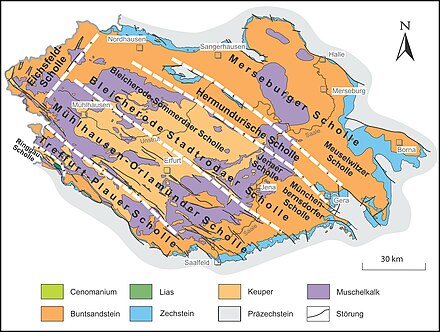
Hermundurian plaice
The Hermundurian plaice is located partly in Thuringia , partly in Saxony-Anhalt , the most north-eastern of the four Hercynian , that is, from northwest to southeast running main floe in the area of the Thuringian Basin and its edge plates .
It extends from the red sandstone of the north Thuringian hill country northwest of the Kyffhäuser Aufbruchs near Nordhausen (Thuringia) over the Kyffhäuser mountains ( Perm ) along with the southwest Zechstein belt near Bad Frankenhausen and the adjoining Windleite ( red sandstone) to the Helme-Unstrut depression near Heldrungen and finally to Schmücke (in Kammlage Muschelkalk ) as well as Hoher Schrecke and Finne (red sandstone); It continues through various flat, wavy , loess-containing Triassic landscapes of the Lower Unstrut Plateau southwest of Naumburg ( Burgenlandkreis , Saxony-Anhalt) and the Altenburg-Zeitz loess hill country south to southeast of that city, to the Ronneburg cross zone ( Ronneburg arable and mining area ) near Gera (again in Thuringia) ) is achieved.
The Hermundurian plaice, together with the Merseburg plaice to the northeast, is grouped together to form the Osterland plaice , named after the Osterland .
Limitations
To the southwest, the Hermundurian plaice is bounded by the Finne fault zone , beyond which the Bleicherode – Stadtrodaer plaice of the north-eastern Thuringian basin joins; its north-western border forms, according to the broadest possible interpretation, the north-eastern arm of the Ohmgebirgs rift zone or its extension northwest of Bischofferode ; in the northeast, the Kyffhäuser-Crimmitschauer fault zone represents a border to the Merseburg plaice .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b D. Franke: Regionalgeologie Ost - Geological online encyclopedia for East Germany