Manna ash
| Manna ash | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Manna ash ( Fraxinus ornus ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Fraxinus ornus | ||||||||||||
| L. |
The manna ash ( Fraxinus ornus ), and Flowering Ash or jewelry Ash called, is a plant of the genus of ash trees ( Fraxinus ) in the family of Olive Family (Oleaceae). It owes its name to the sap that emerges from incised branches and twigs and hardens quickly. In addition to some other ingredients, the juice contains the sweet-tasting, hexavalent alcohol mannitol and is therefore of interest for medicinal use. In southern Italy , the manna ash is grown in plantations to obtain sieve tube juice ("manna").
description

Appearance and leaf
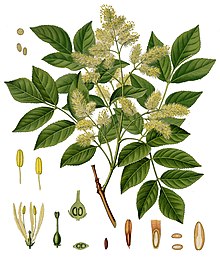
The manna ash is a deciduous, deciduous tree that reaches heights of 5 to 10, rarely up to 25 m. It forms a loose, fairly light and rounded crown. The trunk is round, straight and only forks at a certain height from the ground. The dark gray or blackish-gray, warty bark , in contrast to the common ash, does not have a clear furrow and ledge pattern. The branches are mostly radiant, but are more often bent and twisted than in the common ash. The bark of the twigs is olive to gray-green, round to squashed square and finely dotted with light brown lenticels . The opposite buds are blunt and slightly arched on the front and have only two outer, (silvery to brownish) gray bud scales.
The cross-opposed leaves are unpaired pinnate and about 15 to 20 cm long and oval in outline. There are usually 5 to 9 pinna leaflet available. The clearly stalked leaflets are ovate-lanceolate, pointed at the front, serrated to irregularly serrate and each about 3 to 7 cm long. Their upper side is medium green, the underside is lighter and on the leaf veins , especially at the base of the leaflet, brownish or whitish hairs.
Inflorescence, flower and fruit
The flowering period extends from April to June. The pleasantly fragrant flowers appear at the same time as the leaves. Many flowers stand together in terminal or lateral, initially upright, later overhanging, very dense, about 10 cm long and just as wide, leafy, paniculate inflorescences . The flowers are four-fold. The four sepals are inconspicuous. The four whitish petals are 7 to 15 mm long.
The solitary nut (Samara) is winged on one side, with the very narrow, elongated and approximately 2 cm long wing slightly edged on the front. The fruits ripen in October turn a shiny dark brown.
Chromosome number
The number of chromosomes is 2n = 46.
Occurrence
Natural occurrences of the manna ash are in the eastern Mediterranean area . Locations are proven for Spain, France (including Corsica), Italy (including Sicily), Switzerland, Austria, Hungary, the former Czechoslovakia, the former Yugoslavia, Bulgaria, Romania, Albania, Greece, Turkey, Syria and Lebanon. The manna ash is planted in southern Europe and southern central Europe as an ornamental and street tree. In Germany the manna ash is considered a naturalized neophyte . Here it is seldom found as a pioneer wood on former vineyards and steep slopes in Baden-Württemberg and Franconia. It also shows naturalization tendencies in the settlement areas of North Rhine-Westphalia.
The manna ash is a character species of the Orno-Ostryon association from the order of the Quercetalia pubescentis.
Systematics
The first release of Fraxinus ornus was made in 1753 by Carl Linnaeus in Species Plantarum , 2, S. 1057. A synonym of Fraxinus ornus L. is Fraxinus paniculata Mill.
Fraxinus ornus belongs to the Ornus DC section . from the genus Fraxinus .
One can distinguish between two subspecies:
- Fraxinus ornus subsp. ornus : It occurs from southern Europe and eastern central Europe to the Caucasus.
- Fraxinus ornus subsp. cilicica (Lingelsh.) Yalt. (Syn .: Fraxinus cilicica Lingelsh. ): It occurs in southern Turkey.
