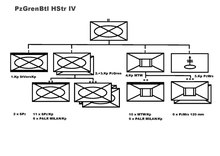
Panzergrenadierruppe (Bundeswehr)
The mechanized infantry force is a branch of service in the army of the Bundeswehr . The German armored infantry troop is one of the army's combat troops and, together with the armored troop, forms the armored group of armored troops . The main weapon system of the armored infantry troops is the Puma infantry fighting vehicle . Mounted is the main task of fighting enemy infantry and tank units in open terrain, dismounted due to their equipment primarily against enemy infantry in partially covered terrain.
assignment
The armored infantry troop of the Bundeswehr is designed as mechanized and armored infantry . A special feature is the quick change of fighting style . The troops fight both mounted from the armored personnel carrier, but can also dismount for infantry combat. The characteristic of the armored infantry troops is their high mobility, which results from the mobility and protection of their armored personnel carriers even in difficult surroundings. They are therefore mostly used in conjunction with battle tanks , and more rarely with infantry for missions in urban combat areas. The armored infantry troops are unrestrictedly capable of combined arms combat (combined forces operations). Shallow fire from barrel weapons is supplemented by steep fire , formerly from mortars , today by barrel artillery. Mortars are no longer part of the armored infantry battalions. Anti-tank weapons and hand-held anti-tank weapons enable the troops to fight against enemy battle tanks and armored personnel carriers, both when mounted and dismounted. Dismounted, Panzer Grenadiers fight enemy infantry, even in urban combat areas or where the terrain is slightly cut through or partially covered with forest , as tanks alone are difficult to use or are threatened to a high degree by enemy infantry. The Panzer Grenadier Troops use the area for their own benefit. In an urban combat area, tank grenadiers are dismounted and are conditionally capable of fighting on-site and in house . If the terrain is suitable, dismounted Panzergrenadiers are reinforced by battle tanks or mixed with them. These provide fire protection , fight battle tanks or enemies in field fortifications .
The Army Service Regulations (HDv) 100/100 (version from the year 2000) characterize the armored infantry troops and their interaction with the armored troops as follows:
“The armored combat troops include the armored troops and the armored infantry troops . [...] Due to their mobility and the protection of their armored combat vehicles, the Panzergrenadierruppe is particularly suitable for the rapid change between mounted and dismounted fighting methods in order to ensure the impact force of armored troops. [...] The direct and close cooperation between the armored troops and the armored infantry troops is, in addition to the cooperation with the combat support, a prerequisite for success. Their versatility and responsiveness enable them to gain and maintain the initiative and bring about a decision. "
The battle of the Panzergrenadier Battalion is characterized in the HDv 231/100 as follows:
"The battalion's battle is characterized by:
- the connection of fire and movement,
- the attack-like impact in combination with battle tanks,
- the quick change of the fighting style between mounted and dismounted fight,
- the close cooperation of the up and down forces,
- the primarily mobile battle , [...] "
history


Army structures I and II
When the Bundeswehr was set up from 1955 onwards, only grenadier units were set up because there were no armored personnel carriers. These belonged to the infantry. The formation of eight grenadier divisions was planned. In Army Structure I , Panzer Grenadiers were only planned as a training battalion in Munster and in the two armored divisions ( 3rd and 4th divisions ) to be set up . Only the training battalion had the US armored personnel carrier M39 - the battalions of the divisions were only equipped with Borgward B 2000 A trucks . Even later, the M39 was not procured nationwide for the armored infantry troops.
Experience from the Second World War and the required ability to conduct combat in a mobile manner, even under nuclear threat, led to the decision to equip the majority of the armored grenadier battalions fully mechanized with tracked vehicles.
In Army Structure II , the grenadier divisions were reclassified into Panzergrenadier divisions from 1959. The newly developed, but scandal-shrouded armored personnel carrier (IFV) HS 30 was sent to the army . Units that did not receive an armored personnel carrier were called the Panzergrenadierbataillon (mot) . Starting in 1962, which were mot units by running the US team transport vehicle M113 to mechanized infantry battalions (MTW) converted. Each armored division was divided into two armored brigades and one armored infantry brigade and each armored infantry division in two armored infantry brigades and one armored brigade. Each Panzergrenadierbrigade consisted of two battalions (SPz), a battalion (mot or MTW), an artillery battalion and brigade units.
