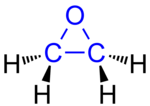
Epoxies
The epoxides , also epoxies , according to the Hantzsch-Widman system oxiranes or according to the exchange nomenclature oxacyclopropanes , are a chemical group of very reactive, cyclic, organic compounds . They contain a three-membered ring in which, compared to cyclopropane, one methylene group has been replaced by an oxygen atom. Epoxy groups thus form the simplest oxygen-containing heterocycles . The oxygen bridge is called an epoxy bridge .
Representative
The simplest and most technically interesting epoxide is ethylene oxide (ethene oxide). It is caused by oxidation of ethene to a silver prepared catalyst ( heterogeneous catalysis ). Due to the ring tension of approx. 115 kJ / mol in a three-membered ring, the ring can be opened relatively easily by nucleophilic attack on a carbon atom. The oxygen atom of the epoxy ring is the leaving group, but remains connected to a carbon atom of the epoxy and is therefore still part of the molecule.
If one or more hydrogen atoms of the ethylene oxide are replaced by organyl residues ( alkyl residues , aryl residues , alkylaryl residues, etc.), these compounds are also oxiranes.
A polymer made of several epoxy segments is a polyepoxy , also epoxy resin . These are used as adhesives or in composite materials.
Epoxides are intermediate products in the manufacture of the flu drug oseltamivir ( Tamiflu ) from shikimic acid contained in Japanese star anise .
Some epoxy resins (e.g. bisphenol A diglycidyl ether and -F) are high-grade allergens , especially those affecting workers who are directly exposed in production (e.g. in the manufacture of aircraft or modern wind turbines ).
Formed by epoxidation of a double bond
Epoxides can be formed at room temperature by the reaction of an alkene and a peroxycarboxylic acid . In addition to the epoxide, a carboxylic acid is formed .
Meta-chloroperbenzoic acid ( MCPBA ) is often used as the peroxycarboxylic acid , since, in contrast to other percarboxylic acids, it is relatively stable and can be handled safely. Other peroxycarboxylic acids that can be used for epoxidation are peroxyformic acid and peroxyacetic acid . They are produced during the reaction from formic acid or acetic acid and hydrogen peroxide ( in-situ process).
See also
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ Brockhaus ABC Chemie , VEB FA Brockhaus Verlag Leipzig 1965, p. 368.
- ↑ Hoffmann-La Roche : Factsheet Tamiflu ( Memento of the original from February 22, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (PDF; 336 kB), as of November 17, 2006.
- ↑ H.-J. Schubert, M. Butz, M. Reymann, U. Schumacher, H. Heise, K. Nimmrich, G. Weiß: Current information on epoxy resin allergy . In: Akt Dermatol . tape 30 , 2004, pp. 143-148 , doi : 10.1055 / s-2004-814510 .
- ↑ KPC Vollhardt, NE Schore: Organic Chemistry . Ed .: H. Butenschön. 4th edition. WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 2005, ISBN 978-3-527-31380-8 , p. 590 .