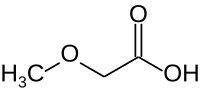
Methoxyacetic acid
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Methoxyacetic acid | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 3 H 6 O 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
clear colorless viscous liquid with a pungent odor |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 90.08 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.1768 g cm −3 (20 ° C ) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
7-9 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
202-204 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
3.57 |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water, in ethanol and in diethyl ether |
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4168 (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Authorization procedure under REACH |
of particular concern : toxic for reproduction ( CMR ) |
||||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
Switzerland: 1 ml m −3 or 3.7 mg m −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
Methoxyacetic acid is a derivative of acetic acid in which one hydrogen on the methyl group has been replaced by a methoxy group . As the outdated name methyl glycolic acid suggests, methoxyacetic acid as the simplest ether carboxylic acid can also be understood as the methyl ether of glycolic acid .
Because of its considerable reprotoxic potential, methoxyacetic acid is included in the list of SVHC substances ( substances of very high concern ) and is only registered as an intermediate in industrial use under strictly controlled conditions.
In consumer-oriented applications, such as B. for cleaning and descaling surfaces, the substance must be substituted by harmless alternatives.
Manufacturing
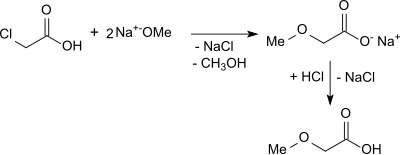
The reaction of monochloroacetic acid with twice the molar amount of sodium methoxide in methanol gives methoxyacetic acid in yields of 90% after acidification with dry hydrogen chloride gas and vacuum distillation.
The synthetic route is inefficient because it starts from relatively expensive raw materials and generates large amounts of the by-product sodium chloride.
In the oxidation of methyl glycol with concentrated nitric acid - even in the presence of vanadium (V) oxide - methoxyacetic acid is obtained in yields of approx. 85%.
The disadvantage of the reaction with (excess) hot nitric acid is the formation of nitrous gases , which, like the excess nitric acid , must be eliminated by adding urea or formaldehyde .
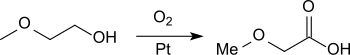
The most useful process for the production of methoxyacetic acid on an industrial scale appears to be the oxidation of methylglycol with air or oxygen in the presence of platinum catalysts in a relatively high (10-30%) aqueous solution at a pH value of ≤ 7 and temperatures around 50 ° C with product yields of up to 95% and space-time yields of 150 g l −1 h −1 .
In the animal and human organism, 2-methoxyacetic acid is formed by the rapid oxidation of 2-methoxyethanol (methyl glycol) by alcohol dehydrogenases .
properties
Methoxyacetic acid is a clear, colorless, viscous and corrosive liquid with a pungent odor that solidifies at 7 ° C to form an glacial acetic acid-like mass. Because of the low solvation energy of the methoxy group, methoxyacetic acid with a pKa value of 3.57 is more acidic than acetic acid (pKa 4.757) and glycolic acid (pKa 3.832).
Highly pure methoxyacetic acid (purity 99.8%, solidification point 8.4 ° C) can be obtained by multi-stage crystallization of the crude distillate freed from acid impurities.
Applications
Because of its reprotoxic properties, common consumer and industrial uses of methoxyacetic acid as a disinfectant or biocide , as well as a cleaner for decalcifying surfaces, are now obsolete. This also applies to substances such as For example, the solvent is 2-methoxyethanol or PVC - plasticizer bis (2-methoxyethyl) phthalate to which are metabolised in the organism to methoxyacetic acid.
Methoxyacetic acid was used in X-ray contrast media as a molecular building block in polyiodinated aromatics .
Methoxyacetic acid inhibits the growth of tumor cells in laboratory tests.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c data sheet methoxyacetic acid from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 13, 2015 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on methoxyacetic acid in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 20, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-328.
- ↑ a b E.J. King: The Thermodynamics of Ionization of Amino Acids. V. The Ionization Constants of 3-Methoxy-DL-alanine (O-Methylserine) and Methoxyacetic Acid . In: J. Amer. Chem. Soc. tape 82 , no. 14 , 1960, p. 3575-3578 , doi : 10.1021 / ja01499a025 .
- ↑ Entry on methoxyacetic acid in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ a b Entry in the SVHC list of the European Chemicals Agency , accessed on October 19, 2015.
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 625-45-6 or methoxyacetic acid ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ Patent US4968840 : Process for preparing methoxyacetic acid. Applied on July 13, 1989 , published November 6, 1990 , Applicant: Nitrokémia Ipartelepek, Inventors: P. Agócs, L. Nagy, J. Pelyva, L. Légradi, Z. Kolonics, C. Söptei.
- ↑ Patent DE2832949 : Process for the production of methoxyacetic acid. Registered on July 27, 1978 , published on October 4, 1979 , applicant: Lonza AG, inventor: U. Michel.
- ↑ Patent DE2936123A1 : Process for the production of alkoxyacetic acids. Applied on September 7, 1979 , published on April 2, 1981 , applicant: Hoechst AG, inventor: EI Leupold, W. Blau, H. Baltes.
- ↑ CA Mebus, F. Welsch: The possible role of one-carbon moieties in 2-methoxyethanol and 2-methoxyacetic acid-induced developmental toxicity . In: Toxicol Appl Pharmacol . tape 99 , no. 1 , 1989, pp. 98-109 , doi : 10.1016 / 0041-008X (89) 90115-4 .
- ↑ Patent DE3345807A1 : Process for the production of pure methoxyacetic acid. Registered on December 17, 1983 , published on June 27, 1985 , applicant: Hoechst AG, inventor: S. Rittner, K. Riedel.
- ↑ Patent US4364921 : Novel triiodinated isophthalic acid diamides as nonionic x-ray contrast media. Registered on March 6, 1980 , published on December 21, 1982 , Applicant: Schering AG, Inventors: U. Speck, P. Blaszkiewicz, D. Seidelmann, U. Klieger.
- ↑ KR Parajuli, Q. Zhang, S. Liu, NK Patel, H. Lu, SX Zeng, G. Wang, C. Zhang, Z. You: Methoxyacetic acid Suppresses prostate cancer cell growth by inducing growth arrest and apoptosis . In: Am. J. Clin. Exp. Urol. tape 2 , no. 4 , 2014, p. 300-312 , PMID 25606576 , PMC 4297326 (free full text).