Chlorpropham
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
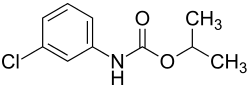
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Chlorpropham | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 12 ClNO 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
Flammable, colorless and odorless solid, technical grade yellow liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 213.66 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.29 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
41.4 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
149 ° C (2.7 hPa) with decomposition |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
1.33 m Pa (25 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
very bad in water (110 mg l −1 at 20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Chlorpropham is a chemical compound from the group of carbamates . It works as a herbicide and was the most frequently used growth regulator (germ inhibitor) in Germany .
history
Chlorpropham was first registered in the US in 1962 and a study of the substance was published in 1987. In the EU, registration followed in October 1996.
properties
Chlorpropham slowly decomposes in alkaline or acidic media and is chemically unstable at elevated temperatures. The effect on plants is based on the destruction of the dividing spindle as a mitosis inhibitor .
Effects
human
Chlorpropham is harmful to human health and possibly carcinogenic (category H351 ).
- Symptoms: irritation of the skin, eyes and respiratory organs.
- Side effects observed: Depression, seizures, movement disorders, nerve damage, digestive disorders with nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
water
- Amphibians and worms: Moderately toxic
- Fish and zooplankton: Slightly toxic
Chlorpropham breaks down slowly in water. At pH 4, 7 and 9 and at 40 ° C., 90% of the substance was still present in a solution after 32 days in the dark.
ground
Chlorpropham is only broken down in the ground at a moderate rate. Half-lives of 65 days at 15 ° C and 30 days at 29 ° C were observed. Chlorpropham has a certain potential to contaminate groundwater because it is water-soluble and is poorly absorbed by earth particles. On the other hand, chlorpropham is strongly absorbed by organic matter, so it is unlikely that the substance can penetrate soil with a high percentage of organic matter.
Areas of application and approval status
Chlorpropham was within the maximum residue amount regulation approved in Germany germination inhibitors for the treatment of potatoes for the purpose of preservation after harvest. Labeling was mandatory, but the substance did not have to be named.
Chlorpropham (CIPC) was allowed to be used as a sprout inhibitor in conventionally grown potatoes. The approval expired on July 31, 2019. However, it was allowed to sell until January 31, 2020 and can be used until October 8, 2020. It is then subject to disposal. Potato stores must be cleaned after the last use.
In this case, in Germany, a note “Treated after harvest” must appear either on the packaging or, in the case of loose goods, on the price tag. The maximum residue limit for potatoes is 500 times higher than for grain. Since the active ingredient penetrates the inside of the potatoes, it can also be detected in peeled and fried potato products. Contrary to popular belief, washing or peeling treated potatoes is not enough to remove the substance. Organic potatoes ( kbA ) must not be treated with Chlorpropham.
| Culture | fixed maximum amount (mg / kg) |
|---|---|
| Oilseeds | 0.1 |
| Tea (Camellia sinensis) | 0.1 |
| hop | 0.1 |
| Grain | 0.02 |
| other plant-based foods except potatoes | 0.05 |
| Potatoes | 10 |
The US government's environmental protection agency (EPA) specifies a maximum recommended daily dose (Reference Dose for Chronic Oral Exposure, RfD) of 0.2 mg / kg body weight (2007).
In Switzerland, the Federal Office for Agriculture only wants to decide on the withdrawal of approval after the evaluation , which should continue until mid-2020. Preparations containing chlorpropham are currently approved as sprout inhibitors for potatoes in Switzerland. In Switzerland, potatoes have a relatively high maximum residue level of 30 milligrams of chlorpropham per kilogram.
literature
- Sandra Müller: Matrix isolation experiments on model peptides (N-methylformamide and acetamidoacetone) or an amino acid precursor (dicyan) and on the herbicide chlorpropham . Bochum 2014, urn : nbn: de: hbz: 294-41401 (dissertation, Ruhr University Bochum).
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on chlorpropham in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Michael A. Kamrin, John H. Montgomery: Agrochemical and Pesticide Desk Reference on CD-ROM . CRC Press, 1999, ISBN 978-0-8493-2179-5 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ Entry on Chlorpropham in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ a b c extoxnet.orst.edu , visited October 1, 2007.
- ^ NRA Special Review of Chlorpropham. (PDF; 164 kB) Australian Pesticides and Veterinary Medicines Authority, November 1997, accessed on June 20, 2017 (English).
- ↑ a b Rahel Sahli: Poison in the French fries? - Potato herbicide under fire. In: srf.ch . November 27, 2019, accessed November 27, 2019 .
- ↑ Directive 2008/58 / EC of the Commission of August 21, 2008 for the 30th amendment of Directive 67/548 / EEC of the Council for the alignment of legal and administrative provisions for the classification, packaging and labeling of dangerous substances to technical progress , accessed on 20th June 2017 .
- ↑ a b c pesticideinfo.org , visited October 1, 2007.
- ↑ RHmV (Maximum Residue Quantity Ordinance) § 3a.
- ↑ EU approval for the active ingredient chlorpropham in plant protection products not renewed . Communication from the Federal Office for Consumer Protection and Food Safety dated June 21, 2019. Accessed on May 21, 2020.
- ↑ Cantonal Laboratory Zurich July 22, 2005 ( memento from June 24, 2007 in the Internet Archive ), visited October 1, 2007.
- ↑ Federal Office for Consumer Protection and Food Safety (BVL) , visited October 1, 2007.
- ↑ chlorpropham; CASRN 101-21-3. (PDF; 574 kB) In: Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS). US EPA , accessed June 20, 2017 .
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Chlorpropham in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on December 6, 2019.
- ↑ Ordinance of the EDI on the maximum levels for pesticide residues in or on products of plant and animal origin. In: admin.ch . Retrieved February 6, 2020 .


