Calcium propionate
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
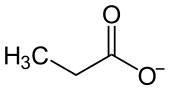
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Calcium propionate | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 10 CaO 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 186.22 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
> 300 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Calcium propionate is an odorless, colorless salt of propionic acid in its pure form with the empirical formula C 6 H 10 CaO 4 . Calcium propionate decomposes at around 300 ° C. If the compound contains unreacted propionic acid from the production process, it has a pungent odor. The fungistatic inhibits the growth of fungi and is used as a preservative (E 282) in food - especially for bread and other baked goods . Calcium propionate is also used in cosmetics or as a feed additive to compound feed .
Manufacturing
Calcium propionate is obtained in a direct synthesis; here calcium oxide and calcium hydroxide are placed in a mixer and reacted with propionic acid. Pure calcium hydroxide could also be used, but since water is formed as a by-product, calcium oxide can be used, which reacts with the water to form calcium hydroxide. Excess water is evaporated under negative pressure (0.6 to 0.95 bar ) at approx. 70–90 ° C.
- Calcium oxide and propionic acid react when heated and under pressure to form calcium propionate and water
Sub-steps of the reaction:
- a)
- b)
properties
Calcium propionate crystallizes as a monohydrate, which releases its water of crystallization at 100 ° C. It decomposes at 350 - 450 ° C with the formation of calcium carbonate .
safety instructions
With prolonged administration of propionic acid and propionates in the feed of rats in doses between 0.6 and 5%, these cause changes in the forestomach ( thickening and inflammation). However, this is classified as a species-specific reaction for rats, since no such effects were observed in other animal species such as mice and rabbits.
See also
- Sodium propionate (E 281)
- Potassium propionate (E 283)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on E 282: Calcium propionate in the European database for food additives, accessed on June 27, 2020.
- ↑ Entry on CALCIUM PROPIONATE in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on February 24, 2020.
- ^ A b Richard J. Lewis, Sr .: Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary . 15th edition. Wiley-Interscience, 2007, ISBN 978-0-471-76865-4 (English).
- ↑ a b c data sheet Calcium propionate hydrate, 97% from AlfaAesar, accessed on December 7, 2019 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Data sheet calcium propionate from Acros, accessed on February 24, 2013.
- ↑ a b Kenkyu Nenpo - Tokyo-toritsu Eisei Kenkyusho. Annual Report of Tokyo Metropolitan Research Laboratory of Public Health. Vol. 27, Pg. 159, 1976.
- ↑ a b Entry on calcium propionate in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ^ A. Renard: "Sur les propionates métalliques" in Comptes rend. hebd. 1887 , 104 , pp. 913-917. Full text
- ↑ CA O'Connell, D. Dollimore: "A study of the decomposition of calcium propionate, using simultaneous TG-DTA" in Thermochimica Acta 2000 , 357-358 , pp. 79-87. doi : 10.1016 / S0040-6031 (00) 00371-3
- ^ AK Galwey, ME Brown: Thermal Decomposition of Ionic Solids: Chemical Properties and Reactivities of Ionic Crystalline Phases . Elsevier, 1999, ISBN 0-08-054279-4 , pp. 451 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ H.-G. Classen, PS Elias, WP Hammes, M. Winter: Toxicological-hygienic assessment of food ingredients and additives. Behr's Verlag, 2001, ISBN 978-3-86022-806-7 .

![{\ mathrm {\ \! \ {\ Biggr]} _ {2}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/574adab1409cb81da6c38bb738ad111e61bbb2d9)
![{\ displaystyle \ mathrm {CaO \ + \ 2 \ C_ {2} H_ {5} {-} COOH \ {\ xrightarrow [{0.6-0.95bar}] {\ triangle}} \ Ca (C_ {2 } H_ {5} {-} COO) _ {2} \ + \ H_ {2} O \ uparrow}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1fc96dd77dcc0b172bef78c2cecb0e23694ff06e)

