Arrow (constellation)
|
Constellation arrow |
|
|---|---|
| Latin name | Sagitta |
| Latin genitive | Sagittae |
| Abbreviation | Sge |
| Right ascension | 18 h 57 m 21 s to 20 h 20 m 45 s |
| declination | + 16 ° 04 ′ 45 ″ to + 21 ° 38 ′ 37 ″ |
| surface | 79,923 deg² rank 86 |
| Completely visible | 90 ° N to 68.6 ° S |
| Observation time for Central Europe | summer |
| Number of stars brighter than 3 mag | 0 |
| Brightest star (size) | γ Sagittae (3.51) |
| Meteor streams | |
|
Neighboring constellations ( clockwise from north ) |
|
| swell | IAU , |
 The Arrow constellation as seen with the naked eye |
|
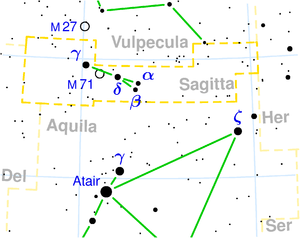
The arrow ( Latin sagitta ) is a constellation of the northern sky.
description
The arrow is the third smallest constellation in the night sky. Four stars of the 3rd and 4th magnitude form an arrow, with the brightest (γ Sagittae) symbolizing the tip.
One finds the constellation between the swan and the eagle (Aquila). It lies in the middle of the star-rich region of the Milky Way and contains the globular star cluster M71 .
history
Many older cultures such as the Persians , Hebrews , Greeks, and Romans saw an arrow in the constellation.
The arrow is one of the 48 classical constellations of antiquity described by Ptolemy .
mythology
In Greek mythology there are several versions according to which divine beings shot an arrow:
The Greek hero Heracles (Hercules) is said to have shot the eagle, which ate the liver of Prometheus who was chained to a rock every day . Prometheus had brought fire to humans and was cruelly punished for it by the gods. Hercules and the eagle have also been transferred to the sky as constellations.
According to another tradition, it was the centaur Chiron who shot the eagle.
Another legend about Hercules tells how he killed the deadly Stymphalian birds with arrows. The birds were seen in the constellations eagle, swan and today's lyre , which is often depicted as a vulture on old star maps.
Another version says that the arrow was shot by the archer at the scorpion who stabbed the sky hunter Orion .
Celestial objects
Stars
| B. | F. | Names or other designations | size | Lj | Spectral class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| γ | 12 | 3.47 m | 260 | M0 III | |
| δ | 7th | 3.82 m (var) | 600 | M2 II + B0 V | |
| α | 5 | Sham | 4.38 m | 430 | G0 II |
| β | 6th | 4.38 m | 440 | G8 IIIaCN | |
| ζ | 8th | 5.03 m | 260 | A1 V + A3 V + F5 | |
| η | 16 | 5.09 m | 160 | K2 III | |
| 13 | VZ | 5.35 m (var) | 1,000 | M3-5 III | |
| 10 | S. | 5.36 m (var) | 2,100 | F7 Ib | |
| 11 | 5.53 m | 460 | B9 III | ||
| 1 | 5.64 m | 300 | A4 V | ||
| ε | 4th | 5.66 m | 480 | G8 IIIv | |
| 15th | Peter 779 | 5.80 m | 58 | G0 V + L4.5 | |
| HR 7780 | 5.81 m | 500 | K5 III | ||
| HR 7662 | 5.97 m | 800 | K3 II-III | ||
| 18th | 6.11 m | 340 | K1 III | ||
| 9 | QZ | 6.23 m (var) | 9,000 | O7.5 Iabf | |
| 2 | 6.25 m | 430 | A2 III – IV | ||
| θ | 17th | 6.52 m | 150 | F5 IV + F2 | |
| 3 | 6.84 m | 450 | A0 V | ||
| HD 231701 | 8.97 m | 360 | F8 V | ||
| WR 124 | 11.50 m (var) | 11,000 | WN8h |
The brightest star in the arrow, γ Sagittae, is a glowing orange red giant 260 light years from Earth . The star has reached the end of its evolution and has expanded to 55 times the diameter of our sun .
The star α Sagittae is around 430 light years away. It is 20 times the diameter of our sun. The name Sham is of Arabic origin and means "arrow".
Double stars
| system | Sizes | distance |
|---|---|---|
| ζ | 5.6 m / 6.0 m / 9.0 m | 0.2 ″ / 8.4 ″ |
| ε | 5.8 m / 8.4 m | 87.3 ″ |
| θ | 6.7 m / 8.9 m / 7.5 m | 11.6 ″ / 91.5 ″ |
| 15th | 5.8 m / 9.4 m / 6.9 m | 162.2 ″ / 215.1 ″ |
ζ Sagittae is a triple system 260 light years away. Two main sequence stars of the spectral type A form a binary star system that is only 0.2 ″. The orbital period is 23.2 years. At a distance of 8.4 ″ there is a third star with an apparent brightness of 9.0 m , which orbits this system on a higher-level orbit. The narrow system can only be resolved with professional telescopes (e.g. by speckle interferometry ), while the wide system can already be observed in a small telescope with a 5 cm aperture.
ε Sagittae is an optical double star and is 87.3 "apart. The companion is a 8.4 m bright background star.
The system 15 Sagittae is of particular interest . It consists of a sun-like star with 1.1 times the solar mass and 1.3 times the solar luminosity and a brown dwarf star with 69 Jupiter masses . The brown dwarf was discovered in 2001. It is 0.8 ″ from the main star and orbits it with a period of 73.3 years. 15 Sagittae also has two optical companions that are already visible in binoculars: a 9th magnitude star at a distance of 162 ″ and a 7th magnitude star at a distance of 215 ″.
Spectroscopic double stars in the arrow are (the orbital period in brackets): δ sagittae (10.14 years), 2 sagittae (7.39 days), 9 sagittae (78.74 days) and 10 sagittae (1.9 years).
Variable stars
| star | size | period | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| δ | 3.7 m to 3.8 m | slowly irregularly changing star | |
| 9 | 6.16 m to 6.23 m | eclipsing star | |
| 10 | 5.2 m to 6.0 m | 8.38 days | classic Cepheids |
| 13 | 5.3 m to 5.6 m | slowly irregularly changing star |
Messier and NGC objects
| Messier (M) | NGC | other | size | Type | Surname |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 71 | 6838 | 8.4 m | Globular clusters | ||
| 6879 | 12.5 m | planetary nebula | |||
| 6886 | 11.4 m | planetary nebula | |||
| IC 4997 | 10.5 m | planetary nebula | |||
| M1-67 |
Wolf-Rayet Ring Nebula ( Emission Nebula ) |
In the arrow is the globular cluster M 71, 13,000 light years away . The French astronomer and comet hunter Charles Messier included it in his catalog of foggy objects ( Messier catalog ). The classification as a globular cluster has long been considered controversial because the cluster is quite loose. It was therefore mostly categorized as a very dense open star cluster.