Canitz Church (Riesa)
The defunct Evangelical Lutheran church in Canitz (town of Riesa ) in the church district of Leisnig - Oschatz in northern Saxony is located in the rural area between Oschatz, Riesa and Strehla .
history
13th to 17th centuries
In connection with the manor of Bero de Kaniz is Canitz 1221 first mentioned. The origin of a church is therefore assumed in the 13th century. Canitz belonged to the feudal lordship of the Burgraves of Meissen . The bishop Johann von Ienzenstein donated the altar of St. Wenceslas between 1376 and 1379 and donated 10 ½ shock new Meißner groschen , as is documented .
Around 1430 to 1431 a bell was installed . In the 16th century - a manor is documented in 1513 - Canitz was owned by the von Pflugk family, who had the old castle built around 1550.
From 1539 the church can be used as a parish church and has been listed as a branch church of the church in Borna since 1630 at the latest. In 1631 the plague broke out in Canitz and claimed 106 lives among the 143 inhabitants. Around 1655 the von Schleinitz family was in the possession of Canitz, the manor owner Andreas Dietrich von Schleinitz gave the church a silver goblet for 25 thaler and 8 groschen. When the subsequent owner Johann Wilhelm Wittmann died in Canitz in 1798, his widow Johanna Sophie Wilhelmine took over the estate as benefactress. During her lifetime she bequeathed 10,000 thalers to the church and 1,000 thalers to the community as "iron capital".
Until 1800
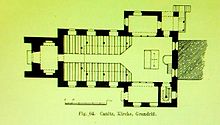
The somewhat unadorned simple church was located next to the manor house and was surrounded by the park of the new castle - built in 1758 and demolished and removed as a result of the land reform in 1947. From 1693 to 1697 the manor owner Andreas Dietrich von Schleinitz had it rebuilt and expanded. A rectangular nave was created with a tower on the west side with an octagonal tower floor and a concluding curved dome. Two two-story prayer rooms were arranged in the chancel.
A new tower, taller and stronger, was added in 1697. Carelessness and the foundation on alluvial sand during construction repeatedly led to the formation of cracks in the tower.
A massive altar was built in around 1672. The chronicles report that the church was extensively rebuilt in 1697. Prussian soldiers looted the church during the Seven Years' War in 1758 and mainly stole the organ pipes made of tin . The new rectory was completed around 1741 .
Around 1784 extensive repairs were carried out on the tower of the church and on the outer walls. At the same time, the roof was completely renewed, new galleries installed and new chairs set up in the church.
Until 1945
In the years 1829 to 1830 the parish farm buildings were rebuilt. Around 1891 the large barn burned down and was not rebuilt. A further renovation of the church took place in the years 1863 and 1869 to 1870. In particular, the church tower, the staircase to the pulpit and the northern prayer room were renewed.
On the occasion of the 200th anniversary of the church, a new organ was installed from the interest of Wittmann's legacy . Another new font made of oak wood with a bronze font completed the inventory . The old Gothic font from the 14th century was placed in the churchyard behind the church in 1863. In 1894, serious cracks were again repaired in the tower.
In 1871 a memorial plaque for the victims of the Franco-German War was placed inside.
A bell was melted down from the original chime in 1914 . In 1921 a memorial stone with the names of the victims of the First World War was attached and consecrated on the outer wall of the church. Since 1931 the Canitz Church has belonged to the Borna Evangelical Lutheran parish .
Again in 1942 a bell of the historical peal from 1431 was delivered for armament purposes. This could be fetched back from the collection point in Hamburg in 1948 . When the Red Army marched in in 1945, Canitz and the church were looted. The church building was badly damaged.
After 1945
In the years 1948 to 1949 the church was renovated and the war damage was removed. In the years 1953 to 1954 an exterior renovation was carried out with the renewal of the facade plaster. The structural condition deteriorated noticeably. The roof had major damage and was therefore leaky. The rainwater destroyed the wooden roof structure. The preservation of this church failed not least because of the lack of provision of materials and construction companies by the state authorities.
In 1967 the church was closed due to dilapidation and acute danger of collapse. It was removed from 1975. The surrounding walls remained up to the eaves level . Some inventory was given away or sold to surrounding churches. Since the church building was lost, services have taken place in the parish room of the rectory at Oschatzer Straße 85.
Peal
The ringing consisted of two bronze bells made by the Schilling bell foundry in Apolda . The bell cage is made of a wooden structure and so are the bell yokes. The bells were cast in 1904 and were consecrated with the church on January 29, 1907.
The following is a data overview:
| No. | Casting date | Caster | diameter | Dimensions | Chime |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1933 | Schilling bell foundry | 575 mm | 122 kg | e ″ |
| 2 | 1430 | Bell foundry unknown | 573 mm | 119 kg | fis ″ |
Bell tower
In 1989 a bell tower was built in the cemetery for the two Canitzer bells. The historic bell from 1431 will ring again.
In November 2005 a support association was founded to rebuild a new church. In the following years the church was cleared of rubble, the rubble of the collapsed roof and tower cleared and the masonry secured. Two historical grave tablets from the 16th century and from 1890 were uncovered and secured. Parts of the galleries and the tower clock were also salvaged and stored. Over 100 tons of reusable masonry has now been sorted out and is waiting to be reused.
