Malononitrile
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
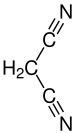
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Malononitrile | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 3 H 2 N 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless to yellow solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 66.06 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.049 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
32 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
220 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
1 h Pa (50 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4146 (34 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
186.4 kJ / mol |
||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
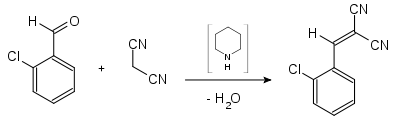
Malononitrile , also propanedinitrile , is a chemical compound from the class of nitriles having the formula CH 2 (CN) 2 . Malononitrile is relatively acidic with a p K s value of 11 in water. Malononitrile can therefore react in a Knoevenagel condensation , for example to produce 2-chlorobenzylidene-malononitrile .
Extraction and presentation
Malononitrile can be produced from chlorocyanoacetylene and ammonia . On an industrial scale, malononitrile is produced by reacting acetonitrile with cyanogen chloride at over 700 ° C. Other possibilities for production start from (2-cyano- N- alkoxy) -acetimidoyl halides, temperatures between 500 and 1000 ° C. also being required.
properties
Malonitrile is a flammable, colorless solid that is easily soluble in water. It decomposes from a temperature of 130 ° C, producing hydrogen cyanide , nitrogen oxides , carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide and an explosion is possible. The heat of decomposition determined by DSC is −108 kJ · mol −1 or −1650 kJ · kg −1 . At lower temperatures, contact with strong bases can lead to violent polymerization, which can also be explosive.
use
In chemistry, malononitrile is a starting material for the Gewald reaction , in which the nitrile condenses with a ketone or aldehyde in the presence of elemental sulfur and a base to form 2-aminothiophenes . Furthermore, malononitrile plays an important role in the synthesis of a variety of pharmaceutical and agrochemical active ingredients. Malononitrile is a starting material for the production of CS gas .
- Synthesis of 2-chlorobenzylidenemalonic acid dinitrile (CS gas)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry on malononitrile. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 5, 2016.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on malonitrile in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-322.
- ↑ Entry on malononitrile in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Data sheet malononitrile (PDF) from Merck , accessed on January 19, 2011.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-23.
- ↑ Evans pK a table (PDF; 245 kB)
- ↑ Peter B. Sargeant: Fluorocyclopropanes. I. Preparation and nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. In: Journal of Organic Chemistry. 35 (3), 1970, pp. 678-682.
- ^ Process for the preparation of malononitrile
- ↑ T. Grewer, O. Klais: Exothermic decomposition - investigations of the characteristic material properties. (= Humanization of working life. Volume 84). VDI-Verlag, Düsseldorf 1988, ISBN 3-18-400855-X , p. 8.
- ↑ Bretherick's Handbook of Reactive Chemical Hazards. 6th edition. Vol. 1, Butherworth-Heinemann, 1999, ISBN 0-7506-3605-X , p. 386.
- ↑ Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Technical Chemistry. 4th, revised and expanded edition. Volume 16, Verlag Chemie, Weinheim 1978, ISBN 3-527-20016-9 , pp. 419-423.