Pivalic acid
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
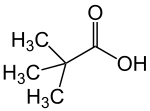
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Pivalic acid | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 5 H 10 O 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless crystals with an unpleasant odor |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 102.13 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
0.91 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
35-36 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
163-164 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
18.6 Pa (70 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
5.03 (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
little in water (25 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Pivalic acid is a methyl branched, short-chain carboxylic acid from the group of four isomeric pentanoic acids , as well as the simplest Koch acid ( tertiary saturated monocarboxylic acids).
presentation
Synthetically, pivalic acid can be obtained by oxidation of pinacolone , by the Grignard reaction from tert-butyl chloride (lower illustration) or by the Koch reaction from 2-methylpropene ( isobutene ), carbon monoxide and water:

properties
The pivalic acid forms colorless, needle-shaped crystals with a pungent odor, which dissolve little in water, but well in ethanol and diethyl ether . Due to steric effects on the molecule, pivalic acid has some special properties compared to other valeric acids, e.g. B. the ester formation or the hydrolysis of the pivalic acid ester is considerably more difficult.
use
Pivalic acid is used in the manufacture of polyvinyl esters (vinyl pivalate) and pharmaceutical preparations. The effect of steric inhibition is used by the use of esters of medicinally active substances, which are then only slowly split and absorbed in the organism, such as. B. testosterone pivalate .
safety instructions
Pivalic acid is flammable, the ignition temperature is approx. 500 ° C, the flash point in a closed crucible is 64 ° C. The acid is irritating to the eyes, respiratory tract, mucous membranes and skin and can also be absorbed through the skin.
Individual evidence
- ^ A b Jürgen Falbe, Manfred Regitz: RÖMPP Lexikon Chemie. Volume 2: Cm-G , 10th edition, Thieme, 1997, ISBN 3-13-734710-6 , p. 991.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j Entry on 2,2-dimethylpropionic acid in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 22, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 97th edition. (Internet version: 2016), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-220.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Dissociation Constants of Organic Acids and Bases, pp. 8-44.
Web links
- Entry to pivalic acid . In: P. J. Linstrom, W. G. Mallard (Eds.): NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69 . National Institute of Standards and Technology , Gaithersburg MD .
- International Chemical Safety Card (ICSC) for Pivalic Acid from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).


