Nitroimidazoles
In pharmacology, nitroimidazoles are a group of substances which are used to treat infections with bacteria and / or protozoa and whose core feature is an imidazole substituted with a nitro group . Imidazole is a five-membered heterocyclic organic compound with two nitrogen atoms .
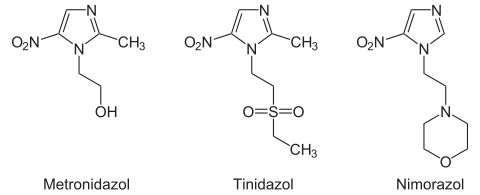
The descendants of 5-nitroimidazole (“5-nitromidazole”) are of particular medical importance. The most important representative is metronidazole ( Clont , Flagyl et al.).
Which also attributable to nitroimidazoles newer agents Delamanid and Pretomanid be used in the treatment of tuberculosis.
development
The development of nitroimidazoles was based on azomycin (2-nitroimidazole) isolated from a Streptomyces species in 1953 , which proved to be highly effective against trichomonads , but could not be used clinically due to its toxicity.
The first and most important representative of the nitroimidazole, metronidazole , was patented by Rhône-Poulenc in 1960 . Newer variants such as Tinidazol ( Simplotan , Sorquetan ) and Nimorazol ( Esclama ) have not been able to establish themselves permanently on the market in Germany.
At the beginning of the 21st century, Delamanid and Pretomanid, two new nitroimidazole derivatives were developed that can be used against multi-resistant tuberculosis pathogens . Delamanid was approved as Deltyba in the EU in 2014 and Pretomanid in the USA in 2019.
Representative
The table contains an overview of the most important representatives.
| Non-proprietary name | Systematic name | operation area | Absorption after oral administration | Half-life |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-nitroimidazoles | ||||
| Metronidazole | 2-methyl-5-nitroimidazole-1-ethanol | Human medicine | > 90% | 7 hours |
| Tinidazole | 1- [2- (2-Ethylsulfonyl) ethyl] -2-methyl-5-nitroimidazole | Human medicine | > 90% | 13 hours |
| Nimorazole | 4- [2- (5-nitroimidazol-1-yl) ethyl] morpholine | Human medicine | high | 10 hours |
| Ornidazole | ( RS ) -1-chloro-3- (2-methyl-5-nitroimidazol-1-yl) propan-2-ol | Human medicine | 13 hours | |
| Fexinidazole | 1-methyl-2 - {[4- (methylthio) phenoxy] methyl} -5-nitro-1 H -imidazole | Human medicine | 14 hours (active metabolites: 15 hours (M1) and 23 hours (M2)) | |
| Dimetridazole | 1,2-dimethyl-5-nitroimidazole | Veterinary medicine | ||
| Carnidazole | O -Methyl N - [2- (2-methyl-5-nitroimidazol-1-yl) ethyl] carbamothioate | Veterinary medicine | ||
| Ronidazole | 1-methyl-2 - [(carbamoyloxy) methyl] -5-nitroimidazole | Veterinary medicine | ||
| 2-nitroimidazoles | ||||
| Benznidazole | N -Benzyl-2-nitroimidazol-1-ylacetamide | Human medicine | > 90% | approx. 12 hours |
| Bicyclic nitroimidazoles | ||||
| Pretomanid | (6 S ) -2-nitro-6 - {[4- (trifluoromethoxy) benzyl] oxy} -6,7-dihydro-5 H -imidazo [2,1- b ] [1,3] oxazine | Human medicine | 16.0 to 17.4 hours | |
| Delamanid | (2 R ) -2-methyl-6-nitro-2 - [(4- {4- [4- (trifluoromethoxy) phenoxy] piperidin-1-yl} phenoxy) methyl] -2,3-dihydroimidazo [2.1 - b ] oxazole | Human medicine | high | 30-38 hours |
Effective spectrum and areas of application
The spectrum of activity includes obligate anaerobic bacteria (with the exception of actinomycetes ) and some protozoa ( Entamoeba histolytica , Trichomonas vaginalis , Giardia lamblia ). Aerobic and facultative anaerobic bacteria ( e.g. propionibacteria ) are resistant.
2- and 5-nitroimidazoles are indicated for the treatment of infections such as trichomoniasis , amine colpitis , giardiasis , amoebic dysentery , amoebic liver abscess and various other anaerobic infections (including Clostridium difficile ). The therapeutic regimen (single or multiple dose) depends on the underlying disease. Possible risks of long-term use have not been researched. Benznidazole is used in human medicine in the treatment of the acute phase of Chagas disease . The active ingredients can be administered orally.
In veterinary medicine, dimetridazole ( Chevi-col ), ronidazole ( Ridzol ) and carnidazole ( Spartrix ) are approved in Germany for the treatment of trichomonas in carrier pigeons, but can also be used in small and pet animals. Use on food-producing animals is prohibited.
