Sclareol
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
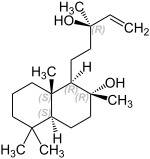
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Sclareol | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Labd-14-en-8,13-diol |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 20 H 36 O 2 | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 308.50 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
95-100 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
218–220 ° C (19 mmHg ) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
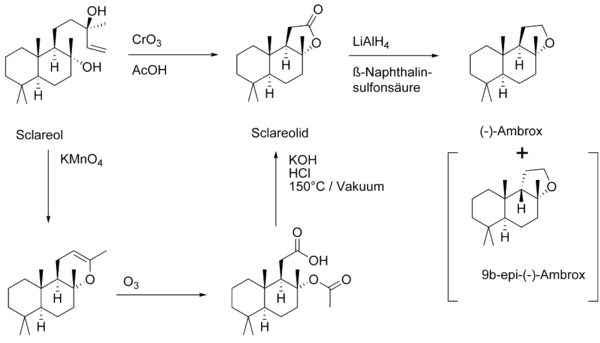
Sclareol is a naturally occurring bicyclic diterpene - alcohol ( terpenoid ). Sclareol has the carbon backbone of the diterpene labdan ; the bicyclic core consists of two fused cyclohexane rings. Sclareol thus belongs to the labdane group . The amber-colored solid has a sweet, balsamic scent.
Extraction and presentation
(-) - Sclareol can be obtained from clary sage ( Salvia sclarea ) by classic steam distillation . In 2010 the enzymatic pathway for biological synthesis was published. Occasionally, an alternative production process was also presented, which describes the expression of sclareol from genetically modified E. coli bacteria . In addition to the desired (-) - sclareol, 13- epi- clareol is also produced, which can be removed by gas chromatography .
The (+) - enantiomer of sclareol can be obtained by extraction from Conyza trihecatactis .
Use and properties
Sclareol is used as a fragrance in cosmetics and perfumes and as a flavoring in food. Sclareol is used especially for the alternative synthesis of Ambrox (instead of Ambrein ).
The key step in technical synthesis is the oxidative breakdown of the side chain through oxidation with chromium trioxide CrO 3 . The subsequent reduction of the lactone with lithium aluminum hydride leads to the diol, which cyclizes in acid to the desired ether. The thermodynamically more stable 9b- epi -Ambrox can arise as a by-product . The reaction can be carried out on a large scale with a yield of 54%.
Sclareol induces apoptosis in human leukemia cells and intestinal tumor cells . The occurrence of cell death is time and dose dependent.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f data sheet Sclareol from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on January 6, 2013 ( PDF ).
- ↑ M. Schalk, L. Daviet: Toward a Biosynthetic Route to Sclareol and Amber Odorants ; in: J. Am. Chem. Soc. , 2012 , 134 (46), pp. 18900-18903; doi : 10.1021 / ja307404u .
- ↑ Torrenegra, R., Robles, J .: Diterpenes and diterpene xylosides from Conyza trihecatactis , in: Phytochemistry 1994 , 35, pp. 195-199.
- ^ B. Schäfer, Chemistry in our time , 2011 , 45, 374 - 388; doi : 10.1002 / ciuz.201100557 .
- ↑ K. Dimasa, D. Kokkinopoulos: The effect of sclareol on growth and cell cycle progression of human leukemic cell lines , In: Leukemia Research , 1999 , 23, 3, 217-234; doi : 10.1016 / S0145-2126 (98) 00134-9 .