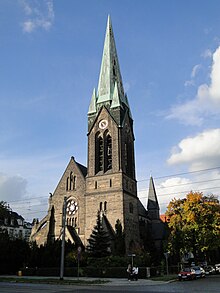Herz-Jesu-Kirche (Dresden)
The Catholic Herz-Jesu-Kirche in Dresden was designed by the architect August Menken and inaugurated in 1905. The neo-Gothic church is dedicated to the Sacred Heart of Jesus as a patronage. It stands on the property at Borsbergstrasse 15 in the Striesen district of Dresden on the border with Johannstadt and is the second largest church of the Dresden deanery .
History and architecture
With her generous donation, the founder Veronika Fischer made the construction of the urgently needed church in the expanding part of Dresden possible at the turn of the century. The neo-Gothic church was built between 1903 and 1905 according to plans by August Mencken from Berlin. In the years 1973–1976 the spire was simplified, the equipment reduced and the chancel redesigned by Egon Körner . The copper roof was replaced in 2016. On April 1, 1947, the St. Luke Passion was premiered by Rudolf Mauersberger in the church.
The neo-Gothic church is a basilica with six bays and ends in a one-bay choir with a polygonal end. The main portal to Borsbergstraße is provided with column shafts made of Rochlitz porphyry tuff and is crowned by a Wimperg . During the Second World War , the church was miraculously saved from destruction. Only the windows of the church were destroyed and later replaced with new glazing based on a design by Bruno Seener. The new windows show biblical scenes such as “The Birth of Our Lord Jesus Christ” or one of the most beautiful depictions of Christ in Dresden “The Good Shepherd” in the sanctuary. A restoration with the attachment of protective glass to the windows was carried out in 2001. The neo-Gothic stone altar contains a relic of Saint Donata . The rich sculptural decoration on the portals and on the capitals inside with plant motifs (ivy, vine leaves, oak and chestnut) and animals (bear, lion, squirrel, birds and snail) is striking. Above the two-part main portal there is a statue of Christ with the call to the Savior ( Mt 11.29 EU ). From the neo-Gothic fittings are preserved: remains of the high altar (today's side altar), the altar table with tabernacle , the pulpit, the baptismal font and a rich wrought iron grating between the vestibule and nave.
Peal
Shortly after the consecration of the church, the renowned Otto bell foundry from Hemelingen / Bremen delivered a four-part bronze bell with a weight of almost 6.5 tons. The bells fell victim to the confiscation of bells during the First World War. New OTTO bells were delivered in 1928, but they were melted down during World War II. The two Otto bells had the same disposition as today's bell. The belfry now houses four bells with the nominal values h 0 - d flat 1 - f sharp 1 - g sharp 1 , with these tones the church chorale " Salve Regina " begins . The big bell with a diameter of 1.65 m and the nominal h 0 , which bears the inscription "Hope 1989", was cast in 1986 in the VEB bell foundry Apolda and was originally intended for the French Cathedral in Berlin . Since the 2800 kg bell sounded too deep for the chimes of the cathedral, but fit into the chimes of the Sacred Heart Church, it was recorded. The "three-king bell" with the nominal dis 1 weighs 1770 kg and has a diameter of 1.35 m. It was cast on September 22, 1990 at Metz in Karlsruhe. As an inscription it bears the quote from Joachim Cardinal Meisner from the Katholikentreffen 1987 in Dresden: “We don't want to follow any other star than that of Bethlehem ”. In addition, the relief of the Magi, as they follow the star at Bethlehem, is carved. In the “Mater Dolorosa bell” the Pietà and the biblical quotation from the Gospel of Luke “Blessed are you who weep now, for you will laugh” ( Lk 6.21 EU ) are inscribed. It sounds with the nominal f sharp 1 and has a weight of 976 kg. The smallest bell, which was the only one to survive from 1929 and was not melted down during World War II, weighs 525 kg and sounds with the nominal g sharp 1 . The complete chime, as it has been heard in this combination since Christmas 1990 in the Dresden district of Johannstadt, only sounds at special solemn celebrations of the Catholic Church. Normal worship heard the bells with dis 1 - F # 1 - G # 1 . For the Angel of the Lord at 12:00 p.m. and 6:00 p.m., only one bell is currently ringing. Every quarter of an hour you will hear a stop (after 15 minutes - 1 stop; after 30 - 2 stops; after 45 - 3 stops; after 60 - 4 stops), at the full hour the number of hours is also played in a lower tone. The time is struck from 8:00 a.m. to 7:00 p.m.
