Hexafluorophosphates
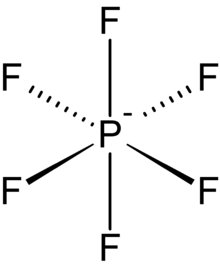
The hexafluorophosphates form a group of substances , whose representatives consisting of a phosphorus atom and six fluorine atoms existing, single negative charge, PF 6 - - anion contained. This octahedral molecule is isoelectronic with sulfur hexafluoride and the hexafluorosilicate dianion, SiF 6 2− and is valence isoelectronic with the highly stable superacid anion fluorantimonate SbF 6 - . The hexafluorophosphates are the salts of the volatile hexafluorophosphoric acid . Like ordinary phosphates , they contain phosphorus in the + V oxidation state .
properties
As a non-coordinating anion, the hexafluorophosphate is a poor nucleophile . In ionic liquids it is susceptible to decomposition with the release of hydrogen fluoride , but is generally very stable in solution. The hydrolysis of the phosphate ions takes place very slowly, even in heated concentrated acids and even more slowly under basic conditions. They are somewhat more stable against anodic oxidation than tetrafluoroborates and perchlorates . Their solubility properties follow those of perchlorates. Thus, potassium and Tetramethylammoniumhexafluorophosphat only moderately soluble in water , while sodium , ammonium and Erdalkalimetallhexafluorophosphate are highly soluble.
Extraction and presentation
The preparation of hexafluorophosphates of alkali metals such as sodium and potassium and of ammonium hexafluorophosphate can take place by reacting the corresponding chlorides or fluorides with hydrofluoric acid and phosphorus pentachloride .
The reaction of the metal fluoride with phosphorus trifluoride, for example with potassium and cesium, also produces the corresponding hexafluorophosphate.
The ammonium hexafluorophosphate can also be prepared by reacting hexachlorophosphazene with hydrogen fluoride .
Nitrosonium and nitrosyl hexafluorophosphate can be prepared by reacting with phosphorus pentabromide and bromine trifluoride .
Lanthanoid hexafluorophosphates can be obtained by reacting hexafluorophosphoric acid with basic lanthanoid carbonate hydrates.
Examples of hexafluorophosphates and their uses
A great many hexafluorophosphates are known and dozens are commercially available for applications. The simplest are purely inorganic salts with metal cations; Examples can be found in the table. The ammonium hexafluorophosphate NH 4 PF 6 and the silver hexafluorophosphate AgPF 6 are particularly important starting materials for the synthesis of other hexafluorophosphates . The most important hexafluorophosphate in terms of production volume is lithium hexafluorophosphate LiPF 6 , which is contained in the electrolytes of most lithium-ion accumulators , lithium batteries and in lithium-ion capacitors . There are also several groups of compounds of hexafluorophosphates that are used as coupling reagents in peptide synthesis , see the table "Hexafluorophosphates with organic cations I".
| important inorganic hexafluorophosphates | |
|---|---|
|
Hexafluorophosphates
with metal cation |
Hexafluorophosphates with others
inorganic cations |
| Lithium hexafluorophosphate Li + PF 6 - | Nitrosyl hexafluorophosphate NO + PF 6 - |
| Sodium hexafluorophosphate Na + PF 6 - | Nitronium hexafluorophosphate NO 2 + PF 6 - |
| Potassium hexafluorophosphate K + PF 6 - | |
| Silver hexafluorophosphate Ag + PF 6 - | Ammonium hexafluorophosphate NH 4 + PF 6 |
| Hexafluorophosphates with organic cations I: | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Phosphonium reagents
|
||||||||
Uronium / Aminium / Imonium reagents
|
| Hexafluorophosphates with organic cations II: |
|---|
| 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate BMIM-PF6 |
| 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate EMIM-PF6 |
| 1-ethyl-3-propylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate EPIM-PF6 |
| Hexafluorophosphates with organic cations III:
Derivatives of ammonium hexafluorophosphate |
|---|
| Tetramethylammonium hexafluorophosphate [TMA] [PF 6 ] |
| Tetraethylammonium hexafluorophosphate [TEA] [PF 6 ] |
| Tetrabutylammonium hexafluorophosphate [TBA] [PF 6 ] |
| Tetrahexylammonium hexafluorophosphate [THA] [PF 6 ] |
Hexafluorophosphates are also used for the electropolishing of alloys. Some are also used in catalysis , e.g. B. the Crabtree catalyst for hydrogenation, which contains monovalent iridium. Hexafluorophosphates are also used as ionic liquids , e.g. B. the examples given in the table. The tetrabutylammonium hexafluorophosphate , when mixed with acetonitrile, is one of the best non-aqueous electrolytes, as it offers a very large potential range (“electrochemical window”) of 6.3V.