Delamanid and pretomanid are used in human medicine, always in combination with other antituberculotics , for the oral treatment of multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis if no other treatment options exist.
Pharmacodynamics
The bactericidal effect of the 2- and 5-nitroimidazoles unfolds intramicrobially, with the highly effective metabolites that damage the bacterial DNA intracellularly only through reduction of the nitro group . The reduction is only made possible by anaerobic metabolism, which explains the use of nitroimidazoles against anaerobes. In the case of DNA damage, adduct formations with neighboring base pairs of a DNA strand are in the foreground, which can lead to strand breaks depending on the strength of the disorder. The nitroimidazoles thus have a bactericidal effect on the one hand, and a mutagenic (mutagenic) effect on the other hand , the metabolites generally having a higher affinity for bacterial cells than for human cells, which makes the use of these mutagenic substances in medicine possible.
Delamanid and Pretomanid are prodrugs . To be effective, an aromatic nitro group must first be activated by reduction in vivo - with the participation of the coenzyme F 420 from Mycobacterium tuberculosis . The resulting reactive products inhibit the mycolic acid synthesis by mycobacteria. The effect is bactericidal.
Contraindications
Nitroimidazole must not be used in diseases of the central or peripheral nervous system , blood disorders, hypersensitivity and severe liver damage. Due to their potentially teratogenic effect, they are only approved during pregnancy and breastfeeding if there are strict indications (life-threatening infections), as the active ingredient crosses the placental barrier.
By inhibiting aldehyde dehydrogenases, nitroimidazoles lead to alcohol intolerance . If alcohol is consumed at the same time, severe side effects and acute intoxication (symptoms of intoxication) can occur. In contrast to other representatives of the group , the nitroimidazole ornidazole ( Tiberal ) does not inhibit aldehyde dehydrogenase and thus does not cause alcohol intolerance.
Side effects
Common undesirable side effects of nitroimidazoles occur in the form of gastrointestinal complaints. In addition, taste disturbances can occur in the form of a metallic taste sensation. Further side effects are headache, dizziness, drowsiness, paresthesia and allergic reactions, rarely also neuropathies , which can be reversible after discontinuation of the intake.
Nitroimidazoles act as mutagens . Metronidazole has been shown to be carcinogenic in mice , but similar studies in hamsters and large epidemiological studies in humans have found no evidence of an increased risk of carcinogenicity in humans.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on nitroimidazoles. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 7, 2014.
- ↑ BM Lee et al .: Predicting nitroimidazole antibiotic resistance mutations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis with protein engineering . In: PLoS Pathogens . tape 16 (2020) , No. 2 , doi : 10.1371 / journal.ppat.1008287 .
- ^ EH Ignatius, KE Dooley: New Drugs for the Treatment of Tuberculosis. In: Clinics in Chest Medicine . tape 40 (2019) , pp. 811–827 , doi : 10.1016 / j.ccm.2019.08.001 .
- ^ A b D. Biermann: EU approval of Delamanid against multiresistant tuberculosis , Pharmazeutische Zeitung, May 14, 2014.
- ↑ a b c A. Mende: US approval for new tuberculosis drug , Pharmazeutische Zeitung, August 15, 2019.
- ↑ a b c d e f g E. Mutschler: drug effects . 7th edition, WVG, Stuttgart 1996, p. 692 ff.
- ↑ a b Technical Information Tiberal (OrPha Swiss GmbH), as of 2004.
- ↑ Information for professionals Fexinidazole Winthrop . As of November 15, 2018.
- ↑ Martindale. The Complete Drug Reference 38th Edition. London; Pharmaceutical Press; 2014. p. 929 f.
- ↑ Compounds | TB Alliance. Retrieved May 7, 2020 .
- ↑ Pretomanid Tablets, Prescription Information ( PDF ), as of August 2019.
- ↑ Alphienes Stanley Xavier, Mageshwaran Lakshmanan: Delamanid: A new armor in combating drug-resistant tuberculosis . In: Journal of Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics . tape 5 , no. 3 , 2014, ISSN 0976-500X , p. 222-224 , doi : 10.4103 / 0976-500X.136121 , PMID 25210407 , PMC 4156838 (free full text).
- ↑ a b K. Aktories: General and special pharmacology and toxicology. 9th edition.
- ↑ a b G. Geisslinger et al .: Mutschler drug effects . 11th edition. WVG, Stuttgart 2019, p. 1048.
- ↑ E. Mutschler: drug effects. 9th edition. Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft, Stuttgart 2008, ISBN 978-3-8047-1952-1 .
- ↑ Sabine Cyrys: Volume of four basic subjects. 2002, ISBN 3-437-42120-4 , p. 427.