Reconstruction project
In the case of a new building, the remaining remains of the wall should be included. Then a “living” church could emerge again with church services, exhibitions and concerts. New users were also considered, such as the Evangelical Lutheran Church of Saxony , the district fire brigade of the Canitz minstrel, the Canitz sports community or the glider pilot club. Donations have been collected from the development association and funding has been applied for. With grants from the regional church and funds from the preservation of monuments, it was possible to secure an emergency. The visible result is the construction progress achieved, the new roof structure with the topping-out ceremony on November 11, 2017. As a result of the emergency protection, the roof was completely re-covered and the planning for an interior design started. Currently the church has a roofed church space and an anteroom, the tower room. The ruinous remains of the masonry of the apse and choir are still in need of renovation . With the popular TV program of the MDR Mach Dich Ran , the Canitzers earned an amount of 70,000 euros for the further development of the Canitzer village church. On September 27, 2019, the check was handed over in the live broadcast Oh Happy Day . The high goal is the 800 year anniversary of the first mention of the church, planned for 2021.
literature
- D. Georg Buchwald : New Saxon Church Gallery, The Ephorie Oschatz. Published by Awed Strauch, Leipzig 1901, Volume 6, pp. 140ff.
- Richard Steche : Saxony Church Gallery, The Inspection Oschatz. Verlag von Hermann Schmidt, Volume 3, pp. 140 ff.
- Construction and art monuments of the Kingdom of Saxony. Issue 27: Oschatz Main Office. Edited by Cornelius Gurlitt . Verlag Meinhold and Sons 1910, pp. 61–67. Digitized
- Church council Borna-Canitz, Pastor Jochen Kinder: Congregational letter , special edition March 2009.
- Matthias Donath , Jörg Blobelt : Protestant churches in the church district Leisnig-Oschatz. Printing printing house Dober, Mügeln; 2011; P. 27.
- Horst Bilz: Heimatbuch Canitz. 1958.
- Values of our homeland: Around Oschatz and Riesa. Akademie-Verlag Bertin, 1977.
- Riesaer Heimat issue 7/1958; Canitz through the ages .
- Cindy Zscherper: Project in Social Studies - Introduce your hometown! Local history: December 9, 2002.
- Rainer Thümmel: Bells in Saxony. Sound between heaven and earth. Edited by the Evangelical Regional Church Office of Saxony . With a foreword by Jochen Bohl and photographs by Klaus-Peter Meißner. Evangelische Verlagsanstalt, Leipzig 2011, ISBN 978-3-374-02871-9 , p. 280.
Web links
- Reconstruction of the Canitz Church
- Canitz church near Ev.-Luth. Liebschützberg parish
- Reconstruction study
- From the ruin to the unique concert hall on Weltbeweger.de ( Memento from June 26, 2016 in the web archive archive.today )
- Historical view of the place Online Collection - Staatliche Kunstsammlungen Dresden
Individual evidence
- ^ A b Canitz in the Digital Historical Directory of Saxony
- ^ D. Georg Buchwald: New Saxon Church Gallery, The Ephorie Oschatz. Published by Awed Strauch, Leipzig 1901, Volume 6, p. 139.
- ^ D. Georg Buchwald: New Saxon Church Gallery, The Ephorie Oschatz. Published by Awed Strauch, Leipzig 1901, Volume 6, p. 140.
- ^ Steche: Saxony Church Gallery, The Inspection Oschatz. Verlag von Hermann Schmidt, Volume 3, p. 75.
- ^ D. Georg Buchwald: New Saxon Church Gallery, The Ephorie Oschatz. Published by Awed Strauch, Leipzig 1901, Volume 6, p. 145.
- ↑ a b c Architectural and art monuments of the Kingdom of Saxony, Issue 27, Amtshauptmannschaft Oschatz. Modifications made by Cornelius Curlitt. Verlag Meinhold and Sons, 1910, p. 61.
- ^ D. Georg Buchwald: New Saxon Church Gallery, The Ephorie Oschatz. Published by Awed Strauch, Leipzig 1901, Volume 6, p. 142.
- ^ D. Georg Buchwald: New Saxon Church Gallery, The Ephorie Oschatz. Published by Awed Strauch, Leipzig 1901, Volume 6, p. 146.
- ↑ a b Rainer Thümmel : Bells in Saxony: Sound between heaven and earth . Evangelische Verlagsanstalt, Leipzig 2011, ISBN 978-3-374-02871-9 , pp. 280 .
- ↑ Friends' Association
- ^ Study - Reconstruction of Canitz Church as a community center. Lienig & Baumeister Architects, accessed on June 7, 2019 .
- ^ District fire brigade
- ^ Canitz marching band ( Memento from June 25, 2016 in the Internet Archive )
- ^ Canitz Sports Association
- ↑ Glider pilot club
- ↑ Congregational Letter-December-2019-January-February-2020.pdf
Coordinates: 51 ° 18 '48 " N , 13 ° 13' 5.8" E