organ

The romantic organ , donated by the state elder Veronika Fischer, was built in 1909 by the Jehmlich brothers . The organ has a pneumatic action and cone wind chests . It has 37 registers , which are divided into three manuals and pedal . In the lateral prospectus fields 34 pipes from the registers Principal Bass 16 ', Octave Bass 8' and Principal 8 'are arranged. During a six-month restoration in 1990 by Jehmlich, no changes to the disposition were made. A major repair of the organ in June 2006 resulted in further sound improvements.
Well-acclaimed organ music regularly takes place on the Jehmlich organ. The organ has the following disposition :
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Coupling : 6 normal coupling, super-octave coupling I / I, II / I, II / II, sub-octave coupling III / II.
- Playing aids : 4 fixed combinations (p, mf, f, ff = Tutti) , 2 free combinations, crescendo roller, automatic pedal switching, holder for roller, hand register, tongue register, coupling.
Church life
From 1991 to 1997 Michael Bautz was parish priest of the Sacred Heart Congregation. During this time, a Catholic kindergarten was created near the parish through his efforts, the parish center was installed in the rectory and renovation work was carried out on the exterior facade and the colored glass windows of the church.
From 1995 to 2001 Gottfried Swoboda worked as pastor for this parish. In 2004, Easter Vigil was celebrated in the church together with Bishop Joachim Reinelt and the Apostolic Nuncio Erwin Josef Ender .
For World Youth Day 2005 in Cologne, the official World Youth Day Cross was carried to the Sacred Heart Church as part of a 40-day foot pilgrimage from Dresden to Cologne. The church was one of the first stops on this pilgrimage .
In November 2005 the parish celebrated the 100th anniversary of the parish fair with a festival week and a pontifical mass .
In the field of ecumenism there are many successful joint steps towards each other, for example the traditional ecumenical worship service with the neighboring Evangelical Lutheran. Erlöser-Andreas-Kirchgemeinde, from the year 2000 by merging Johanneskirchgemeinde, on Reformation Day . The common service begins in the Catholic Sacred Heart Church and is then concluded there after a large procession to the ruins of the Evangelical Trinity Church . For the Ecumenical Church in 2003 in Berlin, this project was presented at a joint stand.
The parish is shaped by many groups and circles, including a. the youth, the lecturers or the church choir . Many offices in the church are filled by voluntary helpers, for example the ministry of the sexton or communion helper .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Georg Dehio: Handbook of German Art Monuments. Saxony I. District of Dresden. Deutscher Kunstverlag, Munich 1996, ISBN 3-422-03043-3 , p. 312.
- ↑ Information on new stocking , accessed on November 22, 2016
- ^ Gerhard Reinhold: Otto bells. Family and company history of the Otto bell foundry dynasty . Self-published, Essen 2019, ISBN 978-3-00-063109-2 , p. 588, in particular pages 515 u. 530 .
- ↑ Gerhard Reinhold: Church bells - Christian world cultural heritage, illustrated using the example of the bell founder Otto, Hemelingen / Bremen . Nijmegen / NL 2019, p. 556, especially p. 479 u. 493 , urn : nbn: nl: ui: 22-2066 / 204770 (dissertation at Radboud Universiteit Nijmegen).
- ↑ Disposition of the organ on the Jehmlich company website
Coordinates: 51 ° 2 ′ 45.5 ″ N , 13 ° 46 ′ 31.7 ″ E