Cicutoxin
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
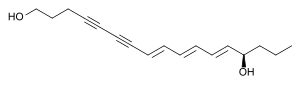
|
||||||||||
| Structural formula of the [all- ( E ) - ( R ) - (-)] - form | ||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | (8 E , 10 E , 12 E , 14 R ) -Heptadeca- 8,10,12-triene-4,6-diyne-1,14-diol | |||||||||
| other names |
Cicutoxin |
|||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 17 H 22 O 2 | |||||||||
| Brief description |
amorphous powder |
|||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 258.35 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||
| Melting point | ||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
Cicutoxin is a toxin of the water hemlock ( Cicuta virosa ). Cicutoxin is an organic compound from the compound class of diynes or polyenes . There are two stereoisomers of the optically active compound ; the (all- E ) - (-) - isomer occurs in nature .
Occurrence
Cicutoxin is the most poisonous and most important component of the polyynes of the water hemlock ( Cicuta virosa ). It is contained in all parts of the plant. The rhizomes have the highest content with up to 0.2%. Related accompanying substances of cicutoxin in the water hemlock are isocicutoxin, a Z-isomer of cicutoxin, with approx. 25%, and virol A and B with approx. 3% each of the total polymer content.
Extraction and presentation
Cicutoxin can be obtained from the rhizomes of the water hemlock by extraction and purification by column chromatography .
properties
Cicutoxin is a colorless solid. As a result of its highly unsaturated character, it is very sensitive and decomposes quickly, especially above 35 ° C. Its specific rotation value is .
Biological importance
Cicutoxin acts as a GABA antagonist . It binds to GABA -dependent chloride channels ( GABA A receptors ), on which its poisonous effect is based.
safety instructions
Cicutoxin makes the water hemlock one of the most dangerous indigenous poisonous plants. Even small amounts of ingested plant material lead to fatal poisoning. The first symptoms of poisoning appear very quickly, already 15-30 minutes after ingestion. The mortality rate is correspondingly high (approx. 30%). The LD 50 (mouse, intraperitoneal ) for cicutoxin is 2.8 mg / kg (isocicutoxin: 38.5 mg / kg). Symptoms of poisoning are dizziness, nausea, abdominal pain and vomiting. The pupils are dilated ( mydriasis ). As a sign of central nervous excitement, spasms and convulsions occur, which can lead to death from respiratory paralysis . There is no specific antidote to cicutoxin poisoning; treatment is symptomatic.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Entry on Cicutoxin. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on November 11, 2014.
- ↑ a b c Entry on Cicutoxin in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ a b Entry on Cicutoxin in the Hazardous Substances Data Bank , accessed July 27, 2012.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ FD Gunstone, John L. Harwood, Fred B Padley: The lipid handbook. 2nd edition, CRC Press, 1994, ISBN 978-0-412-43320-7 , p. 169.
- ↑ Uwai, K. et al. (2000): Exploring the structural basis of neurotoxicity in C (17) -polyacetylenes isolated from water hemlock. J. Med. Chem. 43 (23): 4508-4515, PMID 11087575 .
- ↑ Knutsen, OH. and Paszkowski, P. (1984): New aspects in the treatment of water hemlock poisoning . In: J Toxicol Clin Toxicol . 22: 157-166, PMID 6502788 .
- ↑ Ohta, T. et al. (1999): Absolute Stereochemistry of Cicutoxin and Related Toxic Polyacetylenic Alcohols from Cicuta virosa . In: Tetrahedron 55: 12087-12098.