Army structures III and IV
In Army Structure III, due to the weak infantry , two divisions were reclassified into Jäger divisions ( 2nd and 4th division ). By then, 10 armored and armored infantry divisions of the Army and two other brigades in the 1st Mountain Division had been set up. The grenadier battalions were equipped with MTW M-113. In the Panzer and Panzergrenadier divisions, the Panzergrenadiers were now the only infantry apart from the division hunter battalions.
About ten years after the introduction of the HS 30 , the Marder armored personnel carrier replaced this vehicle. In order to strengthen the anti-tank capabilities of the troops, the Franco-German anti-tank guided missile MILAN was introduced under Defense Minister Georg Leber . The armored infantry battalions (MTW) were equipped with armored personnel carriers. In order to have a strong infantry component in the units for forest combat and local and urban combat, the 4th / grenadier companies of the battalions were mainly equipped with MTW.
In Army Structure IV , the Jäger divisions were reassigned to Panzergrenadier divisions and the brigades were reinforced by a fourth combat troop battalion. The newly established ones battalions were organized as mixed tank or tank grenadier battalions . In the Panzer Grenadier Brigades, the fourth combat companies of the subordinate battalions were equipped with MTW M-113.
There were a total of 64 Panzer Grenadier Battalions, including two for the first time in the Home Guard Brigade 56 in the Territorial Army . This mechanized homeland security brigade was subordinated to the 1st Mountain Division as the fourth brigade.
Army structures V and later
In Army Structure V (N), the brigades were uniformly set up with two tank and tank grenadier battalions each. The Panzergrenadierruppe switched from infantry to armored combat troops , later renamed to armored troops. In the course of the transformation of the Bundeswehr , the tank mortar companies are disbanded. The M113 tank mortars were decommissioned.
education

The training of the armored forces takes place essentially in the training area armored forces , as part of the training center Munster in Munster. The head of the armored troops training area is also the armored troop general and is responsible for training the armored troops. The Army Development Office has been responsible for the further development of the military branch since June 2013 . Individual essential training sections are also carried out at the infantry school, in particular courses on local and forest combat.
With the deployment of the Puma infantry fighting vehicle , it was designed in such a way that the soldiers to be transported may not be more than 1.84 meters tall due to the applicable safety requirements. Larger soldiers who have already been scheduled can no longer be deployed there as tank grenadiers. In the future, the maximum height of 1.84 meters will therefore also be a prerequisite for admission to the career in the tank grenadiers, reports the Defense Commissioner of the German Bundestag in his 2018 annual report.
organization

classification
In the Bundeswehr, the armored infantry initially belonged to the infantry like the Jäger troops . With the implementation of Army Structure 5 (N) in 1995, the Panzer Grenadiers were combined with the armored troops and other armored combat troops in the armored fighting group. Since 2005, the armored infantry troops and the armored troops have been combined in the armored troop group . The armored infantry troops and the armored troops are part of the combat troops of the Bundeswehr.
Active associations
Typically, armored infantry battalions have a headquarters company, three combat companies and another company as a training company. The army has nine active armored infantry battalions with 27 armored infantry companies for 5 mechanized brigades , which are subordinate to the 1st Panzer Division or the 10th Panzer Division and assigned to three corps .
| designation | place | Association | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Panzer Grenadier Battalion 33 | Neustadt am Rübenberge | Tank Training Brigade 9 | |
| Panzer Grenadier Training Battalion 92 | Muenster | Tank Training Brigade 9 | |
| Panzer Grenadier Battalion 112 | rain | Armored Brigade 12 | |
| Panzer Grenadier Battalion 122 | Oberviechtach | Armored Brigade 12 | |
| Panzer Grenadier Battalion 212 | Augustdorf | Armored Brigade 21 | |
| 391th Panzer Grenadier Battalion | bad Salzungen | Panzer Grenadier Brigade 37 | |
| 371th Panzer Grenadier Battalion | Marienberg | Panzer Grenadier Brigade 37 | |
| 401th Panzer Grenadier Battalion | Hagenow | Panzer Grenadier Brigade 41 | |
| Panzer Grenadier Battalion 411 | square | Panzer Grenadier Brigade 41 |
In October 2011 it was decided to relocate Panzer Battalion 33 to Panzer Grenadier Battalion 33 .
