Lorraine (Romansh)
Romance Lorraine ( French lorrain roman ) - not to be confused with the German - Lorraine Rhine and Moselle Franconian dialects , in the east and north of the Lorraine department of Moselle - belongs to the Langues d'oïl , which are often used as separate languages as well as dialects of French .
Romanesque Lorraine - like Walloon - originally had a strong influence on Germanic language elements and was therefore close to the neighboring German dialects . The Romansh-Lorraine dialect was preserved most originally and longest in the Alsatian Pays Which , which administratively corresponds to the canton of Lapoutroie . This canton comprises five Romano-Lorraine-speaking municipalities in the Vosges above Colmar . The local tradition is represented by the Musée du Pays Which in the locality of Frélandgroomed. The French name which (pronounced " welsch ") is itself a Germanism, which is different from the name of the Alemannic Alsatians and the Franconian Lorraine for the Romance language areas in the region bordering the Romance Lorraine, Franche-Comté and the Swiss canton Jura derives.
Classification and Distribution
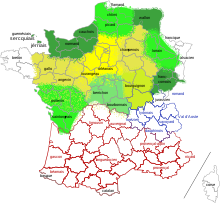
The Sprachinstitut (observatoire linguistique) Linguasphere distinguishes between seven variants of Romance Lorraine:
- Argonian (French: argonnais ) in the area of Argonnen , Woëvre , east of the French departments Ardennes , Meuse , Meurthe-et-Moselle
- Longovician (Longovicien) in the Longwy area , Longuyon
- Gaumesisch (gaumais) in the Arrondissement de Virton area , Province of Luxembourg , Belgium
- Messinian or Metzerisch (messin) in the Metz area and the surrounding area and the entire Francophone part of the Moselle department
- Nanceisch (or Nanzigerisch) (nancéien) in the Nancy area , south of the department of Meurthe-et-Moselle
- Spinalisch (spinalien) in the Épinal area , central Vosges in the Vosges department
- Deodatic (déodatien) in the Saint-Dié-des-Vosges area , Upper Vosges
After 1870, the members of the Stanislas von Nancy Academy were able to record 132 variants of Romanesque-Lorraine dialects (patois) between Thionville in the north and Rupt-sur-Moselle in the south, which, however, only means a diversification of the main variants into sub-variants.