Sodium tetrachloroaurate (III)
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| __ Na + __ Au 3+ __ Cl - | ||||||||||||||||
| Crystal system | ||||||||||||||||
| Space group |
P 2 1 / n (No. 14, position 2) |
|||||||||||||||
| Lattice parameters |
|
|||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Sodium tetrachloroaurate (III) | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | Na [AuCl 4 ] | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
crystalline solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 361.756 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.8 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
decomposes above 100 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Sodium tetrachloroaurate , Na [AuCl 4 ] is the sodium - salt of chloroauric .
Extraction and presentation
The dihydrate of sodium tetrachloroaurate can be obtained by reacting an acidic solution of gold (III) chloride or tetrachloroauric acid with sodium chloride .
properties
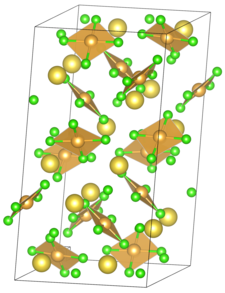
Sodium tetrachloroaurate is a crystalline solid which decomposes at 100 ° C. It is soluble in water. The salt crystallizes in a monoclinic crystal system with space group P 2 1 / n (space group no. 14, position 2) . The lattice parameters are a = 11.277 Å , b = 11.234 Å, c = 20.584 Å and Z = 12. The number of degrees of the β angle is 104.58 °. The distance between gold and chlorine is 2.277 Å and that of sodium and chlorine is between 2.82 Å and 3.19 Å.
use
Sodium tetrachloroaurate is used in chemotherapeutic agents and as a catalyst in the removal of tert- butyl (dimethyl) silyl (TBS) protective groups. It is selective in the presence of aromatic TBS ethers, aliphatic triisopropylsilyl ethers, aliphatic tert-butyl (diphenyl) silyl ethers, or hindered aliphatic TBS ethers. With excess catalyst, TBS ethers can also be converted into 4-methoxybenzyl ethers or methyl ethers.
safety instructions
The substance causes severe burns to the skin and serious damage to the eyes. If swallowed, it is harmful to health, as it can cause burns to the mouth and throat , as well as perforation of the esophagus and stomach .
In the event of fire, hydrogen chloride , sodium oxide and gold oxides can be formed. Violent reactions can occur with bases , oxidizing agents , ammonia and metals .
literature
- Sodium tetrachloroaurate (III) hydrate data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on February 8, 2019 ( PDF ).
- Data sheet sodium gold chloride from Wieland Edelmetalle, accessed on February 8, 2019.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Brockhaus Encyclopedia in twenty volumes . Brockhaus, 1969, ISBN 3-7653-0322-4 , p. 460 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j data sheet Sodium tetrachloroaurate (III) dihydrate from AlfaAesar, accessed on February 8, 2019 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ^ AP Hagen: Inorganic Reactions and Methods, The Formation of Bonds to Halogens . John Wiley & Sons, 2009, ISBN 978-0-470-14539-5 , pp. 102 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ PG Jones, R. Hohbein, E. Schwarzmann: Anhydrous sodium tetrachloroaurate (III) . Acta Cryst., 1988, pp. 1164-1166 , doi : 10.1107 / S0108270188002756 .


![{\ displaystyle {\ ce {H [AuCl4] + NaCl -> Na [AuCl4] + HCl}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/33a4338b58853589f262049d2a0b10f0ba9db840)