Hunter troop (Bundeswehr)

The Jägertruppe is a branch of the army and, together with the paratroopers and the mountain troops, forms the infantry group , which, along with the armored troops and the armored infantry troops , is part of the combat troops . The task of the hunter troop is to fight infantry in the low mountain range , in forests and in built-up combat areas .
Mission and skill profile
The Bundeswehr's hunter troop was designed as light , motorized infantry for fighting in terrain that is unfavorable for battle tanks and for protecting rear areas.
The troops are usually brought into the operational area by unarmored or only lightly armored vehicles , some of which can float . Due to their light equipment, the hunter troops, like the mountain troops, can be made airmobile by transport helicopters or other aircraft and landed in order to be used surprisingly at focal points. With the arrival of the GTK Boxer , the mobility and protection on land was increased, but at the same time the air mobility of the fighter troops was reduced, as they can only be transported by air with transport aircraft .
In the operational area, the hunters ' troops fought on foot primarily with light weapons such as the mountain troops and paratroopers' enemy infantry. The operational area is often characterized by impassable, i.e. covered and / or cut through or built-up terrain. In the built-up area, hunters fight in local and urban warfare .
In order to fight tanks , the hunter troops form tank destruction troops equipped with anti-tank weapons.
The anti-tank troops with anti - tank missile systems of the heavy hunter companies that are made mobile on weasels are qualified to a limited extent. Fire support is provided with movable made on Wiesel machine guns , as well as on the wheeled vehicle Wolf leaving ended mortar .
Hunters are partially protected against fire with light weapons and NBC weapons by the transport armor (TPz) Fuchs and the GTK Boxer . When dismounted, hunters are only protected against NBC weapons by their personal equipment, and against artillery fire only in field positions . By equipping them with TPz and GTK, the hunter troops approach the battle of the armored troops and take on combat missions for them in sub-combat rooms that are unfavorable for them like individual villages and in forest areas as grenadier forces. This is also shown in principle by the subordination to mechanized brigades.
The German infantry is conditionally capable of operating combined forces and can, if necessary, receive support from armored troops and artillery against mechanized troops and enemy infantry. These support the hunter troops by fighting against enemy armored vehicles, the armored personnel carriers also against enemy infantry with the on-board machine cannon. An increase in interaction with other combat troops through networked combat management and an increase in combat value is achieved through the infantryman of the future system . Due to its own weight, however, this forces the hunter troops to leave other equipment on the combat vehicles, especially necessary for longer endurance, such as field and bivouac equipment, and binds the troops to them. The coordination with the artillery within the framework of the joint armed forces tactical fire support (STF) is carried out by the Joint Fire Support Team (JFST) of the heavy companies.
Infantry lead the battle in defense from positions and in attacking enemy field positions, especially in forest combat as well as in local and house combat in urban areas. The attack type of operation is carried out by the hunter troops in the terrain that is favorable for them using the raid troop procedure . Infantry is not able to use the delay type of operation to slow down and channel attacks by enemy mechanized troops .
Hunters are qualified for hunting , especially in their own rear area against weak breached or airborne troops , against special forces or irregular forces.
On missions abroad , hunters are often deployed in scouting troops or patrols on foot or with protected wheeled vehicles, to secure marching paths and mounted as escorts for convoys and, to a limited extent, for hunting .
In contrast to hunters, security associations in the rear only secure stationary objects and special guide means such as rods. These are not capable of infantry combat because they lack organically heavy weapons and they are not fully trained for infantry combat. Special artillery resources are secured by backup batteries.
history
In the Bundeswehr , after the experiences of the Second World War, especially with Operation Bagration , the battle was to be carried out flexibly with predominantly mechanized , i.e. armored, formations. The tasks of the infantry accompanying their own tanks were taken over by the armored infantry as mechanized infantry.
The hunter troop was therefore set up as motorized infantry for the dismounted fight in an unfavorable focus area. In the field army, however, in contrast to the tank grenadiers, only occasionally where the terrain was particularly unfavorable for the tank troops or where mechanization was delayed due to the lack of appropriate weapon systems.
Each of the field divisions had two non-active divisional fighter battalions that were to be used in infantry focal points. The exception to this was the 6th Panzer Grenadier Division Schleswig-Holstein, whose Jäger battalions were active and partially active. However, these were equipped with M113 armored transport vehicles and were therefore more like the Panzergrenadierkompanien (MTW) of the armored infantry battalions .
