Southern crown
|
Southern Crown Constellation |
|
|---|---|
| Latin name | Corona Australis |
| Latin genitive | Coronae Australis |
| Abbreviation | CrA |
| Right ascension | 17 h 58 m 30 s to 19 h 19 m 05 s |
| declination | −45 ° 30 ′ 59 ″ to −36 ° 46 ′ 43 ″ |
| surface | 127.696 deg² rank 80 |
| Completely visible | 44.7 ° N to 90 ° S |
| Observation time for Central Europe | Summer (partially) |
| Number of stars brighter than 3 mag | 0 |
| Brightest star (size) | Alfecca Meridiana (4.10) |
| Meteor streams |
no |
|
Neighboring constellations ( clockwise from north ) |
|
| swell | IAU , |
 From the Uranometria by Johann Bayer , called Corona Meridionalis there. |
|
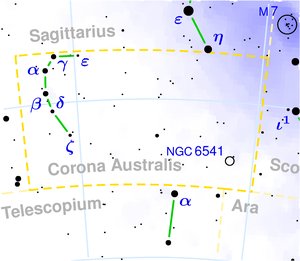
The southern crown ( Latin : Corona Australis , historically also Corona Meridionalis ) is a constellation of the southern sky.
description
The southern crown is an inconspicuous constellation south of the striking summer constellation Sagittarius (Sagittarius). It consists of an arc of stars, the brightest of which only reach the 4th magnitude .
From Germany, only its northernmost stars can be seen deep in the summer sky.
history
The southern crown is one of the 48 constellations of ancient astronomy mentioned by Ptolemy . It forms the heavenly counterpart to the Northern Crown (Corona Borealis).
In 1932 the name was officially changed by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) to "Corona Austrina" (with the genitive "Coronae Austrinae"). However, the original name "Corona Australis" is more common.
Celestial objects
Stars
| B. | F. | Names or other designations | size | Lj | Spectral class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | 4.10 m | 400 | G7 II | ||
| α | Alfecca meridiana , Alphekka meridiana | 4.1 m | 100 | A2 V | |
| γ | 4.23 m | 120 | F8 + F8 | ||
| δ | 4.57 m | 200 | K1 III | ||
| θ | 4.63 m | 90 | F1 | ||
| ζ | 4.74 m | 200 | A0 | ||
| ε | 4.7 to 5.0 m | 90 | F1 V | ||
| λ | 5.11 m | ||||
| μ | 5.20 m | ||||
| η 1 | 5.46 m | ||||
| η 2 | 5.60 m | ||||
| κ 2 | 5.67 m | 500 | B9 + A0 |
The brightest star is β Coronae Australis, a yellowish star of the spectral class G7 about 400 light-years away .
α Coronae Australis is 100 light years away. Part of the name Alfecca Meridiana is of ancient Arabic origin. It could be derived from al-fakkah (the broken one), and refer to a “broken ring” of stars (the southern crown constellation).
Double stars
| object | Sizes | distance |
|---|---|---|
| γ | 4.8 m / 5.1 m | 1.3 " |
| κ | 5.7 m / 6.3 m | 21.4 " |
γ Coronae Australis is a binary star system 120 light years away , which consists of two whitish-yellow stars of the spectral class F8. When viewed from Earth, the distance between the stars is 1.3 arc seconds . To optically separate them, you need a medium-sized telescope with an opening of 8 to 10 cm.
The system κ Coronae Australis, 500 light years away, consists of two whitish-blue stars of the spectral classes B9 and A0. Due to the wide angular distance of 21.4 arc seconds, the stars can be separated in prism binoculars .
Variable stars
| object | size | period | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| ε CrA | 4.7 m - 5.0 m | 1.4403 days | Beta Lyrae Star |
| R. | 11.5 m | Variable star |
ε Coronae Australis is a variable star of the Beta-Lyrae type . With a regular period of 1.4403 days, its brightness changes from 4.7 to 5.0 m . It is 90 light years away and belongs to the spectral class F1.
NGC objects
| NGC | other | size | Type | Surname |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6541 | 6.1 m | Globular clusters |
The globular cluster NGC 6541 is about 22,000 light years away. In the prism binoculars it can be seen as a bright, misty spot. In a medium-sized telescope (from 15 cm opening) it can be resolved into single stars and offers a very beautiful sight. The globular cluster NGC 6541 was discovered on March 19, 1826 by the Italian astronomer Niccolò Cacciatore .