Not active associations
In 2008 the following two non-active tank grenadier battalions (without large material) were set up:
| designation | place | Association | Force category | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 908th Panzer Grenadier Battalion | square | Panzergrenadierbrigade 41 , economic troop unit: Panzergrenadierbataillon 411 | - | |
| 909th Panzer Grenadier Battalion | Marienberg | Panzergrenadierbrigade 37 , economic troop unit: Panzergrenadierbataillon 371 | - |
Associations decommissioned
equipment
Main weapon system
The main weapon system of the armored infantry battalions is the Marder 1A3 and 1A5 armored personnel carriers . Mounted on the tower, the anti-tank weapon MILAN or MELLS (multi-role light guided missile system) allows the combat of armored vehicles.
The Puma armored personnel carrier is in the inflow, some armored infantry battalions are being converted. Each of the 3 combat companies of a battalion is to receive 14 Puma infantry fighting vehicles, plus 2 infantry fighting vehicles as a mobile command post for the battalion commander, so that each battalion will have 44 infantry fighting vehicles .
The Jaguar 1A3 tank destroyers and M113 tank mortars were retired in 2005 and 2006.
The anti-tank defense is to be provided by equipping each platoon or group with the PARS 3 LR , and fire support by the artillery's Howitzer 2000 .
Infantry systems
The anti-tank weapon MILAN and the Panzerfaust 3 are available for dismounted combat of armored vehicles . Each dismounted squad also usually has an MG3 machine gun with them. Each company also has soldiers armed with the G22 sniper rifle . The heavy Panzerfaust FFV Carl Gustaf has only been used for battlefield lighting since 1986 . Only mounted crews ( gunner , driver, commander) are often armed with the MP2 (Uzi) or MP7 submachine gun instead of the G36 . Since 2007, an equipment system has been introduced for parts of the Panzer Grenadier Troops under the name Infantryman of the Future , which offers individual soldiers better personal protection as well as new weapon systems and ensures digital networking.
uniform
The weapon color of the Panzer Grenadier Troops, shown for example as the color of the braids and collar tabs , is (hunter) green . The beret is also green. The armor and beret color is shared by the Panzergrenadier troop with other infantry troops such as the hunter troop . The silver beret badge is framed by an oak wreath, the German flag, two crossed 98k carbines and an armored personnel carrier. The driver, gunner and commander of the armored personnel carrier wear a one-piece tank combination instead of field pants and a field blouse.
Tactical sign
The armored infantry troop is designed as mechanized infantry . The military symbol is a combination of a lying oval for the armored troops and the crossed lines as a symbol for the infantry, according to their fighting style. The oval stands for a continuous crawler belt. The St. Andrew's cross represented crossed rifles, bandeliers or swords and is the basic symbol of all infantry units of NATO . Individual vehicles and units of the Panzer Grenadier Troops are marked with different tactical symbols according to their task and affiliation. In the course of time there were also special tactical signs for armored infantry battalions with special equipment. Examples: The Panzergrenadierbataillone (mot) carried a St. Andrew's cross with two circles, which stood for the motorization . The battalions with armored personnel carriers instead of armored personnel carriers led instead of the stylized chain next to the St. Andrew's cross a rectangle with a line inscribed on both sides. However, the latter two tactical signs are no longer in use with the decommissioning of these types of battalions.
war cry
The battle cry is a triple tank grenadier - turn! On it! Over it! The rank in command calls Panzergrenadiers , what the troops with it ! On it! Over it! replied. In contrast to this, as with the PzGrenBtl 112, a former hunter battalion, the battle cry of the hunter troop (Horrido - Joho!) Was also widespread.
The battle cries of individual companies or battalions can, however, differ in part. An example is the call of the former 2nd Company of the Panzer Grenadier Battalion 72nd Company Commander : Zwote ... - Company Sergeant (Spieß) : Clear to ... - Company replied: ... Battle .
The armored mortar companies had deviating battle cries - so the former 6th Company (heavy company - three mortar trains and a Panzerjägerzug) PzGrenBtl 72: rank: Warning ... - Company replied ... Fire what the command of mortar group leader for the loader's the grenade in dropping the pipe was equivalent. The former 6th Company PzGrenBtl 52: Rank: Appoint ... - Company: Fire!
During Army Structure IV, the 5th companies were the mortar platoons (6th companies did not exist at that time). In 5th / 193: Rank: Mortar on ... - Company replied: ... strike . The battle cry of the 5./72 (it became the 6./72) had the battle cry: Attention - serve!