Only between the years 1970 and 1981 in Army Structure III were two major hunter units in the field army with the 2nd and 4th Jägerdivision set up in the terrain in southern Lower Saxony and northern Hesse as well as in Bavaria and Franconia , each of which had further large unit components Tank battalions were. Their former hunter battalions, which were later converted back to tank grenadier battalions, can be recognized by the oak leaves in the battalion badges, the internal association badges.
In the territorial army, hunter battalions were among the most common formations and were mostly inactive. The task of the hunters in the territorial army was to protect rear areas and the corps supply rooms against troops that had broken through or landed in the air . The homeland security brigades also had outdated M48 main battle tanks and tank destroyers , both of which were used as tank destroyers. The task of the homeland security troops of the territorial army - which should not be confused with the homeland security battalions - and which consisted of hunter battalions in the masses, included the fight against covert forces .
In a broader sense, this also included the units of the homeland security force with the homeland security battalions and security battalions. In contrast to the hunter troop in the narrower sense, security battalions were not capable of extensive infantry combat, especially due to the lack of heavy infantry weapons.
After reunification , the 37 Free State of Saxony Jägerbrigade was re- established in the field army with one battalion for hunters, mountain hunters and paratroopers. When the brigade was reclassified as an Panzergrenadierbrigade in 2007, the subordinate Jäger Battalion 371 became the Panzergrenadierbataillon 371 .
The non-active homeland security battalions in the military areas of the armed forces base were disbanded by 2007. With the exception of the newly established airmobile Jägerregiment 1 and the Jäger Battalion of the Franco-German Brigade, the Jäger troop was dissolved. The fighter regiment that followed the approach of the air cavalry represented a new direction for the military. With the transformation of the Bundeswehr , the light and mobile fighter units experienced a renaissance . In 2010 the Jäger Battalion 291 of the Franco-German brigade was reorganized and stationed as the first combat unit of the Bundeswehr in France. In 2011, a security battalion was planned for the first time since the 1990s with the security battalion 12.
The importance of the infantry in foreign missions has increased compared to the importance in the Cold War , as heavily armored vehicles should either be consciously avoided or the operational areas and the enemy situation are unfavorable for their use. Firstly, their weight and size significantly reduce mobility in countries with poor infrastructure and highly indented terrain, and secondly, enemy mostly irregular forces rarely have mechanized vehicles that would require their own battle tanks to fight. At the same time, the costs for the shipment to the country of use, the repairs there and the replenishment logistics, especially with fuel, are high.
In the course of the realignment of the Bundeswehr and the taking of the structure HEER2011, the Jägerregiment 1 was reorganized into the Jäger Battalion 1 with three Jäger companies with GTK Boxers and a heavy Jäger company and was subordinated to the Panzer Brigade 21 of the 1st Panzer Division . The concept of the air mechanized brigade , whose infantry element was the 1st Jägerregiment, was discontinued. The tank battalion 413 was reclassified to the Jägerbataillon 413 and subordinated to the Panzergrenadierbrigade 41 . In Rotenburg (Wümme) the Jäger Battalion 91 was reorganized and subordinated to the Panzerlehrbrigade 9 . The large mechanized units of the Bundeswehr thus contain parts for asymmetrical use in order to release the mechanized units from an operational option for which they are only partially qualified.
The Jäger Battalion 291 with two Jäger companies and the Jäger Battalion 292 with three Jäger companies of the Franco-German Brigade were retained. In Schwarzenborn , the 921 Jäger Battalion was re-planned as a non-active unit . All of the Jäger Battalions, with the exception of Jäger Battalion 291, have their own fire support, each with a heavy Jäger company.
outlook
The Bundeswehr thus comprises five active hunter battalions with 14 hunter companies and 4 heavy hunter companies, which are subordinate to the 1st Panzer Division.
The 10th Panzer Division , in addition to the two Jäger battalions of the DF Brigade, is subordinated to the Mountain Infantry Brigade 23 with 9 Mountain Hunter companies and 3 heavy Jäger companies as an independent infantry brigade.
