General Defense Plan
The General Defense Plan (GDP) is the operation plan of a NATO Army Corps, which defines the operations of the unit up to the division level from the deployment of the troops to the start of the fighting. The GDP is released by the NATO command authorities after a phase of tension or immediately after the outbreak of war and is generally subject to the highest security level (“Secret” / “NATO Secret”).
content
The GDP describes the intentions, goals and the operational structure of the defense type of operation for the combat and combat support troops of the respective unit in the real case of war. It includes all measures for the transition from a state of peace to a state of war. This includes the management and connection of the subordinate units and the consideration of the fighting ability of the troops in the expected terrain ("infantry / tank terrain"). In general, it follows the prevailing NATO doctrine of forward defense , flexible response, etc. and is based on the respective advance warning time, which is necessary in order to take up the GDP positions in the case of hostile opponents, after alerting and mobilization, and the higher-level association to report full combat readiness . The GDP of an army corps should, among other things, ensure the cohesion of the defense of the neighboring corps. The basis of the GDP is the terrain and the respective enemy situation assessment.
history
During the Cold War , NATO's GDPs had the general goal of smashing Warsaw Pact attack groups with their superior armored forces as early as possible in the border area. With different weighting, these control measures were directed towards the 1st operational squadron or the subsequent 2nd operational squadron of the Warsaw Pact and, at favorable times, the initiation of local counter-attacks. The aim of these measures is to restore the integrity of NATO territory. The operational planning of the 5th Army of the NVA roughly mirrored the General Defense Plans of the Allied Corps. It was assumed that the General Defense Plan would proceed according to a certain automatism after the activation of the highest NATO alert level GENERAL ALERT in the initial phase of the fighting. The GDP 31001 of Army Group CENTAG and GDP 88 of Army Group NORTHAG have become known . Both the GDPs of NATO and the operational plans of the Warsaw Pact were based on an attack scenario from the other side, which later turned out to be unfounded. The OPLAN (Operations Plan) is part of the GDP. The EUCOM OPLAN 4102 "Defense of Western Europe" was valid for Western Europe and replaced the OPLAN 4102-84 on March 1, 1985.
Chain of command
The GDP is released to the divisions by corps order from SACEUR , which determines temporally and geographically which detachment areas, up to the "sharp GDP positions" / areas of the combat troops (usually tank , tank grenadier and fighter battalions ) in their respective area of responsibility. The CINCUSAREUR (Commander in Chief United States Europe) ensures the military security of the respective borders. In the case of the NATO Army Group Center (CENTAG), these extend from Schmiedeköpfe / Göttingen district (NB 6492) to Dreisesselberg / Bavarian Forest (VQ 1305). The command authority (Operational Command OPCOM) and the operational control (Operational Control OPCON) is transferred to the respective NATO troop leaders.
" Before the start of an aggression, CENTAG completes the planned deployment movements as a deterrent measure, dislocates the forces and resources in the defined GDP areas, ensures the continuous defense of the assigned sector, counteracts the aggression at the appropriate level in order to protect the integrity of NATO territory To maintain or restore, fight the enemy on the inner-German and the FRG / CSSR border by fighting the cover troops in front of the front line of defense, defending KAUFUNGER WALD (NB 5088) and KNÜLL-GEBIRGE (NB 3041). guarantees, in close cooperation with the NATO Army Group North (NORTHAG), the cohesion of the defense between the two army groups and prevents the enemy from breaking through to the Rhine. "
structure
The General Defense Plan is generally structured as follows:
Opposing attack after a short warning time
An enemy attack after a short warning time is taken into account. Troop units that are currently on training areas (e.g. Grafenwoehr or Bergen-Hohne) at the time of the enemy attack will not arrive at their designated GDP positions within 24 hours. In this case, the cover forces deployed near the border must take over after increasing the level of readiness to MILITARY VIGILANCE and possibly lead the first border battles. In addition, if possible, further available tank battalions or compiled task forces are provided with first priority for the immediate support of the cover forces. Combat support troops follow in second priority, v. a. Artillery.
enlightenment
Airborne or ground-based reconnaissance results are included in the respective enemy situation assessment , from which further operational measures can be derived. To assess the situation, knowledge about the presumed intention of the enemy, the strength and composition of his attack formations, his grouping of 1st and 2nd squadron , the location of his staging area , readiness to use NBC weapons , planned attack axes , deployment , morale, etc. needed.
