Access ditch
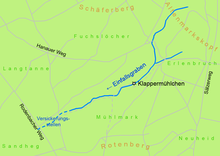
The access ditch is a 2.1 km long stream in the city forest north of Alzenau in Lower Franconia . The brook, also popularly called Feldbach , flows in a south-westerly direction through parts of the Bulau , a larger contiguous wooded area between Kinzig and Kahl . The area around the access ditch has no drainage and is located in the Spessart Nature Park .
geography
course
The source of the access ditch is actually located at the foot of the Altenmarkskopf (269 m), near the border with Hesse . However, this upper course of the stream often has no water in summer. In some places, a small trickle often forms , which immediately seeps into the sandy soil after a few meters.
Near a refuge , in the forest area Einfallgraben , another small brook forms. The source of the brook is located there on dry days . The access ditch now flows into a narrow gorge about eight meters deep , where it has its only tributary, a small stream coming from the left. The access ditch now meets the so-called Klappermühlchen .
The rattle mill
The Klappermühlchen is a miniature mill house in the Alzenau city forest. It has a small undershot water wheel that is operated by the water power of the access ditch. Part of its water is bundled via an artificially created channel, the mill channel, and directed onto the mill wheel. This then turns a disc that is studded with dwarf figures. The dwarfs walk through a window inside the house. With the help of this disc, four tiny hammers are moved that hit two different metal plates. Due to their different lengths and strengths, each time the hammer blows, a different tone is created. The “rattling” of the mill can be heard from several hundred meters away. The mill house was built in 1913 and is now cared for on a voluntary basis. The area around the Klappermühlchen is fenced and must not be entered.
Infiltration points
After only a few kilometers of flowing, the access ditch becomes smaller and smaller due to the sandy bulwark soil. In a sand hole it finally seeps away completely ( 50 ° 6 ′ 13.9 ″ N , 9 ° 3 ′ 10.1 ″ E ). Here attempts have often been made in vain to continue digging the creek bed in other ways. Since the beginning of the 21st century, the main infiltration point has shifted further and further upstream.
Nearby, the sandy Bulauboden also bothered the brook at the Antoniusgrotte in Alzenau , north of the 2305 state road . Similar to the access ditch, it will never reach its destination above ground.
The stream that flows out of the lake at the Barbarossa spring in Hesse also seeps away into the sandy soil after only a short distance.
Flora and fauna
Moss and heather grow in the sandy area at the access ditch . The wood dung beetle and the tree frog feel particularly at home in the damp, wooded area. Wild boars and deer wallow in the mud pools of the access ditch .
See also
Web links
- Map of the access trench on the BayernAtlas of the Bavarian State Government ( information )
Individual evidence
- ↑ Google Earth
- ↑ BayernViewer of the Bavarian Surveying Administration ( Memento of the original from April 8, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
Coordinates: 50 ° 6 ′ 54 ″ N , 9 ° 4 ′ 17 ″ E