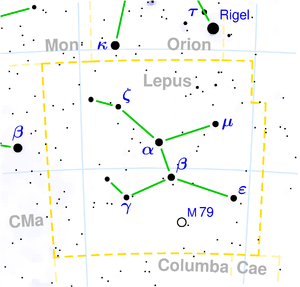
Hare (constellation)
|
Constellation Rabbit |
|
|---|---|
| Latin name | Lepus |
| Latin genitive | Leporis |
| Abbreviation | Lep |
| Right ascension | 04 h 55 m 02 s to 06 h 12 m 52 s |
| declination | −27 ° 16 ′ 44 ″ to −10 ° 48 ′ 50 ″ |
| surface | 290.291 deg² rank 51 |
| Completely visible | 63 ° N to 90 ° S |
| Observation time for Central Europe | winter |
| Number of stars brighter than 3 mag | 2 |
| Brightest star (size) | Arneb (2.58) |
| Meteor streams | |
|
Neighboring constellations ( clockwise from north ) |
|
| swell | IAU , |
The hare ( Latin Lepus ) is a constellation near the celestial equator .
description
The hare can be found south of the showy Orion . Seen from Germany, it stands relatively low above the southern horizon in the winter evenings.
Two of its stars are brighter than the 3rd magnitude .
The globular cluster M 79 is located in the rabbit .
history
The hare is one of the classic 48 constellations of antiquity mentioned by Ptolemy .
mythology
In ancient Egypt , the constellation represented the god of death Anubis , a human figure with a dog's head. According to another interpretation, it was the boat of the god Osiris .
The interpretation of the constellation as a hare by the ancient Greeks probably goes back to the neighboring sky hunter Orion and the Great Dog . Every night the hare is chased across the sky by the Big Dog.
Celestial objects
Stars
| B. | F. | Names or other designations | Apparent brightness likes | Lj | Spectral class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | 11 | Arneb , Arnab | 2.58 | 1200 | F0 Ib |
| β | 9 | Nihal , Nibal | 2.81 | 160 | G5 II |
| μ | 5 | 3.0 to 3.4 | 200 | B9 III | |
| ε | 2 | 3.19 | 150 | K5 III | |
| ζ | 14th | Zeta Leporis | 3.55 | 70.5 | A2 IV-V (n) |
| γ | 13 | Gamma Leporis | 3.59 | 29.3 | F6V + G5 |
| η | 16 | Eta Leporis | 3.72 | 49.1 | F2 V |
| δ | 15th | 3.76 | 150 | G8 III | |
| λ | 4.29 | ||||
| κ | 4.36 | 250 | B8 + F1 | ||
| ι | 4.45 | ||||
| θ | 4.67 | ||||
| 17th | 4.92 | ||||
| 19th | 5.28 | ||||
| ν | 5.25 | ||||
| R, Karmesinstern, Hind's purple star | 5.5 to 11.7 | ||||
| 10 | 5.53 | ||||
| 1 | 5.74 | ||||
| 12 | 5.88 | ||||
| Peter 229 | 8.14 | M1 V + T6 V |
Alpha Leporis is a super giant of the spectral class F0 Ib, about 1200 light years away . It is a star with 10 times the mass, 75 times the diameter and 13,000 times the luminosity of our sun . The name Arneb is derived from the Arabic "al-arnab" for "the hare".
Beta Leporis is 159 light years away. It is a yellowish glowing giant star of the spectral class G4 II. The name Nihal also comes from Arabic and means something like "camels that quench their thirst".
Zeta Leporis is a white-bluish main sequence star in transition to a subgiant . It is currently 70.5 light years away; 861,000 years ago, however, due to its own motion, it probably came within 4.17 light years of the sun , a little closer than Alpha Centauri today . In 2001 an extensive asteroid belt was detected around the star, the mass of which exceeds that of the main belt in the solar system by more than 200 times.
The star Gliese 229 is one of the closest neighbors of our sun at a distance of 19 light years. It is a red dwarf star of the spectral class M1 V. To observe it you need at least prism binoculars . In 1998 a companion star was discovered, a brown dwarf with 20 to 50 times the mass of the planet Jupiter .
Double stars
| system | Apparent brightness likes | distance |
|---|---|---|
| γ | 3.6 / 6.2 | 97 " |
| κ Lep | 4.4 / 7.3 | 2.6 " |
Gamma Leporis is a binary star system only 29.3 light years away. The two components can already be observed with a small telescope .
Variable stars
| star | Apparent brightness likes | period | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| μ Lep | 3.0 to 3.4 | about 2 days | Alpha 2 -Canum Venaticorum Star |
| RX Lep | 5.0 to 7.0 | irregular | Semi-regular variable star |
| R. | 5.5 to 11.7 | 430 days | Mira star |
| T | 7.4 to 14.3 | 370 days | Mira star |
My Leporis , 150 light-years away, is a variable star whose brightness fluctuates by 0.2 magnitudes over a period of about 2 days.
The RX Leporis, 500 light years away, changes its brightness with no discernible period.
R Leporis is a Mira type star about 1400 light years away , which changes its brightness strongly with a period of about 430 days. It belongs to the spectral class C7.6e and is one of the reddest objects in the night sky. Sometimes it is also known as the "Karmesinstern" or "Hind's purple star" (named after the British astronomer John Russel Hind , who described its variability). During the brightness maximum it can be seen with the naked eye. However, a telescope is required to observe the impressive color.
Messier and NGC objects
| Messier (M) | NGC | other | Apparent brightness likes | Type | Surname |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 79 | 1904 | 8th | Globular clusters |
The globular cluster M79, 40,000 light years away, is located in Hare . Even in the binoculars it appears as a misty spot. In a middle telescope, the edge area can be resolved into single stars. However, it is difficult to observe from Germany because it is low in the sky.
literature
- Wilhelm Gundel : Lagoos . In: Paulys Realencyclopadie der classischen Antiquity Science (RE). Volume XII, 1, Stuttgart 1924, Sp. 458-461.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Archive link ( Memento of the original from July 4, 2012 on WebCite ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.