Neuron-specific enolase
| Neuron-specific enolase | ||
|---|---|---|

|
||
| Model according to 1TE6 | ||
|
Existing structural data : 1TE6 , 2AKM , 2AKZ , 3UCC , 3UCD , 3UJE , 3UJF , 3UJR , 3UJS |
||
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 433 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Homodimer, heterodimer | |
| Cofactor | 2 mg 2+ | |
| Isoforms | α / γ, γ / γ | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene names | ENO2 ; ENOG | |
| External IDs | ||
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 4.2.1.11 , lyase | |
| Response type | Elimination | |
| Substrate | 2-phospho-D-glycerate | |
| Products | Phosphoenolpyruvate + H 2 O | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Homology family | Enolase 3 | |
| Parent taxon | Creature | |
| Orthologue | ||
| human | House mouse | |
| Entrez | 2026 | 13807 |
| Ensemble | ENSG00000111674 | ENSMUSG00000004267 |
| UniProt | P09104 | P17183 |
| Refseq (mRNA) | NM_001975 | NM_001302642 |
| Refseq (protein) | NP_001966 | NP_001289571 |
| Gene locus | Chr 12: 6.91 - 6.92 Mb | Chr 6: 124.76 - 124.77 Mb |
| PubMed search | 2026 |
13807
|
The neuron-specific enolase (NSE, ENOG), Eng .: neuro specific enolase , is an enzyme (organic catalyst ) of the glucose metabolism . It occurs in various isoforms in the nerve cells (neurons) of the brain and peripheral nerve tissue as well as in neuroendocrine tissues , v. a. in the so-called APUD cells .
Elevated serum levels of NSE are the result of cardiovascular events, cerebral trauma , various tumor diseases, scleroderma, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease or poor handling of blood samples due to the breakdown of erythrocytes or platelets. The upper limit value in the serum in adults is given differently by different laboratories as 10, 12, 16.3 and 18.5 μg / l.
NSE belongs to one of three groups of enzymes which are collectively referred to as enolases , all of which catalyze the same reaction and which are found in all living things that utilize glucose. While α-enolases are tissue-unspecific, β-enolases are only localized in muscle cells and γ-enolases only in nerve tissue. In fact, it is a homo- or heterodimer made up of three possible subunits (α, β, γ) that are combined with one another. Of these combinations, five are actually encountered: α / α in embryos and tissue-unspecific in adults; α / β and β / β in striated muscles; and α / γ and γ / γ in neurons. The heterodimers are preferably synthesized during ontogenesis .
Catalyzed reaction
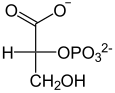 |
 |
ADP ATP pyruvate kinase |

|
||
| D - 2-phosphoglycerate | Phosphoenolpyruvate | Pyruvate |
2-phosphoglycerate splits off a water molecule; it arises phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP). Due to the resulting double bond , the phosphate group of PEP is bound unstably and is easily transferred to ADP with formation of ATP ; pyruvic acid or pyruvate is produced from the PEP .
rating
NSE for benign diseases
Increased concentrations of NSE in the blood serum are found in
- benign lung disease
- Diseases of the brain or nerve cells.
- In diseases of the brain, increased values for NSE can also be found in the liquor (brain water). This applies e.g. B. for meningitis ( meningitis ), stroke , intracerebral hemorrhage , subarachnoid hemorrhage , cerebral hypoxia (insufficient supply of oxygen), encephalomyelitis disseminata (multiple sclerosis), Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and other diseases that lead to the degeneration of nerve cells. NSE is a prognostic factor for patients with cerebral hypoxia. Significantly increased NSE values in the serum (> 33 μg / l) in the first few days after resuscitation indicate an unfavorable prognosis.
- Pregnancies with neural tube defects in the child
NSE in malignant diseases
NSE is a tumor marker for very different tumors. In small cell lung cancer , NSE is the central tumor marker; it correlates with the extent of the disease, but not with the location and type of metastasis. Successful chemotherapy leads to a decrease in the initially elevated NSE values. NSE increases can also be found in neuroblastoma , neuroendocrine tumors , seminoma (testicular tumor), Ewing's sarcoma, and with lower sensitivity in kidney cancer and other tumor diseases. NSE is not suitable for the search for tumors or for the initial diagnosis, but it is suitable for monitoring a course or a treatment.
Disruptions
NSE is found in higher concentrations in erythrocytes (red blood cells) and in thrombocytes (blood platelets). Therefore, increased NSE values are found in the serum when the red blood cells are destroyed (e.g. in the event of hemolysis ) or the blood platelets (e.g. in the event of undesired coagulation in the analysis tube or improper centrifugation).
Inhibitors
The enolase is inhibited by fluoride . This is used in blood samples if you want to determine the glucose values. Due to the inhibited enzyme, glycolysis cannot take place in the test tube, so that glucose does not break down.
Individual evidence
- ↑ PROSITE PDOC00148
- ↑ UniProt entry
- ↑ Entry on phosphoenolpyruvate. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on April 14, 2011.
- ↑ Todd A. Swanson, Sandra I. Kim and Marc J. Glucksman: BRS Biochemistry, Molecular Biology, and Genetics . Lippincott Raven; 5th edition 2010; ISBN 978-0-7817-9875-4 ; P. 65
literature
- Xuejun You: Clinical and molecular cytogenetic characterization of aesthetic neuroblastomas . Berlin 2002, DNB 965421600 , urn : nbn: de: kobv: 11-10017701 (dissertation).
![{\ mathrm {{\ xrightarrow [{Enolase}] {- Water}}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f85bf9432f7fef6872de42b38cf4c6826038c435)