Division of troops
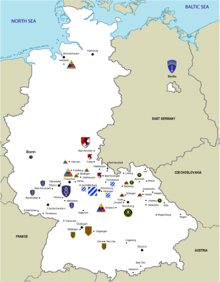
The defense section of the 5th US Corps and the limits to the III. Bundeswehr Corps in the north and the VII US Corps in the south with dividing lines. The guidelines ALPHA, CONCORD, BRADFORD, CHICAGO, DENVER, ENFIELD, FARGO, GULFPORT and HARTFORD are defined. The GDP also defines the division of troops in the V Corps, the operational structure of the division of its own forces and the composition of the units in the combat zone. So z. B. be ordered that an armored infantry brigade with three battalions defended side by side. Two armored infantry battalions on the flanks and one armored battalion in the center and focus. US or British associations often divide them into task forces for the execution of a specific assignment. The division of troops follows the guidance lines and the assigned defense strip. The width for the corps is around 70–80 km and for the division 40 km. The depth of defense for the corps is 120 km, and 60–70 km for the division. The positions of the rocket artillery and operational-tactical nuclear weapons (short-range missiles such as Lance launchers) are provided at a distance of 30 to 40 km from the VRV. The guidance lines (security line, VRV, demarcation lines of the individual combat units, sequence line for attack, etc.) divide the battlefield into sectors and provide an overview of the course of the fighting. The location of the command posts and command posts (either in fixed, bunkered systems or on staff and command vehicles), which are relocated after certain times in order to evade enemy reconnaissance and combat, are also specified.
Operation management
The planned operation is divided into several phases. The forces of the corps are divided into main and advanced cover forces. The task of the cover forces is to conduct a delay battle within certain defined delay lines until the point in time at which the main forces or reinforcements report that they have moved into the VRV and are fully operational.
The basic phases are:
- Development of the corps and the action of the corps' cover forces
- Actions of the cover forces of the divisions in the upstream security strip (e.g. tank reconnaissance) - Conduct the delay battle for a certain time
- Massing and fighting of the main forces at the VRV (Panzer- / Panzergrenadierdivisionen)
The defense is conducted in two squadrons: operational reserve and cover forces. After the NATO SIMPLE ALERT alarm level is triggered, the BGS is removed from the border security and this is taken over by the NATO army. It is assumed that there will be a short warning time (36/48 hours) due to the enemy's deployment movements and that not all units of the corps will reach their GDP positions in time within this time. The same applies to reinforcements from overseas ( REFORGER measures). For this reason, cover troops ( armored reconnaissance aircraft , US Air Cavalry Regiment, etc.), which are already in a higher degree of combat readiness in peacetime, have to bear the brunt of the fighting in the initial phase of the first days of the war.
The task of the cover forces is to occupy the defensive strips ordered from the evacuation rooms. There the cover forces have to cover the development of the main forces, separate the Federal Border Guard from the border security and occupy defined sections in the security strip. In addition, a delayed battle with enemy forces is to be conducted up to a certain lead line for x hours.
The corps has to occupy the assigned defense strip on orders, to defend a pre-planned line and to smash the enemy close to the inner-German border, to keep important key areas, to prepare the possible use of nuclear weapons, to receive, support and deploy reinforcement forces (e US and Canadian Armored and Mechanized Divisions). In addition, enemy forces that have broken in must be repulsed by counter-attacks on NATO territory. The associations receive their individual orders from the GDP. These can be as follows:
- 11th Panzer Reconnaissance Regiment ( 11th Pz AufklRgt ), subordinate to the corps, occupied the commanded cover section, ensured the deployment and deployment of the main forces of the corps and defended the cover section.