The fighters, made manoeuvrable with armored wheeled transport tanks, once again assumed the role of motorized grenadier troops in the army. The introduction of modern armored vehicles and weapon carriers increases protection and mobility, but at the same time the troops are tied to the vehicles. In order to increase the fighting strength of the infantry even in dismounted combat, the infantry combat equipment Infantryman of the Future (IdZ-Gladius) is introduced.
Overall, the 27 armored infantry companies in nine battalions stand against 21 hunter and mountain hunter companies with an additional 7 heavy hunter companies in eight battalions and 12 paratrooper companies with 2 heavy paratrooper companies in two regiments.
education
The infantry is trained at the Infantry Training Center (formerly the Infantry School) in Hammelburg . Their commander is also the general of the infantry , who is responsible for the armed forces of the hunter, paratrooper and mountain troops. The Army Development Office has been responsible for the further development of the military branch since June 2013 .
The training includes general infantry skills for the types of combat defense and attack on foot in local and house combat and in forest combat , with and without the support of other types of troops, especially the armored infantry troops, as well as in hunting combat . In addition, the hunter troop can be deployed in asymmetrical combat against covert enemy forces .
In general, this includes combat service of all troops in urban or hiding to strong overcast grounds with assault by fire and movement in the raiding party process , which of combat defense from field positions with counter-attack as well as monitoring and mastering of spaces through foot patrols and patrols with armored wheeled vehicles. Defense and attack from and on field positions in open terrain, which were still taught in the early days, are no longer carried out.
General courses are Einsatzersthelfer A , pioneering all troops with the creation of locks with Razor Wire and S wire , the explosives service as well as waters overcome, antitank all troops with antitank hand weapons by the Anti-Armor squad , NBC defense of all troops and air defense of all troops on land.
The earlier proximity of the Jäger troop to the Panzergrenadier troop consisted not only in the acquisition of equipment such as the MTW M113 , with which the divisional fighter battalions were equipped, but also in the earlier joint training of infantry officers to become Panzergrenadier and fighter officers. The training of sergeant ranks, however, was carried out together with the hunter sergeants of the paratrooper troops and the mountain troops. This always resulted in a divergence in the understanding of the task and its implementation.
organization
classification
The Jägertruppe one of the combat troops of the army and forms with the paratroopers and mountain units are the infantry of the army. The mountain fighters and the paratroopers are independent branches of the army, but are derived from the hunter troop. In contrast to the mountain fighters or the paratroopers , the hunter troops are not equipped and trained with parachutes for combat in high mountains or for air landing. In addition to the infantry , dismounted tank grenadiers also wage infantry combat in the army. A distinction must be made between the hunters' troops and the other security forces in association, unit or partial unit strength. Their job is to secure objects, rooms or facilities as well as staffs or special operational resources. These security forces are not equipped for infantry combat due to their assignment, as they lack the support of an organic heavy company and they are not fully trained for infantry combat. In the armed forces of the Air Force and the Navy, their own forces take on the security task. They have no infantry combat mission. Historically, the name Feldjäger derives from the hunter troop. The designation Panzerjäger has been derived from the root of the word Jäger since it was established as a type of service in the Wehrmacht through tank hunting. However, they are to be distinguished by equipment and training and belong to the armored forces.
structure
A hunter battalion is basically divided into 1st / staff and supply company , 2nd / - 4th / hunter company with I / - III / hunter platoon, IV / anti-tank / fire support platoon and, today, a sniper group, whose soldiers depend on the situation subordinate to the fighter platoons, and a 5th / Heavy Jäger company for immediate fire support with mortars, anti-tank guided weapons for anti-tank defense and machine cannons each in pull strength as well as a reconnaissance platoon. Small drones are available as reconnaissance vehicles. A dog handler train is sometimes integrated into some infantry units.
