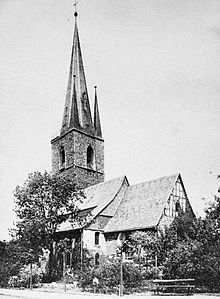St. Petri (Nordhausen)
The Protestant St. Petri Church was a church in Nordhausen in Thuringia . It was destroyed in the Second World War, only the church tower remained, which is known today as the Petri Tower and serves as a lookout tower.
history
In the earlier release mountain Petersberg mentioned probably a Germanic place of worship as was Dingstätte . A church of St. Petri was first mentioned in a document on this site in 1220. The construction of the church, which existed until 1945, began in 1334. A craft and residential quarter developed around the church, the church tower was built from 1362 to 1377. In 1522 , the first Protestant sermon was given in the church of Lorenz Süße , the prior of the nearby Augustinian monastery Nordhausen held.
On December 9, 1660, one of the four side helmets of the church tower was thrown down by a storm. A second was removed soon after to make room for a wind section. The church tower, fitted with four bells, received a tower watchman's apartment in 1731 . In 1772 a new church tower ball with a trumpet angel was placed on the spire. Due to damage inside the church due to moisture, a comprehensive renovation of the church building took place in 1900. At this time, a staircase was built on the north side.
On the night of April 3 to 4, 1945, the church fell victim to attacks by British bomb squadrons on Nordhausen. Many people sought protection in the house of God and died. The building received several direct hits. The burning tower crashed onto the church roof. Petri Church and the city quarter were razed to the ground. Only the ruins of the church tower remained. After the church rubble had been removed, the stump of the tower was left standing. It received a makeshift roof in 1954, which was replaced by a tower helmet on April 4, 1987 .
Now 62 meters high, the tower has been used as a lookout tower since 1994 . The Petersberg area was redesigned from 2000 to 2004 for the second Thuringian State Garden Show , creating areas for recreational activities with sports and play facilities, hedge gardens and water features.
Furnishing
- The pulpit was built in 1612 in the baroque style. It was carved out of wood. Its parapet was divided into 7 fields, which (from left to right) contained biblical representations as relief : Christ's baptism, Annunciation, Adoration of the Shepherds, Let the little children come to me, Christ as a good shepherd, Christ's transfiguration, the sacrifice of Isaac. Below each was a matching Bible verse in a cartridge . The individual fields were separated by eight figures of the apostles, which stood on pedestals carried by women's heads . The pulpit was carried by a figure representing Christophorus with the baby Jesus.
- The baroque altar took the place of a Gothic predecessor in 1751 . It was decorated with a Corinthian column structure. To the left and right stood the figures of Peter and Paul . Since there was no altar leaf, the colorful glass choir window (from 1901) appeared in its place. As a relic , the altar had a small potty containing a hardened mass. This was venerated as Mother Mary's milk.
- The epitaph of the mayor Ernst and his wife was on the north wall of the choir and was a Renaissance architecture with celled columns on the side, carved cheeks, cornices and two oil paintings arranged one above the other. The upper one showed the resurrection of Christ and the dead kneeling at the foot of the cross.
- The epitaph of the town clerk Johann Pfeiffer from 1552 consisted of a simple plate made of dark gray alabaster . It showed the full standing image of the deceased. A Latin tombstone was written around it.
- The bronze baptismal font from 1429 was in the choir room. It measures 84 cm in height and 68 cm in diameter and is now in the Justus Jonas Church . Its volume is approx. 90 liters. The kuppa is worn by four bearded men in 15th century clothing. A lettering band in Gothic minuscule surrounds the lower edge of the cup, indicating the year of its creation. The outer surface of the font is divided into 16 fields by tracery panels. In these there are male figures in high relief , from which John the Baptist, Peter, Paul, James and Laurentius can be clearly identified.
- The church treasure consisted of 4 old chalices, a silver host box, a baptismal jug and a baptismal bowl. The latter was silver and partially gold-plated. It was an Augsburg work from around 1550. Its broad rim was decorated with acanthus tendrils, pearl and threaded rods.
organ
In 1597 an organ was built. A lightning strike damaged it on July 1st, 1658. In the following year the organ was repaired and added two stops and a Rückpositiv . On December 9, 1660, a storm wreaked havoc in the church and badly damaged the organ. In 1674 the organ was removed and rebuilt in 1679. During a snowstorm with a thunderstorm on January 11, 1682, lightning struck the church and melted the pipes .
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nothing more is known about the organ until the 20th century; records were destroyed by fire. On April 7, 1913, the community raised money to build a new organ. This was done in 1914 by P. Furtwängler & Hammer from Hanover. Georg Sbach, organist at St. Blasii, designed the disposition . The organ was pneumatic.
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Coupling : I / II, I / III, II / III, II / I, III / I, III / II, I / P, II / P, III / P, upper octave coupling (III + I, II + I, III + II, III), sub-octave coupling (II + I, III + II, III)
- Playing aids : roller , sills , fixed combinations (tongues, tutti), a free combination
The organ was destroyed along with the church.
Pastor
swell
- Johannes Schäfer: Nordhäuser Orgelchronik - History of the organ works in the thousand-year-old town of Nordhausen am Harz in Max Schneider (Hrsg.): Contributions to music research , Buchhandlung des Waisenhauses GmbH Halle / Saale Berlin, 1939
- August Stolberg / Friedrich Stolberg: The architectural and art monuments of the city of Nordhausen . In: The thousand year old Nordhausen , Volume II., Nordhausen, 1927, pp. 552–557
- Robert Treutler: Churches in Nordhausen - A foray through church life . Verlag Neukirchner, 9/1997, pp. 23-27
Web links
- The tower at www.nordhausen.de
- St. Petri Church at www.nordhausen-wiki.de
- Pictures of the church ruins before 1987
Individual evidence
- ↑ Information about the tower at www.harzlife.de Retrieved on April 1, 2014
Coordinates: 51 ° 30 ′ 1.2 ″ N , 10 ° 47 ′ 49.4 ″ E