Belt tongues
| Belt tongues | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
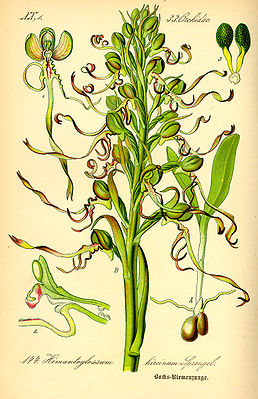
Buck's strap tongue ( Himantoglossum hircinum ), illustration |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Himantoglossum | ||||||||||||
| Blast |
The genus of the strap ends ( Himantoglossum ) in the family of orchids (Orchidaceae) contains only a few species. They are native to the warmer areas of Europe, only the Bocks strap tongue is also found in northern Europe.
description
They are strong, perennial herbaceous plants with two elongated oval tubers as persistence organs. The leaf rosette sprouts in autumn and is largely complete by winter. The leaves are elongated to belt-shaped. The leaves begin to wither or have already wilted during the flowering period .
The flowering period extends, depending on the location, from April to August. The terminal, racemose inflorescence is covered with numerous flowers . The bracts are long and towers over the ovary . This is twisted so that the flowers are resupinated . The petals are greenish to purple. The three outer petals and the side petals adhere to each other and form a hood. The three-lobed lip is greatly elongated, especially the middle lobe. This is linearly shaped and twisted to the left; it often ends deeply. The side lobes are shorter and have a wavy edge. The base of the lip forms a spur. The column is short, the stamen contains two pollinia that hang over small stalks (caudiculae) on a common adhesive disc (viscidium), which is surrounded by a hemispherical membrane (bursicula). The scar is round to rounded-off square. The separating tissue between stigma and stamen (rostellum) is clearly developed.
The flowers are pollinated by various bees from the genera Andrena , Apis and Colletes . The spur contains small amounts of sugary nectar.
The number of chromosomes is 2n = 36.
distribution
The belt tongues are common throughout the Mediterranean. In Western Europe, its area extends north to England, in the southwest the distribution extends to North Africa. To the east, Iran is reached via Turkey. The locations are always on dry, chalky soils in a sunny to partially shaded location. In addition to grasslands, abandoned fields and various Mediterranean shrub communities, sparse forests are also populated.
Systematics
Within the orchids, the belt tongues are classified in the tribe Orchideae . Related genera are Anacamptis , Neotinea , Ophrys , Serapias and Steveniella . The two species of the mastorchis ( Barlia ) and the bearded orchis ( Comperia comperiana ) are particularly closely related, which some authors therefore add to the strap tongues. The corresponding genera are also separately monophyletic , the cladogram is as follows:
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
The species in the genus of belt tongues are:
- Adriatic belt tongue ( Himantoglossum adriaticum H.Baumann , Syn .: Himantoglossum hircinum subsp. Adriaticum (H.Baumann) H.Sund. ): It occurs in Italy, Austria, Hungary, Czech Republic and on the northwestern Balkan peninsula.
-
Spurred belt tongue ( Himantoglossum calcaratum (Beck) Schltr. , Syn .: Himantoglossum caprinum subsp. Calcaratum (Beck) H.Baumann & R.Lorenz ): It occurs in south-eastern Europe and in the north-western Turkey in two subspecies.
- Himantoglossum calcaratum subsp. calcaratum : It occurs in Southeastern Europe.
- Himantoglossum calcaratum subsp. jankae (Somlyay, Kreutz & Óvári) RMBateman, Molnar & Sramkó (Syn .: Himantoglossum jankae Somlyay, Kreutz & Óvári ): It occurs from southern Slovakia to northwestern Turkey.
-
Goat strap tongue ( Himantoglossum caprinum (M.Bieb.) Spreng. , Syn .: Himantoglossum affine (Boiss.) Schltr. ): It occurs in two subspecies and one variety:
- Himantoglossum caprinum subsp. caprinum : It occurs from eastern Central Europe to Iran.
- Rumelian strap tongue ( Himantoglossum caprinum subsp. Rumelicum H.Baumann & R.Lorenz , syn .: Himantoglossum jankae subsp. Rumelicum (H.Baumann & R.Lorenz) J.Ponert , Himantoglossum caprinum subsp. Rumelicum H.Baumann & R.Lorenz ) : It occurs from eastern Central Europe to Israel.
- Himantoglossum caprinum var. Robustissimum (Kreutz) RMBateman, Molnar & Sramkó (Syn .: Himantoglossum jankae subsp. Robustissimum (Kreutz) Kreutz , Himantoglossum caprinum subsp. Robustissimum Kreutz ): It occurs in Turkey.
- Bearded Orchis ( Himantoglossum comperianum (Steven) P.Delforge , Syn .: Comperia comperiana (Steven) Asch. & Graebn. ): It occurs from the southeastern Aegean to western Iran and the southwestern Crimea .
- Caucasian strap tongue ( Himantoglossum formosum (Steven) K.Koch ): It occurs from the eastern Caucasus to northwestern Iran.
- Himantoglossum galilaeum Shifman : The species first described in 2008 occurs in Israel.
- Buck's strap tongue ( Himantoglossum hircinum (L.) Spreng. ): It occurs in Europe, in northwest Africa and in Iraq.
- Metlesics Mastorchis ( Himantoglossum metlesicsianum (WPTeschner) P.Delforge , Syn .: Barlia metlesicsiana W.P.Teschner ): It occurs on La Palma and Tenerife .
- Taurus strap tongue ( Himantoglossum montis-tauri Kreutz & W.Lüders ): It occurs in southwestern Turkey.
- Giant orchid ( Himantoglossum robertianum (Loisel.) P. Delforge , Syn .: Barlia robertiana (Loisel.) Greuter , Orchis robertiana Loisel. ): It occurs in the Mediterranean area.
And the hybrids:
- Himantoglossum caprinum nothosubsp. samariense (C.Alibertis & A.Alibertis) JMHShaw (Syn .: Himantoglossum × samariense C.Alibertis & A.Alibertis = Himantoglossum caprinum subsp. caprinum × Himantoglossum caprinum subsp. rumelicum ): It occurs in Crete.
- In 2004, an intergeneric hybrid between the Taurus belt tongue ( Himantoglossum montis-tauri ) and the related Bearded Orchis ( Comperia comperiana ) was described as × Comptoglossum agiasense .
literature
- Helmut Baumann , Siegfried Künkele, Richard Lorenz: Orchids of Europe with adjacent areas . Verlag Eugen Ulmer, Stuttgart, 2006. ISBN 3-8001-4162-0 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Alec M. Pridgeon, Phillip Cribb, Mark W. Chase, Finn Rasmussen (eds.): Genera Orchidacearum. Orchidoideae (Part one) . Oxford University Press, New York and Oxford 2001, ISBN 0-19-850710-0 , pp. 279-284 .
- ^ Richard M. Bateman, Peter M. Hollingsworth, Jillian Preston, Luo Yi-Bo, Alec M. Pridgeon, Mark W. Chase: Molecular phylogenetics and evolution of Orchidinae and selected habenariinae (Orchidaceae) . In: Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society . tape 142 , no. 1 , 2003, doi : 10.1046 / j.1095-8339.2003.00157.x .
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Rafaël Govaerts (Ed.): Himantoglossum. In: World Checklist of Selected Plant Families (WCSP) - The Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew . Retrieved July 12, 2018.
- ↑ IA Karatzas: × Comptoglossum agiasense, a rare hybrid of Lesvos. In: Journal Europäische Orchideen 36 (4) 2004, pp. 951–956.



