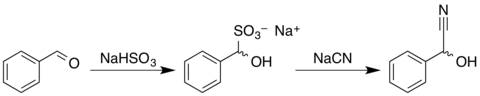
Mandelonitrile
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Simplified structural formula with no clear stereochemistry | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Mandelonitrile | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 7 NO | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
yellow liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 133.15 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point | ||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.530 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Mandelonitrile is a chemical compound from the group of substituted nitriles and alcohols , it is the nitrile of mandelic acid . It occurs in two stereoisomeric forms.
Occurrence
Mandelonitrile occurs naturally in small amounts in the seeds of some fruits. Mandelonitrile is the aglycon of the cyanogenic glycosides prunasin and amygdalin . Prunasin beta-glucosidase is an enzyme that converts prunasin and water to D- glucose and mandelonitrile.
Extraction and presentation
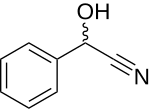
Mandelonitrile can be obtained by reacting benzaldehyde with sodium hydrogen sulfite and then reacting the reaction product with an aqueous solution of sodium cyanide or potassium cyanide to form the racemate .
properties
Mandelonitrile is a flammable, hardly inflammable, yellow liquid that is very sparingly soluble in water. It decomposes when heated above 170 ° C.
use
The naturally occurring ( R ) - (+) - enantiomer is used as an intermediate in the synthesis of optically active compounds such as α-hydroxycarboxylic acids, α-hydroxy aldehydes, α-hydroxy ketones and 2-amino alcohols.
safety instructions
The vapors of mandelonitrile can form an explosive mixture with air ( flash point 86 ° C). Mandelonitrile causes serious eye damage and is toxic in contact with the skin and if inhaled.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Entry on mandelonitrile in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 9, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c data sheet mandelonitrile, technical grade at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on June 25, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c d e entry on mandelonitrile. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 25, 2017.
- ↑ Data sheet DL-mandelonitrile (PDF) from Merck , accessed on June 25, 2017.
- ^ Emil Lehnartz: Introduction to Chemical Physiology . Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-662-36817-6 , pp. 267 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Franz v. Bruchhausen, Gerd Dannhardt, Siegfried Ebel, August W. Frahm, Eberhard Hackenthal, Ulrike Holzgrabe: Hagers Handbook of Pharmaceutical Practice Volume 8: Substances EO . Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-642-57994-3 , pp. 808 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ BB Corson, Ruth A. Dodge, SA Harris, JS Yeaw: Mandelic Acid In: Organic Syntheses . 6, 1926, p. 58, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.006.0058 ; Coll. Vol. 1, 1941, p. 336 ( PDF ).