- 3rd Panzer Division ( 3rd PzDiv ) is deployed in the north sector and the 8th Infantry Division ( 8th InfDiv ) in the south. Both divisions take up the commanding defense strip and prepare the defense.
- The 2nd Brigade of the 8th Infantry Division (2nd / 8th Inf Div) is deployed in the depths as a corps unit. The 2nd / 8th InfDiv marches, secured by the 8th InfDiv, to the FARGO leadership line, passes the OPCON of the 3rd Panzer Division and occupies deadlock positions in the vicinity of LAUTERBACH (NB 2809) - OTTRAU (NB 2728). There it remains subject to the command of the V Army Corps.
The aim of the defense operation of the V US Corps is to destroy the main forces (seven Panzer and Mot rifle divisions ) of the 1st Squadron of the Warsaw Pact east of the Vogelsberg in the Bad Hersfeld - Fulda - Bad Brückenau area .
Fire support (artillery fire plan)
For fire support, on the one hand nuclear fire support (command / release of nuclear weapons use) and on the other hand general and direct fire support from high-angle weapons such as mortars / tank mortars of the tactical management level and artillery of the operational management level are used. The basis for this is the artillery fire plan as part of the overall operation plan , which identifies the firing positions of the batteries and their pre-planned fireplaces (barrage for artillery and mortars). To this end, the corps , divisional and brigade artillery have different priorities when fighting enemy targets. In the first phase, the corps artillery assumes fire support for the cover troops. The divisional artillery conducts direct fire fighting from the fireplaces of their artillery battalions in front of the combat strip of the divisions to which they are subordinate. The divisional artillery is reinforced with field artillery brigades.
Pioneer Support (Pioneers Blocking Plan)
When the NATO SIMPLE ALERT alarm is triggered, the pioneers ( tank pioneers and special pioneers ) begin with pioneer technical measures (construction of obstacles and barriers, relocation of anti-rifle / anti-tank mines in the pioneer-reinforced area) in the rooms provided for this purpose. The use of nuclear mines ( ADMs and other nuclear blocking ammunition by nuclear mine laying teams) is based on different criteria. ADMs were provided for in GDP 31001. Analogous to the artillery fire plan, the pioneer measures are shown on the map for the pioneers' blocking plan. All pioneering technical measures are aimed at promoting the maneuverability of one's own troops and inhibiting that of the enemy. These include the expansion of bolt positions , obstacles in the security strip, erection of obstacles and barriers, blocking of terrain sections, mine use, as well as the construction of field camps, expanded position systems for your own troops in the depth, etc.
Air support
Immediate air support through battlefield closure and close air support is guaranteed by an air fleet. The control is carried out by flight control officers.
ABC use
The use of biological-chemical weapons primarily serves as a retaliatory measure for attacks by the Warsaw Pact with chemical weapons . C-weapons are primarily used as part of fire support for artillery and engineer units. The aim of these measures is to inhibit certain sections of the terrain for the movement of the enemy by channeling enemy attack groups, and to contaminate supply points and command posts.
Further sections of the GDP
- Telecommunication measures (wire and radio connections)
- Radio electronic combat (ELOKA)
- Air defense / army air defense
- Army Aviation Forces
- Protection of the rear corps area
- Deployment and deployment
- military police
- Use of foreign reinforcements
- confidentiality
- Deceptive measures
- Cooperation with the Federal Border Guard
literature
Web links
- US and NATO Military Planning on Mission of V Corps / US Army During Crises and in Wartime. December 16, 1982. This extensive document of 1982 presents major parts of the secret operational plan 33001 (General Defense Plan) for the US Army's V Corps in Germany, which was expected to bear the initial brunt of any Warsaw Pact attack. It was prepared by the East German Stasi (State Security) intelligence agency. This operational plan is the basis for defensive actions of the US V Army Corps within NATO's Central Army Group (CENTAG) and consists of two parts, the so called basic plan (OPLAN) and a part with annexes. The OPLAN includes information about the wartime intentions, objectives, and operational defensive structure of CENTAG. The annex part lists details such as the operational structure of the US V Army Corps, definitions of defense zones, and usage principles for nuclear and chemical weapons.