Rank designations
The lowest rank in the Panzergrenadier troops is the Panzergrenadier . He corresponds to the rank of rifleman, radio operator, hunter etc. ( → see here ) of other branches of service. The other ranks correspond to the general ranks of the Bundeswehr .
|
|
||
| Lower rank | Higher rank | |
| - | Panzergrenadier | Private |
|
Rank group : Teams-NCOs-NCO-NCOs-Lieutenant-Captains-Staff officers-Generals |
||
Trivia
Panzergrenadiers or Grenis are the object of many jokes because of their physically demanding fighting style. For example, the following rhymes have jokingly prevailed within the Bundeswehr:
- It's not a human, it's not an animal - it's an Panzergrenadier.
- God created people, God created animals, but not grenadiers, because these goddamn monkeys were created by the Bundeswehr.
- Never step on a green stone, because it could be a Panzergreni.
- Based on the Erlkönig's ballad : If you walk so late through night and wind, it's Greni with his locker. He keeps him safe, he keeps him warm, it was night alarm again. (But it gets worse, a Falli / OA comes with his room)
It is also often rumored that the grenadier's greatest enemy is the lawnmower , as it deprives them of food and cover . This is countered with the statement that the tank grenadiers are not allowed to dig deeper than 1.50 m, as they would meet pioneers there.
literature
- Klaus Christian Richter (Ed.): Panzer Grenadiers. A branch of service in the mirror of its history . 2. revised and additional edition. Munster 2006, ISBN 3-00-014858-2 .
- Horst Riemann: German Panzer Grenadiers . ES Mittler & Sohn, Herford 1989, ISBN 3-8132-0326-3 .
- Ferdinand von Senger and Etterlin : The Panzer Grenadiers . JF Lehmanns, Munich 1961.
- Reinhard Scholzen : The infantry of the Bundeswehr. Motorbuch Verlag, Stuttgart 2011, ISBN 978-3-613-03293-4 .
- André Deinhardt : Panzer Grenadiers - a branch of the Cold War from 1960 to 1970, security policy and armed forces of the Federal Republic of Germany . tape 11 . Oldenbourg Wissenschaftsverlag, Munich 2012, ISBN 978-3-486-70464-8 .
- Marcel Bohnert & Andy Neumann: Panzer Grenadiers in combat in Afghanistan . In: Freundeskreis der Panzergrenadierruppe (Ed.) Panzergrenadiers. A branch of service through the ages . Munster et al. 2016, ISBN 3-933802-35-0 , pp. 42 ff .
Web links
- The armored forces. Federal Ministry of Defense , head of the press and information staff, accessed on October 12, 2010 .
- Freundeskreis-panzergrenadiere.de. Freundeskreis der Panzergrenadierruppe e. V., accessed on October 12, 2010 .
- Thomas Hartwig: Panzer Grenadier Battalions. In: Panzermodellbau - the German side all about 1:35 military models. Retrieved October 12, 2010 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ What is the task of the armored forces? Federal Ministry of Defense , head of the press and information staff, accessed on October 12, 2010 .
- ↑ Federal Ministry of Defense (ed.): HDv 100/100 Troop Leadership (TF) . No. 233 , 2000.
- ↑ Federal Ministry of Defense (ed.): HDv 231/100 (zE), Das Panzergrenadierbataillon . No. 1003 , 2001.
- ^ The stationing of the Bundeswehr - October 2011 (PDF; 2.8 MB) BMVg, accessed on October 26, 2010 .
- ↑ New weapon against tanks: Upgrade for the Marder. In: https://www.bundeswehr.de . PIZ German Army, April 17, 2018, accessed on December 6, 2018 .
- ↑ a b The equivalent, higher and lower ranks are given in accordance with ZDv 14/5 B 185, cf. The Federal Minister of Defense (ed.): ZDv 14/5. Soldiers Act . DSK AV110100174, change status July 17, 2008. Bonn August 21, 1978, rank designations in the Bundeswehr, p. B 185 (Not to be confused with the Law on the Legal Status of Soldiers (Soldiers Act) . The order of the ranks shown in the info box does not necessarily correspond to one of the regular rank sequences provided for in the Soldiers' Career Ordinance , nor does it necessarily correspond to the rank hierarchy described in the Superiors Ordinance a managerial relationship ).