Metronidazole
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
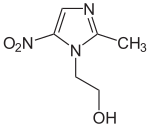
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Metronidazole | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 9 N 3 O 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white or pale yellow crystalline powder |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action |
DNA strand breaks |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 171.15 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
159-163 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
2.5 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Metronidazole is the main representative of the nitroimidazoles . This group of antibiotics is suitable for the treatment of bacterial infections caused by anaerobes or protozoal infections . The active ingredient was patented by Rhône-Poulenc in 1960 .
Mode of action and spectrum
Metronidazole, after electron transfer to its nitro group , the nucleic acid synthesis inhibited by strand breaks and acts mutagenic . The reducing reaction required for this only takes place under low-oxygen conditions and thus develops an antimicrobial effect on anaerobic microbes.
Metronidazole has a bactericidal effect against (obligate) anaerobes such as Helicobacter , Gardnerella and Campylobacter as well as harmful to some protozoa such as Trichomonas , Entamoeba histolytica and Giardia . It is (anaerobic growth) in whose cell environment under certain conditions by reduction in highly reactive intermediates such as acetamide and N - oxamic acid converted, the (2-hydroxyethyl) by complex formation or causing strand breaks , the DNA damaging the exciter.
In the treatment of the skin diseases rosacea and perioral dermatitis , not only the direct antibiotic effect is important, but also non-specific, anti-inflammatory effects.
Pharmacokinetics
The plasma half-life is about seven to eight hours. Metronidazole is well distributed throughout the body and is easily accessible to the liquor . As an antiprotozoic agent (e.g. against Trichomonas ), a high single dose of 2000 milligrams is usually used. Uncomplicated bacterial infections are treated with a lower dosage of 400 milligrams or less for a longer period of five to six days. With a higher dosage (1000 to 2000 mg daily) the duration of therapy is shortened to one to three days. Nitroimidazoles should generally not be used for longer than ten days, as the possible risks of long-term therapy have not been researched.
application
Metronidazole can be used orally , intravenously , rectally , intravaginally or locally for trichomonas infections , which mainly affect the vagina and the male urethra . The active ingredient tastes bitter, which is why tablets should not be crushed before oral administration. In addition, metronidazole has been established and approved for many years in dermatology (skin medicine) for the treatment of rosacea and against perioral dermatitis .
It is used in supportive antibiotic therapy for periodontitis with anaerobic infestation (e.g. Porphyromonas gingivalis ).
The active ingredient is almost completely absorbed in the intestine , broken down via the liver and excreted via the kidneys . The plasma half-life is approximately seven hours. When used non-locally, it also reaches the cerebral fluid and abscesses in antibiotic concentrations. Due to its immunosuppressive effect, it is used for chronic inflammatory bowel diseases. In the treatment of fistulas in Crohn's disease , this effect interacts with the antibiotic effect.
Metronidazole is used in antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous enterocolitis caused by Clostridioides difficile and until recently was the drug of first choice. The antibiotic is usually administered orally for this purpose and intravenously only in exceptional cases .
In veterinary medicine it is used against various trichomonads and flagellate infections. Giardia does not kill the drug, but it does reduce the growth of this pathogen. In addition, metronidazole is also used in dogs for bacterial overgrowth of the small intestine ( Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth , SIBO).
Contraindications and side effects
Metronidazole must not be used in cases of CNS disorders, blood disorders, hypersensitivity, during breastfeeding and in case of severe liver damage. Alcohol must be avoided during metronidazole treatment, as otherwise particularly severe side effects (nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness or reddened skin on the head and neck area) are to be expected ( acetaldehyde syndrome ). During pregnancy or pregnancy , due to its potentially teratogenic effect , metronidazole may only be used if there are strict indications (life-threatening infections), since the active ingredient crosses the placental barrier. There are contradicting reports, especially on safety in early pregnancy. In birds , the product should not be used during the mating and breeding season.
The use in animals that are used for food production is generally prohibited in the European Union according to the EU Maximum Residue Quantity Regulation for food of animal origin .
