene (C 10 H 8 ).
Hydrocarbons, which correspond in structure to Platonic solids , are called Platonic hydrocarbons . These include tetrahedrane , cubane and dodecahedrane .
Hydrocarbons with the same empirical formula can have different structural formulas (linkages of the carbon atoms). They are then constitutional isomers . They are found in alkanes from butanes and in most other hydrocarbons. The classic cis - trans isomerism sometimes occurs on CC double bonds. Simple branched hydrocarbons can, as the example 3-methylhexane shows, be chiral . The carbon atom in position number 3 becomes the stereocenter , the connection is asymmetric and a distinction is made between the ( R ) - and ( S ) -enantiomers.
properties
Many non-polar hydrocarbons are insoluble in water, but are readily soluble in most organic solvents . This means that hydrocarbons are hydrophobic , i.e. also lipophilic .
Gaseous hydrocarbons burn very quickly and with a hot flame; the energy released is great. Liquid hydrocarbons with a low boiling point evaporate easily; Due to their low flash point , fires are easy to start. The optimal (complete) combustion of hydrocarbons produces water and carbon dioxide , while insufficient (incomplete) combustion can also produce carbon monoxide or carbon (soot). The reactivity of the alkanes depends on their chain length. Long-chain alkanes are relatively inert (not very reactive). If hydrocarbons burn with a sooty flame, this can also be an indication of a higher carbon content in the compound (longer chain length).
In addition to redox reactions when they are burned, alkanes enter into substitution reactions , whereby hydrogen atoms can be exchanged for other atoms and groups of atoms, but mainly halogens. Alkenes and alkynes, on the other hand, are very reactive and react with many substances by adding to the CC multiple bond ( addition reaction ).
The comparatively high tendency of the carbon atoms to form chains CCC-… (concatenation or katenization, English catenation , from Latin catena , chain ') is decisive for the variety of hydrocarbons and is based on the higher binding energy of the covalent C – C bonds (356 kJ / mol) compared to higher homologues of the 14th group (e.g. Si – Si (226 kJ / mol), Ge – Ge (186 kJ / mol)). Furthermore, the C – H bond is also thermodynamically more stable than the Si – H, Ge – H or Sn – H bond. This explains why there is a greater variety of hydrocarbons than silicon or germanium hydrocarbons.
use

Alkanes are often used as fossil fuels in mixtures such as biogas , liquid gas , gasoline , diesel fuel , heating oil , kerosene and petroleum . The most important alkanes are the low molecular weight alkanes methane , ethane and propane . Alkanes such as n -butane , isopentane , various hexanes and the cycloalkane cyclohexane are components of motor gasoline .
The hydrocarbons serve as starting materials for a large number of industrially important chemical synthesis processes. Alkenes such as ethene and cyclohexene , alkynes such as ethyne and polyenes such as 1,3-butadiene , isoprene and cyclopentadiene are of industrial importance . Many arenes are of industrial importance, including benzene , toluene , xylene and styrene .
The polymerization products of hydrocarbons such as polystyrene , polyethylene , polypropylene , polyethine , many copolymers and halogenated hydrocarbon polymers such as polyvinyl chloride and polytetrafluoroethylene are important . In addition, hydrocarbons serve as lipophilic solvents.
Ecological damage
Hydrocarbons make up - according to the definition of the World Health Organization WHO - the main part of the volatile organic compounds (abbreviated also VOC); if they are emitted, these are considered to be environmentally harmful. In order to reduce emissions z. B. in Switzerland levied an incentive tax on these emissions . Next has methane gas a significant greenhouse effect .
See also
literature
- Handbook of Experimental Chemistry Secondary Area II, Volume 9, Hydrocarbon, Aulis Verlag Deubner & Co. KG.
- Karl-Heinz Lautenschläger, Werner Schröter, Joachim Teschner, Hildegard Bibrack, Taschenbuch der Chemie , 18th edition, Harri Deutsch, Frankfurt (Main), 2001.
- JC Jones: Hydrocarbons. Physical Properties and their Relevance to Utilization . JC Jones & Ventus Publishing ApS, 2010. ISBN 978-87-7681-513-4 ( PDF at bookboon.com ).
- Hartung, Birgitta (1984) Potential hydrocarbon host rocks in the deep sea. Geosciences in our time; 2, 6; 208-211; doi : 10.2312 / geosciences . 1984.2.208 .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on hydrocarbons . In: IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology (the “Gold Book”) . doi : 10.1351 / goldbook.H02889 Version: 2.3.2.
- ↑ Catherine E. Housecroft, Alan G. Sharpe: Inorganic Chemistry , 4th Edition, Pearson Education, Amsterdam, 2012, pp. 433f.
- ↑ SAEFL : The air pollution in the cantons ., 1997
