Sodium propionate
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
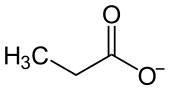 |
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Sodium propionate | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 3 H 5 NaO 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
hygroscopic white powder with a characteristic odor |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 96.06 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
287 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Sodium propionate is the sodium salt of propionic acid and thus a propionate , which also includes calcium and potassium propionate . Propionates, and propionic acid in general, are present in many foods, such as cheese (Swiss cheese: 3105.4 mg / kg), coffee (87.7 mg / kg) or seafood (97.4 mg / kg).
Manufacturing
Sodium propionate is made using propionic acid, sodium hydroxide , hydrogen peroxide, and water. The reaction is followed by filtering and drying. The dry matter is sieved and the sodium propionate obtained is packaged. When sodium propionate is heated with sulfuric acid , the propionic acid becomes olfactory (smell) recognizable.
properties
Sodium propionate is a white hygroscopic salt of propionic acid that melts at 287 ° C. Sodium propionate is broken down in the gastrointestinal tract of humans, so that cations and propionic acid are formed.
use
Sodium propionate is used in the food industry as a nutritional or food additive z. B. used as a preservative . It is also used, for example, as a fungistatic (to avoid mold infestation when storing grain) and as a feed additive (e.g. in dairy cows to reduce the risk of ketosis ).
Sodium propionate and other propionates are by the European Food Safety Authority - classified as safe and approved as a food additive (EFSA European Food Safety Authority). Certain foods, such as B. bread and baked goods can contain up to 3000 mg / kg.
safety instructions
Sodium propionate irritates the skin, mucous membranes, eyes and airways in high doses. However, when dermal exposure to solutions with levels of up to 20%, neither local nor systemic effects are generally expected. The administration of sodium propionate to dogs (1282.5 mg / kg / day) as part of a test for safety in humans did not reveal any toxicological abnormalities within 104 weeks. There were no behavioral problems or serious changes in biometric data. In toxicological studies with mice, rabbits and rats, sodium propionate showed effects on the behavior of the animals with relatively low acute toxicity ( LD 50 6.322 g / kg (mouse, oral) and 1.64 g / kg (rabbit, dermal)). sometimes excitement) and the respiratory system ( shortness of breath ). With prolonged administration of propionic acid and propionates in the feed of rats in doses between 0.6 and 5%, these cause changes in the forestomach ( thickening and inflammation). However, this is classified as a species-specific reaction for rats, since no such effects were observed in other animal species such as mice and rabbits. This fact is confirmed by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). In particular, the authority could not find any harmful facts in humans. This is due, among other things, to the fact that humans do not have a forestomach and a connection to human cell components has been excluded.
See also
- Propionic acid (E 280)
- Calcium propionate (E 282)
- Potassium propionate (E 283)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on E 281: Sodium propionate in the European database for food additives, accessed on June 27, 2020.
- ↑ entry to SODIUM PROPIONATE in CosIng database of the European Commission, accessed on 17 April 2020th
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on sodium propionate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on December 16, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Sodium propionate data sheet from Acros, accessed on February 22, 2010.
- ^ GWA Milne: Gardner's Commercially Important Chemicals Synonyms, Trade Names, and Properties . John Wiley & Sons, 2005, ISBN 0-471-73661-9 , pp. 573 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Nippon Eiseigaku Zasshi. Japanese Journal of Hygiene. , 1973, Vol. 28, p. 463.
- ↑ a b Entry on sodium propionate in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ^ Journal of Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology. 1949, Vol. 31, p. 60.
- ↑ a b European Food Safety Authority (EFSA): Scientific Opinion on the re-evaluation of propionic acid (E 280), sodium propionate (E 281), calcium propionate (E 282) and potassium propionate (E 283) as food additives. Ed .: EFSA Journal. Parma, Italy 2014, p. 42–43 , doi : 10.2903 / j.efsa.2014.3779 .
- ↑ European Food Safety Authority (EFSA): Scientific Opinion on the re-evaluation of propionic acid (E 280), sodium propionate (E 281), calcium propionate (E 282) and potassium propionate (E 283) as food additives. Ed .: EFSA Journal. Parma, Italy 2014, p. 12 , doi : 10.2903 / j.efsa.2014.3779 .
- ↑ Hager's Handbook of Pharmaceutical Practice - For pharmacists, drug manufacturers, druggists, doctors and medical officers. Second supplementary volume. Springer, Heidelberg, Germany.
- ↑ European Food Safety Authority (EFSA): Scientific Opinion on the re-evaluation of propionic acid (E 280), sodium propionate (E 281), calcium propionate (E 282) and potassium propionate (E 283) as food additives. Ed .: EFSA Journal. Parma, Italy 2014, p. 30 , doi : 10.2903 / j.efsa.2014.3779 .
- ↑ European Food Safety Authority (EFSA): Scientific Opinion on the re-evaluation of propionic acid (E 280), sodium propionate (E 281), calcium propionate (E 282) and potassium propionate (E 283) as food additives. Ed .: EFSA Journal. Parma, Italy 2014, p. 28–29 , doi : 10.2903 / j.efsa.2014.3779 .
- ↑ Gigiena i Sanitariya: HYSAAV . Vol. 35 (3) edition. 1970, p. 96 .
- ↑ H.-G. Classen, PS Elias, WP Hammes, M. Winter: Toxicological-hygienic assessment of food ingredients and additives . Behr's Verlag, 2001, ISBN 978-3-86022-806-7 .
- ↑ European Food Safety Authority (EFSA): Scientific Opinion on the re-evaluation of propionic acid (E 280), sodium propionate (E 281), calcium propionate (E 282) and potassium propionate (E 283) as food additives. Ed .: EFSA Journal. Parma, Italy 2014, p. 31 , doi : 10.2903 / j.efsa.2014.3779 .