Active units
| designation | place | Association | Area | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jäger Battalion 1 | Schwarzenborn | Armored Brigade 21 | army | Emerged from Jägerregiment 1 in 2015 | |
| Hunter Battalion 91 | Rotenburg (Wümme) | Tank Training Brigade 9 | army | Restructured in 2015 | |
| Jäger Battalion 291 | Illkirch-Graffenstaden ( France ) | Franco-German Brigade | army | 4. / Reconnaissance company | |
| Jäger Battalion 292 | Donaueschingen | Franco-German Brigade | army | In 1993 emerged from Jägerbataillon 552 and Panzergrenadierbataillon 292 | |
| 413rd Hunter Battalion | Torgelow | Panzer Grenadier Brigade 41 | army | 2015 emerged from PzBtl 413 |
Not active associations
| designation | place | Association | Area | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jäger Battalion 921 | Schwarzenborn | Armored Brigade 21 | army | Set up in 2015, economic troop unit Jägerbataillon 1, 1 combat company each in Schwarzenborn, Rotenburg (Wümme) and Torgelow |
The Jägerregiment 1 was set up as an airmobile regiment that was brought into the operational area by helicopter and supported there by support helicopters and carried out the fight in and around key areas. To this end, the regiment led its own pioneers and anti-aircraft forces in company strength . The regiment is currently in the process of being reclassified as a "classic" hunter battalion. The air defense component has already been decommissioned for this purpose. The two Jäger Battalions 291 and 292 are part of the Franco-German Brigade . The Jägerbataillon 291, which was reorganized in 2010, as a mixed hunter and reconnaissance battalion, is subordinate to two hunter companies and a reconnaissance company as well as a supply and support company.
The 2011 security battalion 12 was also part of the infantry, but serves as a training association. The army uniform wearers in the guard battalion at the Federal Ministry of Defense are also included in the hunter troop . The main task of this federation of the armed forces base is the protocol service . It also provides security services. In the event of a defense , the guard battalion is planned as a security association. The naval and air force uniform wearers in the guard battalion receive a similar training, but are not assigned to a military class due to the tradition of the naval and air force branches.
Units decommissioned
equipment
Main weapon systems


The main weapon systems of the hunter troops are handguns in connection with the infantry equipment infantryman of the future . Compared to mechanized units, the Bundeswehr's hunter troops have little large equipment. Weasels are used as airborne weapon carriers in the heavy hunter companies. Upgrade kits are the 20 mm automatic cannon and the TOW anti-tank system . 120 mm mortars are loaded onto Wolf type off-road vehicles . The hunter companies have the MILAN anti-tank weapon for anti-tank defense , the HK GMW grenade machine weapon and snipers for fire support .
The floating armored transport vehicle (TPz) Fuchs and the GTK Boxer are available as group transport vehicles. Fuchs and Boxer offer protection against NBC weapons and are armored against fire with light weapons.
Uniforms
The weapon color of the hunter troop, here as the color of the braids and collar tabs as well as the beret color , is (hunter) green . The gun color is shared by the hunter troop with the other infantry troops and the armored infantry troops . The beret badge of the hunting troop is a golden oak leaf with a stylized border as a traditional German symbol. At the moment only the hunters of Jäger Battalion 1, Jäger Battalion 91 and Jäger Battalion 413 wear the golden oak leaves. The hunters of the Franco-German brigade , like the grenadiers of the guard battalion, wear an association-specific and non-military-specific beret badge.
Military symbols
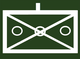
The basic military symbol of the hunter troop is the St. Andrew's cross, following the general NATO scheme. The St. Andrew's Cross is the basic symbol of all NATO infantry units. It stands for crossed rifles, swords or bandeliers . Depending on the equipment and structure, this basic symbol is used in variations for the associations of the hunter troops. Examples:
 |
Tactical (basic) symbol of the hunter troops and infantry |
| Infantry training center , formerly an infantry school | |
 |
all-terrain motorized hunter company |
| 4th company of the motorized grenadier battalion 133 (movable by means of commercially available vehicles). | |
| Homeland Security Regiment 74. The upper horizontal line marks units of the Territorial Army | |
| 4th MTW Company of the 42nd Panzer Grenadier Battalion. The tactical sign is similar to the - meanwhile decommissioned - Jäger companies ( MTW ). |
Rank designations
Rank designation of the lowest rank soldier in units of the hunter, parachute and mountain troops is hunter . He corresponded to the rank designations Schützen, Funker, Panzergrenadier etc. of other military branches, branches of the armed forces and military organizational areas. The other ranks corresponded to the general ranks of the Bundeswehr .