Side effects can manifest themselves in the form of headache , dizziness , paresthesia , allergic reactions , disturbances in the function of the gastrointestinal tract ( vomiting , diarrhea , nausea ) and neuropathies . A metallic taste and discoloration of the urine may also occur. Occasionally, a decrease in peripheral leukocytes ( leukopenia and granulocytopenia ) is observed - in very rare cases a decrease in blood platelets ( thrombocytopenia ) and an absence of certain white blood cells ( agranulocytosis ) have been observed, in which case blood counts should be checked quickly. When used locally in the area of the genital mucous membranes, painful reactions (burning sensation) when urinating ( dysuria ), bladder inflammation ( cystitis ) and urinary incontinence can occur.
It is known that the skin diseases that are treated with metronidazole are accompanied by a general, unspecific hypersensitivity. When metronidazole is applied locally to the skin of the face, unspecific reactions such as burning, itching or reddening of the skin are therefore possible, but these cannot definitely be attributed to the active ingredient. Long-term damage to the skin organ is not to be expected with long-term use, which may be necessary in special cases of skin diseases.
Carcinogenicity and Mutagenicity
Metronidazole has been shown to be carcinogenic in mice , but similar studies in hamsters and large epidemiological studies in humans have found no evidence of an increased risk of carcinogenicity in humans. The mutagenicity of metronidazole has also been demonstrated in bacteria using the Ames test . However, both in vitro studies with mammalian cells and in vivo studies with rodents and humans could not provide sufficient evidence for a mutagenic effect of metronidazole.
Trade names
Monopreparations
Anaerobex (A), Arilin (D, CH), Ariline (A), Clont (D), Dumozol (CH), Elyzol (D, CH), Flagyl (D, CH), Metrosa (D), Nidazea (A , CH), Perilox (CH), Rosalox (CH), Rosiced (A, D), Rozex (CH), Trichex (A), Vagi-Metro (D), Vagimid (D), numerous generics (D, A, CH)
- Veterinary medicine (combination with spiramycin ): Stomorgyl (A), Suanatem (D, A)
Web links
- Entry on metronidazole at Vetpharm, accessed on August 11, 2012.
- Metronidazole against bacteria on Gesundheit.de
literature
- H. Lüllmann, K. Mohr, M. Wehling: Pharmacology and Toxicology . Thieme, Stuttgart 2003, ISBN 3-13-368515-5 .
- W. Forth (Ed.), D. Henschler, W. Rummel, K. Starke: General and special pharmacology and toxicology . 6th edition. BI-Wiss.-Verlag, Mannheim / Leipzig / Vienna / Zurich 1992, p. 705, ISBN 3-411-15026-2 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d data sheet METRONIDAZOLE CRS (PDF) at EDQM , accessed on February 12, 2009.
- ↑ a b entry on metronidazole. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 16, 2019.
- ↑ a b c Entry on metronidazole in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 11, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Manfred Schubert-Zsilavecz, Hermann J. Roth: Medicinal Chemistry: Targets - Drugs - Chemical Biology . 2., completely reworked. and exp. Ed. Dt. Apotheker-Verlag, Stuttgart 2010, ISBN 978-3-7692-5002-2 (191 tables).
- ↑ C. Wenisch, B. Parschalk, M. Hasenhündl, AM Hirschl, W. Graninger: Comparison of vancomycin, teicoplanin, metronidazole, and fusidic acid for the treatment of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea. In: Clinical Infectious Diseases . Volume 22, Number 5, May 1996, pp. 813-818, PMID 8722937 .
- ↑ Fred A. Zar et al .: A comparison of vancomycin and metronidazole for the treatment of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea, stratified by disease severity. "Clinical Infectious Diseases 45.3. 2007, pp. 302-307. PMID 1759930
- ↑ Stuart Johnson et al .: Vancomycin, metronidazole, or Tolevamer for Clostridium difficile infection: results from two multinational, randomized, controlled trials . In: Clinical Infectious Diseases , 59.3, 2014, pp. 345-354. PMID 24799326
- ↑ Clostridium difficile infection: Guideline-compliant diagnostic and treatment options ( Memento of November 14, 2015 in the Internet Archive ).
- ^ Red List , 2015, p. 1633.