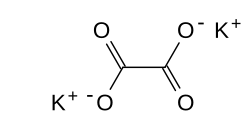
Potassium oxalate
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Potassium oxalate | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | K 2 C 2 O 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless and odorless solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 184.23 g mol −1 (as monohydrate) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
2.13 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
397 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
good in water (360 g l −1 at 20 ° C, anhydrous substance) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−1346.0 kJ / mol |
||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Potassium oxalate is a crystalline chemical compound that can be in the form of its hydrate or anhydrous. Oxalates are the salts of oxalic acid (also clover acid ).
Occurrence and representation
Potassium oxalate occurs naturally in wood sorrel ( Oxalis acetosella L. ) in dissolved form in the plant sap. It can be synthesized by reacting equivalent amounts of oxalic acid and potassium hydroxide or potassium carbonate ( potash ).
properties
As a monohydrate, potassium oxalate forms colorless crystals that are readily soluble in water. Above 100 ° C, the hydrated salt changes into the anhydrous form. The resulting anhydrate shows a melting point of 397 ° C. With further heating from 500 ° C a decomposition takes place with separation of carbon monoxide and formation of potassium carbonate .
The monohydrate crystallizes in a monoclinic crystal lattice. Two polymorphic forms are known for the anhydrate . The form, which is stable at room temperature, forms an orthorhombic crystal lattice. The crystal structure of the high temperature form is tetragonal .
use
Water-soluble oxalates are used in electroplating and in analytical chemistry for calcium determination , since calcium oxalate is precipitated from a solution as a poorly soluble calcium salt. Many rust removal agents contain oxalic acid salts because they complex heavy metal ions and thus make them water-soluble.
safety instructions
Potassium oxalate has irritating to corrosive effects on mucous membranes and skin. All potassium oxalates are poisonous in higher concentrations due to the disruption of calcium metabolism and thus causing kidney dysfunction. As an antidote, aqueous magnesium salt solution is administered to prevent the formation of the kidney-blocking calcium oxalate crystals and to convert the crystals that have already formed into the more water-soluble form magnesium oxalate.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on DIPOTASSIUM OXALATE in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on March 4, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on potassium oxalate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d Mohamed, MA; Galwey, AK; Halawy, SA: The activities of some metal oxides in promoting the thermal decomposition of potassium oxalate in Thermochim. Acta 387 (2002) 63-74, doi : 10.1016 / S0040-6031 (01) 00830-9 .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-23.
- ↑ a b c Masuda, Y .; Ito, R .; Matsuda, T .; Ito, Y .: The thermal phase transition of anhydrous potassium oxalate in Thermochim. Acta 131 (1988) 291-296, doi : 10.1016 / 0040-6031 (88) 80083-2 .