- General Defense Plan (GDP): Vol. 15, GDP 1 / 87th - 12th Panzer Division
- NATO GDP 1958
- Summary Operations Plan 33001 (GDP / General Defense Plan) V Corps / USA on Wilson Center Digital Archive (en.)
Notes and individual references
- ↑ Gift from Heaven. The old NATO doctrine is obsolete. Now the alliance is looking for a new raison d'etre. DER SPIEGEL 42/1990. Issued October 15, 1990.
- ↑ Reaction speed in the German army at http://logeion.net/
- ^ A conversation with the former GDR military planner Siegfried Lautsch. From preventive war planning to realizing that a modern war can no longer be won? Aachen Peace Magazine. aixpaix.de
- ↑ Oliver Bange, Bernd Lemke: Ways to reunification: The two German states in their alliances. 1970 to 1990 (Contributions to Military History, Volume 75. De Gruyter Oldenbourg. 2013. ISBN 978-3-486-71719-8 )
- ↑ 3rd Panzer Division, Operation Order No. 1 for the delay in the combat zone I. (NL) Corps (GDP 88 Part III, March 6, 1989) in BArch, BH 8-3 / 434 and I. (GE) Corps, GDP 88 in: BArch, BH 8-3 / 437
- ^ Secret planning of the National People's Army of the German Democratic Republic in the 1980s by Siegfried Lautsch. Austrian military magazine. 03/2016
- ^ East German Ministry of State Security, US and NATO Military Planning on Mission of V. Corps / US Army during Crises and in Wartime (Exerpt). December 16, 1982. The plan is endorsed by the US Department of the Army and, after consultation with NATO, became part of NATO planning. This operations plan lays the groundwork for the deployment of V Corps to lead the defense within NATO's Central Army Group (CENTAG). The plan consists of the so-called basic plan (OPLAN) and attachments. Aside from general information on intentions, goals, operational defense of CENTAG, OPLAN provides detailed instructions for V Corps and its combat and support troops, as well as general orders for cooperation and command and control within V Corps. 18 attachments and 33 appendixes explain among other things the operational structure of the corps, boundaries of the corps and division areas for defensive operations, general rules of operation and their safeguards. Finally, they cover the guidelines for use of nuclear and chemical weapons and include attachments covering the planned deployment of outside reinforcements under the command of V Corps / USA. Wilson Center Digital Archive - International History Declassified
- ↑ EUCOM OPLAN 4102, "Defense of Western Europe" replaced OPLAN 4102-84, March 01, 1985, Top Secret; replaced OPLAN 4102-84, July 2, 1984, Top Secret. Supplemented by CTNCUSAREUR OPLAN 4102. USCINCEUR OPLAN 4999-98, "Defense of Western Europe In General War" probably replaced OPLAN 4102 and was likely rescinded itself. On Globalsecurity.org
- ↑ synonymous with the disposal areas
- ↑ a b c GDP 31001 , published in the Parallel History Project
- ^ History. Fulda Gap. Where the Red Army wanted to break through to the west. The “Fulda Gap” between Hesse and Thuringia was considered the most dangerous point of the Cold War. A new exhibition shows how the attack of the Soviet tanks was expected here. The world. September 24, 2013
- ↑ according to US Army coordinates, MGRS / Military Grid Reference System
- ↑ Assumption that the enemy will gain air superiority in the early stages of combat