Carbendazim
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Carbendazim | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 9 H 9 N 3 O 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless and odorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 191.19 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.5 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
302–307 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
0.09 mPa (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
Switzerland: 10 mg m −3 (measured as inhalable dust ) |
|||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Carbendazim is a commonly used worldwide pesticide ( fungicide ) from the group of benzimidazole - carbamates .
Extraction and presentation
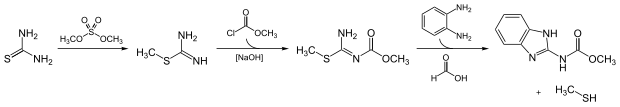
Carbendazim can be obtained by a multistep reaction. First, thiourea and dimethyl sulfate are reacted, which then react with methyl chloroformate in the presence of sodium hydroxide . The product reacts with o- phenylenediamine and formic acid to form carbendazim and methanethiol (methyl mercaptan).
properties
Carbendazim is a colorless, odorless solid that is practically insoluble in water. It has no anticholinesterase activity and has been produced commercially since the 1970s. It also occurs as a metabolite of other benzimidazole fungicides.
Use and approval
Carbendazim has been approved by the EU Commission as a fungicide in the cultivation of grain, sugar beet, rapeseed and maize. In Germany and Austria, it was used primarily in the cultivation of cereals, today no preparation with this active ingredient is permitted in either country. In Switzerland, the active ingredient was withdrawn in 2016. Products containing the active ingredient could be used until the end of 2018 with an expiry period. It is also used as an anti-fungal agent in silicone sealants.
safety instructions
Carbendazim is classified as germ cell mutagen category 1B (according to the CLP regulation ), so it is one of the substances for which damage to germ cells has been proven in animal experiments.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Entry on carbendazim in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 10, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on Carbendazim in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB) of the University of Hertfordshire , accessed on February 28, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d Environmental Health Criteria (EHC) for Carbendazim , accessed November 19, 2014.
- ↑ Entry on carbendazim in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers and / or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 10605-21-7 ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook . William Andrew, 1996, ISBN 0-8155-1853-6 , pp. 414 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Withdrawn active substances from Appendix 1 of the PSMV. August 1, 2019, accessed September 20, 2019 .
- ^ Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on carbendazim in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on March 11, 2016.