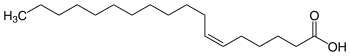
Petroselinic acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Petroselinic acid | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 18 H 34 O 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
White dust |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 282.47 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.8700 g cm −3 (40 ° C ) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
29.8 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4533 (40 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Petroselinic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid , it is a naturally occurring isomer of oleic acid . Its systematic name is ( Z ) -6-octadecenoic acid (delta-6- cis -octadecenoic acid ); it is an omega-12 fatty acid due to the location of its double bond .
The trans isomer is petroselaidic acid (trans -6-octadecenoic acid), which occurs in various plants together with petroselinic acid.
Occurrence
Petroselinic acid occurs as an ester of glycerine - i.e. as glyceride - in specific vegetable and animal oils and fats. It was first isolated from parsley seed oil in 1909 . With the exception of umbellifers (in coriander oil ), petroselinic acid was found in particularly large quantities or as the main fatty acid in the aralia family , in Griselinia (Griseliniaceae) and in the Garryaceae . In the Picramniaceae it is the companion of tariric acid . In addition, it could occasionally be found in milkweed plants (Mallotus), Pentaphylacaceae (Ternstroemia), Candida spp. , in human hair fat and on the skin surface.
The occurrence of petroselinic acid as the main fatty acid is considered in the chemosystematics as a feature of closely related families within the Apiales as well as within the Garryales . In addition to petroselinic acid, oleic acid can always be detected.
Extraction and presentation
Fatty acids can be obtained from the corresponding triacylglycerides by alkaline saponification by boiling the corresponding fats or oils with bases . The saponification itself initially supplies their salts. The free fatty acids are obtained by neutralization with (mineral) acids. Since the natural fats and oils always contain many different fatty acids, the resulting mixture is usually separated. Petroselinic acid is commercially available.
properties
Physical Properties
Pure petroselinic acid is described as a powder or a highly viscous, colorless, oily and almost odorless liquid at room temperature. The molar mass is 282.47 g mol. The fatty acid is insoluble in water but soluble in methanol .
Chemical properties
Like oleic acid, petroselinic acid, unlike polyunsaturated fatty acids (e.g. linolenic acid ), is only slightly sensitive to oxidation. The main point of attack of the oxidation is the C = C double bond. It is particularly promoted by light, heat or dissolved metal ions and proceeds mainly via radical reaction mechanisms. An important intermediate step in the oxidation is the formation of hydroperoxides (-OOH) when the C = C double bond is broken. The functional group (–OOH) itself also forms radicals and thus promotes an oxidative chain reaction. Further, hydroperoxides to ketones decompose and, if it comes to a split of the simple carbon-carbon bond, even to aldehydes or carboxylic acids .
Petroselinic acid and especially its salts are amphiphilic , that is, they contain both a polar, hydrophilic part (the carboxy group ) and a non-polar, lipophilic part (the hydrocarbon chain).
Biological properties
Compared to oleic acid, petroselinic acid has a stronger inhibitory effect on bacteria, a lower inhibitory effect on cell division and the slower biological degradation.
proof
The detection and determination of the content of petroselinic acid as well as other fatty acids in fats is usually carried out by gas chromatography of the methyl ester ; In addition, the unsaturated isomers can be separated using silver nitrate thin-layer chromatography . A second detection method is the bromine water sample for C = C multiple bonds.
use
Petroselinic acid is used as a component of mixtures for the manufacture of cosmetics. It can be split into lauric and adipic acid , two important basic chemical substances (detergent and nylon production).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Data sheet Petroselinic acid, ≥ 99%, powder from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on January 30, 2012 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-402.
- ^ DGF German Society for Fat Science eV
- ^ Albert J. Dijkstra, Richard J. Hamilton, Wolf Hamm: Trans Fatty Acids. Blackwell, 2008, ISBN 978-1-4051-5691-2 , p. 8.
- ^ E. Vongerichten, A. Köhler: About petroselinic acid, a new oleic acid. In: Chem. Ber. 42, (1909), 1638.
- ^ FC Palazzo, A. Tamburello: Sopra l'acido iso-oleico dei semi di edera, Atti della Accademia Nazionale die Lincei. In: Rendiconti. Class di science fisiche, matematiche e naturali. 5th ser. 23 (1914), 352.
- ↑ Beate Breuer, Thomas Stuhlfauth, Heinrich Fock, Herbert Huber: Fatty acids of some cornaceae, hydrangeaceae, aquifoliaceae, hamamelidaceae and styracaceae. In: Phytochemistry. 26, 1987, pp. 1441-1445, doi : 10.1016 / S0031-9422 (00) 81830-0 .
- ↑ M. Tsujimoto, H. Koyanagi: On Nigaki Oil. In: Bull. Chem. Soc. Japan 8 (1933), 161.
- ↑ Thomas Stuhlfauth: Chemosystematic studies on the fatty acid composition of fruit and seed oils of the Pittosporaceae as well as some kinds of the Rutales and Araliales. Diploma thesis, University of Kaiserslautern (1984), 52-55.
- ↑ 6- Octadecenoic acid from PlantFA Database, accessed November 30, 2017.
- ↑ T. Stuhlfauth, H. Fock, H. Huber, K. Klug: The distribution of fatty acids including petroselinic and tariric acids in the fruit and seed oils of the Pittosporaceae, Araliaceae, Umbelliferae, Simarubaceae and Rutaceae. In: Biochemical Systematics and Ecology. 13, 1985, pp. 447-453, doi : 10.1016 / 0305-1978 (85) 90091-2 .
- ↑ HM Jenkin, LE Anderson, RT Holman, IA Ismail, FD Gunstone: The effect of isomeric cis-octadecenoic acids on the growth of Leptosira interrogans serotype patoc. In: Journal of Bacteriology. 98, (1969), 1026.
- ↑ HM Jenkin, LE Anderson, RT Holman, IA Ismail, FD Gunstone: The effect of isomeric cis-octadecenoic acids on the growth of monkey kidney cells (LLC-MK 2 ). In: Experimental Cell Research 59, (1970), 1.
- ↑ LD Lawson, FA Kumerow: β-oxidation of the coenzyme a esters of vaccenic, elaidic, and petroselinic acids by rat heart mitochondria In: Lipids. 14: 501 (1979).
- ↑ B. Breuer, T. Stuhlfauth, HP Fock: Separation of Fatty Acids or Methyl Esters Including Positional and Geometric Isomers by Alumina Argentation Thin-Layer Chromatography. In: Journal of Chromatographic Science . 25, 1987, pp. 302-306, doi : 10.1093 / chromsci / 25.7.302 .
- ↑ European Patent Office, publication number 0001013178, document identification DE69927466T3 , February 11, 2010.