Use as a medicinal plant
Manna, the air-dried sap obtained by cutting into the bark (called manna cannelata ) from 8 to 10 year old trees, is used as a medicinal drug .
The juice contains up to 90% mannitol in addition to stachyosis and other sugars; Fraxin also occurs in traces .
Application: Manna is a mild laxative and can be used, for example, for hemorrhoids and intestinal fissures or other diseases in which defecation with loose stools is desired. Even Sweden herbal blends often contain Manna. Here, too, the active ingredient is the sweet-tasting mannitol . Mannitol is a polyol and got its name from the manna ash. Mannitol is hardly absorbed in the intestine, but holds back water there, thereby increasing the intestinal contents and thus stimulating peristalsis . As an "osmotic laxative", Manna may only be taken long-term after consulting a doctor. When administered intravenously, mannitol leads to severe diuresis , as is desirable, for example, in the event of poisoning and impending kidney failure . However, the medical use of mannitol in acute kidney failure is controversial and can even be harmful to health. In addition, mannitol has a certain importance as a sugar substitute for diabetics , since the substance is broken down independently of insulin . Mannitol is also used as a filler and binder for tablets.
Today you win mannitol mostly by hydrogenation of glucose or invert .
Common names
Exist or for manna ash also passed the other German trivial name : flowers ash, flowering ash, manna, Himmelsthau, Leympawm ( Middle High German ), lidbaum ( Old High German ), Limbom (Old High German), Linboum (Old High German), Mama ash, Wieläsch and dwarf ash.
supporting documents
literature
- Bruno P. Kremer: Trees. Native and introduced species in Europe (= Steinbach's natural guide ). New, revised edition. Mosaik, Munich 1996, ISBN 3-576-10554-9 .
- Eckehart J. Jäger, Klaus Werner (Ed.): Excursion flora from Germany . Founded by Werner Rothmaler. 10th edited edition. tape 4 : Vascular Plants: Critical Volume . Elsevier, Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Munich / Heidelberg 2005, ISBN 3-8274-1496-2 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Erich Oberdorfer : Plant-sociological excursion flora for Germany and neighboring areas . With the collaboration of Angelika Schwabe and Theo Müller. 8th, heavily revised and expanded edition. Eugen Ulmer, Stuttgart (Hohenheim) 2001, ISBN 3-8001-3131-5 , pp. 747 .
- ^ A b Fraxinus ornus in the Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), USDA , ARS , National Genetic Resources Program. National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland.
- ↑ F. Wolfgang Bomble: Critical and little-known species of vascular plants in the Aachen region III. Yearbook of the Bochum Botanical Association. Vol. 6, 2015, pp. 13–21 PDF (2 MB)
- ↑ First publication scanned at biodiversitylibrary.org .
- ↑ Entry at tropicos .
- ↑ a b c Rafaël Govaerts (Ed.): Fraxinus ornus. In: World Checklist of Selected Plant Families (WCSP) - The Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew . Retrieved December 11, 2017.
- ↑ a b c d Ingrid and Peter Schönfelder: The new manual of medicinal plants , Franckh-Kosmos Verlagsgesellschaft, 2011, ISBN 3-440-09387-5
- ↑ Bo Yang, Jing Xu, Fengying Xu, Zui Zou, Chaoyang Ye: Intravascular Administration of Mannitol for Acute Kidney Injury Prevention: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis . In: PLoS ONE . tape 9 , no. 1 , January 14, 2014, doi : 10.1371 / journal.pone.0085029 , PMID 24454783 , PMC 3891750 (free full text).
- ^ Georg August Pritzel , Carl Jessen : The German folk names of plants. New contribution to the German linguistic treasure. Philipp Cohen, Hannover 1882, page 155. ( online ).
Web links
- Manna ash. In: FloraWeb.de.
- Manna ash . In: BiolFlor, the database of biological-ecological characteristics of the flora of Germany.
- Fraxinus ornus L. In: Info Flora , the national data and information center for Swiss flora . Retrieved January 21, 2016.