Quinacridone
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Linear trans isomer | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Quinacridone | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 20 H 12 N 2 O 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
red to purple powder |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 312.32 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.46 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water (0.02 mg ml −1 at 20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Quinacridone (short: QAC from English Quinacridone ) is an industrial organic pigment and organic semiconductor with red to purple hues. It is used for the production of lacquers , plastics and printing inks , as well as for various special applications (including artists' colors ). Quinacridone forms the basic structure of the quinacridone pigments .
Structure and properties
Quinacridone consists of five six-membered rings in a row and is structurally derived from the basic structure of the acridone by doubling the acridone structure and placing it next to one another in such a way that two peripheral six-membered rings overlap. The rings on both sides of the central six-membered ring are heteroaromatic and structurally correspond to the 4-pyridone .
| Isomeric quinacridones |
|---|
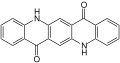 Linear trans isomer |
 Linear cis isomer |
 Angular cis isomer |
 Angular trans isomer |
The five rings can condense into both an angular and a linear quinaridone form ( related to the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pentacene ) . Both forms can also each as cis - and trans - isomer occur. This results in four different isomers of quinacridone, of which only the linear trans isomer is important.
The linear trans -quinacridone (CI Pigment Violet 19) can be crystallized in four different crystal structures - the crystal modifications alpha-I (cloudy red-violet), alpha-II (red), beta (red-violet) and gamma (red). The alpha modifications transform into other phases at high temperature. The beta and gamma modifications are characterized by high chemical and thermal stability - both modifications are therefore used for technical applications.
The crystal structure of the beta modification is characterized by the fact that the molecules are connected to a chain along the direction of the hydrogen bonds (H bonds), with each molecule being connected to two neighbors via two hydrogen bonds each. The gamma modification of quinacridone, on the other hand, is defined by a crystal structure in which the molecules are oriented in a crossed manner along the direction of the hydrogen bonds (hunter's fence structure). This packing motif connects each molecule with four neighbors via a hydrogen bond.
Quinacridone is found in most solvents such as B. water insoluble at room temperature. It is readily soluble in trifluoroacetic acid or in concentrated sulfuric acid. It is therefore not absorbed by the human body, i.e. H. it is not bioavailable and therefore non-toxic.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on quinacridone in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 28, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b Entry on quinacridone pigments. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on December 18, 2014.
- ^ A b E. F. Paulus, FJJ Leusen, MU Schmidt: Crystal structures of Quinacridones. In: Cryst. Closely. Comm. 2007 , 9 , pp. 131-143; doi: 10.1039 / B613059C .
- ↑ W. Herbst, K. Hunger: Industrial organic pigments. Production, properties, application . 2nd edition, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 1995, ISBN 3-527-28744-2 .
- ^ GD Potts, W. Jones, JF Bullock, SJ Andrews, SJ Maginn: The crystal structure of quinacridone: an archetypal pigment. In: J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1994 , pp. 2565-2566; doi: 10.1039 / C39940002565 .