determination
The hexafluorophosphate of concentrated aqueous solutions can be precipitated and thereby determined. Until 1963, nitrone ( Busch reagent , protonated in acidic solution as C 20 H 17 N 4 + ) and the gravimetric method, in which the dried precipitate is weighed, were used as the precipitation reagent . Since 1963, tetraphenylarsonium chloride has been used as a precipitation reagent for PF 6 - :
The determination can also be carried out gravimetrically, or an amperometric titration is carried out.
Individual evidence
- ^ Paul J. Dyson, Tilmann J. Geldbach: Metal Catalysed Reactions in Ionic Liquids . Springer Science & Business Media, 2006, ISBN 978-1-4020-3915-7 , pp. 27 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Allen E. Gebala, Mark M. Jones: The acid catalyzed hydrolysis of hexafluorophosphate. In: Journal of Inorganic and Nuclear Chemistry. 31, 1969, p. 771, doi: 10.1016 / 0022-1902 (69) 80024-2 .
- ↑ In Sung Chun, Sung Jin Moon, Young Mee Na, Young-A. Lee, Kyung Ho Yoo, Ok-Sang Jung: Selective and sensitive recognition of hexafluorophosphate via an unusual equilibrium between a cationic square host and a guest. In: Inorganic Chemistry Communications. 10, 2007, p. 967, doi: 10.1016 / j.inoche.2007.05.008 .
- ↑ Ole Hammerich, Bernd Speiser: Organic Electrochemistry, Fifth Edition Revised and Expanded . CRC Press, 2015, ISBN 978-1-4200-8402-3 , pp. 326 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Arthur DF Toy: The Chemistry of Phosphorus Pergamon Texts in Inorganic Chemistry . Elsevier, 1973, ISBN 978-1-4831-4741-3 , pp. 537 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b c J.H. Simons: Fluorine Chemistry . Elsevier, 2012, ISBN 0-323-14724-0 , pp. 56 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Stanley Kirschner: Inorganic Syntheses . John Wiley & Sons, 2009, ISBN 0-470-13289-2 , pp. 180 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ a b Willy Lange, Emil Müller: About the salts of phosphorus-hexafluoric acid, HPF 6 . In: Reports of the German Chemical Society (A and B Series) . tape 63 , no. 5 . Wiley, May 7, 1930, pp. 1058-1070 , doi : 10.1002 / cber.19300630510 ( wiley.com ).
- ↑ a b c d William John Williams: Handbook of Anion Determination . Butterworth-Heinemann, London Boston Sydney a. a. 1979, ISBN 0-408-71306-2 , Hexafluorophosphate, p. 428 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Antonia Perez De Los Rios, Francisco Jose Hernandez Fernandez: Ionic Liquids in Separation Technology . Elsevier, 2014, ISBN 978-0-444-63262-3 , pp. 62 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Peter Wasserscheid, Thomas Welton: Ionic Liquids in Synthesis . 2nd, completely rev. and enl. ed. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2008, ISBN 978-3-527-31239-9 , Electrochemical Properties of Ionic Liquids, p. 147 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b Harold E. Affsprung, Vernon S. Archer: Gravimetric Determination of Hexafluorophosphate as Tetraphenylarsonium Hexafluorophosphate. In: ACS (Ed.): Analytical Chemistry . tape 35 , no. 12 , November 1, 1963, pp. 1912–1913 , doi : 10.1021 / ac60205a036 (English, acs.org ).
- ↑ a b Harold E. Affsprung, Vernon S. Archer: Determination of Hexafluorophosphate by Amperometric Titration with Tetraphenylarsonium Chloride. In: ACS (Ed.): Analytical Chemistry . tape 35 , no. 8 , July 1, 1963, p. 976-978 , doi : 10.1021 / ac60201a017 (English, acs.org ).