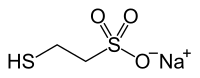
Mesna
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Mesna | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Sodium 2-sulfanylethanesulfonate ( IUPAC ) |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 2 H 5 NaO 3 S 2 | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 164.18 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Mesna (2- M ercapto e than s ulfonat- Na trium; trade name: Uromitexan , manufactured by Baxter International ) is a drug , of a so-called Zytoprotektor at a chemotherapy for neutralizing toxic metabolic products ( metabolites ) is used in the context of therapy with Oxazaphosphorines are formed. The oxazaphosphorines include cyclophosphamide , ifosfamide, and trofosfamide .
With its sulfhydryl group , Mesna binds and neutralizes the toxic metabolite acrolein , which can cause hemorrhagic cystitis with hematuria and is also responsible for other side effects. Acrolein is produced by biotransformation of the oxazaphosphorines in the liver .
In addition, the patients receive plenty of fluids, which helps ensure that the harmful metabolic products can be excreted more quickly via the kidneys . Another sulfhydryl group donor is, for example, N -acetylcysteine , which is often used together with mesna.
Mesna had another application as a mucolytic ; in this indication it was marketed under the name Mistabronco . With the expiry of the approval on June 30, 2008, this preparation was withdrawn from the market.
history
Lipovisch began the synthesis in 1945, which Schramm continued in 1955. The thiol was introduced because of the expectorant effect discovered in 1960.
In 1966 UCB-Chemie received the patent for Mesna and in 1972 it came onto the market.
Norbert Brock and colleagues found that the bladder and kidney toxicity of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide is due to the acrolein that is formed. Based on this fact, they examined thiols as a detoxifying substance and discovered a uroprotective effect for mesna.
synthesis
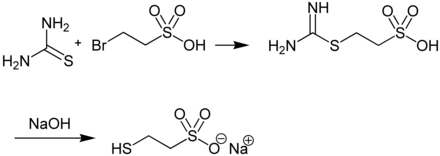
Mesna is produced in a two-step synthesis from thiourea and 2-bromoethanesulfonic acid:
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d data sheet Sodium 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 9, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ J. Büntzel, F. Bruns, D. Lüftner, D. Pollmann, S. Schildhauer: Protective drugs (organ protectors). In: H. Link, C. Bokemeyer, P. Feyer (eds.): Supportive therapy for malignant diseases. Deutscher Ärzteverlag, 2006, ISBN 3-7691-0466-8 , pp. 99–114, limited preview in the Google book search.
- ↑ Rang, Dales et al., (2007): Pharmacology, Sixth Edition , Churchill Livingstone, Elsevier.
- ↑ Pharmazeutische Zeitung 26/2008 of June 24, 2008 (online) .
- ^ A b Wolf-Dieter Müller-Jahncke , Christoph Friedrich , Ulrich Meyer: Medicinal history . 2nd, revised and expanded edition. Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft mbH, Stuttgart 2005, ISBN 978-3-8047-2113-5 , p. 184 f .
- ^ Axel Kleemann , Jürgen Engel, Bernd Kutscher and Dietmar Reichert: Pharmaceutical Substances , 4th edition (2000), 2 volumes published by Thieme-Verlag Stuttgart, ISBN 978-1-58890-031-9 ; online since 2003 with biannual additions and updates.
Web links
- BC Cancer Agency: Drug Manual for Mesna (PDF file; 104 kB)