Army uniform wearers in the BMVg guard battalion are called grenadiers in the lowest rank , and until 1991 as hunters . Until the 1960s in the infantry branch has the name given to the lowest was commissioned officer ranks Oberjäger and bar top hunters . However, there was no legal basis for this informal and widespread practice in the form of a corresponding order from the Federal President .
|
|
||
| Lower rank | Higher rank | |
| - | Hunter | Private |
|
Rank group : Teams-NCOs-NCO-NCOs-Lieutenant-Captains-Staff officers-Generals |
||
war cry
The battle cry of the hunters' troops is Horrido - Joho! Horrido or Horridoh is an old greeting and hunting call of the hunter language. The greeting came up as a battle cry of military units from 1631 after the Hessian sovereign Wilhelm V of Hessen-Kassel was the first military hunter unit ever to be set up from foresters and hunters who were knowledgeable about weapons.
Horrido - Joho! is also the battle cry of the mountain troops , military police and army reconnaissance troops in Germany . The battle cry of the guard battalion, however, is Semper talis .
See also
literature
- Sören Sünkler: The special units of the Bundeswehr . Motorbuch Verlag, 2007, ISBN 3-613-02592-2 .
- Otto Münter: Short story of the German hunter troop . In: Deutscher Jägerbund e. V. (Ed.): Festschrift Jägertage 1986 . 1986.
- Erwin Rommel : Infantry attack . Voggenreiter, Potsdam 1937, DNB 575884878 .
Web links
- The infantry troops. Federal Ministry of Defense , head of the press and information staff, accessed on October 12, 2010 .
- Website. Federation of German Infantry V., accessed on October 13, 2010 .
- Website. Kameradschaft Hammelburger Lehrbataillon e. V., accessed on October 13, 2010 .
Remarks
- ↑ The 1st Jägerregiment served as airborne infantry for tactical air landings.
Individual evidence
- ^ Finding aid for inventory BH 11 "Infantry". (No longer available online.) Federal Archives, archived from the original on February 25, 2014 ; Retrieved October 23, 2010 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ https://www.bundeswehr.de/de/organisation/heer/organisation/1-panzerdivision/panzerbrigade-21/jaegerbataillon-921
- ↑ cf. Iller disaster . The death of Kempten . In: Der Spiegel . No. 24 , 1957 ( online ).
- ↑ Federal President Theodor Heuss et al .: Order of the Federal President on the rank designations, the appointment and dismissal as well as the uniform of the volunteer soldiers from July 23, 1955 . In: Federal Law Gazette Part 1 . tape 1955 , 23 of July 25, 1955. Bonn July 23, 1956, p. 452 ff . ( HTML [PDF; accessed May 12, 2015]).
- ↑ Federal President Theodor Heuss et al .: Second order of the Federal President on the rank designations, the appointment and dismissal as well as the uniform of the volunteer soldiers from February 1, 1956 . In: Federal Law Gazette Part 1 . tape 1956 , 4 of February 2, 1956. Bonn July 23, 1956, p. 63 ff . ( HTML [PDF; accessed May 12, 2015]).
- ^ Federal President Theodor Heuss et al .: Order of the Federal President on the rank designations and the uniform of soldiers from May 5, 1956 . In: Federal Law Gazette Part 1 . tape 1956 , 22 of May 14, 1956. Bonn 7 May 1956, p. 422 ff . ( HTML [PDF; accessed May 12, 2015]).
- ↑ Federal President Theodor Heuss et al .: Second order of the Federal President on the rank designations and the uniform of soldiers from July 26, 1957 . In: Federal Law Gazette Part 1 . tape 1957 , 39 of August 7, 1957. Bonn July 26, 1957, p. 1056 ( HTML [PDF; accessed May 12, 2015]).
- ↑ a b The equivalent, higher and lower ranks are given in accordance with ZDv 14/5 B 185, cf. The Federal Minister of Defense (ed.): ZDv 14/5. Soldiers Act . DSK AV110100174, change status July 17, 2008. Bonn August 21, 1978, rank designations in the Bundeswehr, p. B 185 (Not to be confused with the Law on the Legal Status of Soldiers (Soldiers Act) . The order of the ranks shown in the info box does not necessarily correspond to one of the regular rank sequences provided for in the Soldiers' Career Ordinance , nor does it necessarily correspond to the rank hierarchy described in the Superiors Ordinance a managerial relationship ).




