Isovaleric acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
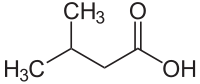
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Isovaleric acid | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 5 H 10 O 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, strongly malodorous liquid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 102.13 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
0.93 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
<−30 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
175-177 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
0.5 hPa (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
little in water (25 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4033 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Isovaleric acid ( 3-methylbutyric acid ) is a methyl-branched, short-chain and saturated fatty acid , the monocarboxylic acid belongs to the hemi terpenes . The name comes from the fact that it is one of the four constitutional isomers of valeric acid and is therefore one of the pentanoic acids .
Occurrence
Isovaleric acid is the main valeric acid in valerian and can be isolated in large quantities from its roots . It is also found esterified in many natural substances , for example in alkaloids or in valepotriates .
Isovaleric acid is a metabolite of leucine . Foot odor is based - besides other short-chain fatty acids - in particular on the presence of isovaleric acid, which is formed by bacteria from the amino acid leucine found in sweat .
properties
The flash point of the liquid is 78 ° C (measured in a closed cup), the ignition temperature is 385 ° C. If the liquid is heated above its flash point, its vapors can form an explosive mixture with air . The lower explosion limit is 1.4% by volume or 60 g / m 3 and the upper explosion limit is approximately 7.3% by volume or approximately 310 g / m 3 . The smell of isovaleric acid is very similar to the smell of sweat feet.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b W. Karrer : Constitution and occurrence of organic plant matter. 2nd edition, Springer, 1976, ISBN 978-3-0348-5143-5 , p. 288.
- ↑ Entry on ISOVALERIC ACID in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on June 30, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Entry on 3-methylbutyric acid in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 10, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-342.
- ↑ Entry on 3-methylbutyric acid. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on September 30, 2014.
- ↑ a b F. Kanda, E. Yagi, M. Fukuda, K. Nakajima, T. Ohta, O. Nakata: Elucidation of chemical compounds responsible for foot malodour . In: British Journal of Dermatology . tape 122 , no. 6 , June 1990, ISSN 1365-2133 , pp. 771–776 , doi : 10.1111 / j.1365-2133.1990.tb06265.x , PMID 2369557 (English): “Iso-valeric acid was present in all the subjects with foot odor […] The smell of iso-valeric acid was found to resemble most clearly that of foot odor ” .
- ↑ a b Katsutoshi Ara, Masakatsu Hama, Syunichi Akiba u. a .: Foot odor due to microbial metabolism and its control . In: Canadian Journal of Microbiology . tape 52 , no. 4 , April 2006, p. 357-364 , doi : 10.1139 / w05-130 , PMID 16699586 .


