Steam boiler
A steam boiler is a closed, heated pressure vessel or a pressure pipe system that is used to generate water vapor at a pressure higher than atmospheric (p> 1.013 bar absolute) or hot water at temperatures above 100 ° C for heating and operating purposes.
If the steam boiler is used to generate steam, it is called a steam generator . Depending on the use of steam, saturated steam or superheated steam is generated in a steam boiler .
Dimensions
The size of steam boilers is wide. It ranges from small steam boilers in the household (steam cleaner, steam iron) and in rattling boats to tower steam boilers in steam power plants with a height of up to 155 m with a steam output of up to 3600 t / h.
For example, the dimensions of the modern, lignite-powered unit K of the Niederaussem power plant are :
- 168 m boiler house height,
- 2620 tons of steam per hour,
- a thermal output of 2306 MW ,
- a fuel consumption of 847 t per hour,
with design parameters 274 bar and 580 ° C ( live steam ) or 600 ° C ( secondary steam after reheater).
Boiler with firing
The heat can be supplied by firing with gaseous, liquid or solid fuels .
Evaporator without firing
The heat transfer can take place by radiation or conduction,
- when a radiation source, such as focused solar radiation , supplies energy,
- if a cooling medium in the primary circuit of a reactor supplies energy from nuclear fissure heat,
- a product from an exothermic chemical process heats the heat exchanger,
- resistance heating works with electrical energy,
- Waste heat is supplied to a gas turbine in a combined cycle power plant or an internal combustion engine or gas engine
etc.
The waste heat that can be used in this way arises from chemical reactions or from the physical melting of raw materials. The prerequisites for the heat flow are sufficient
- Temperature differences and
- Mass flows
- Transfer surfaces
In the case of the directly fired boilers, the fuels used are coal , crude oil , natural gas and increasingly also biomass and waste .
In the case of solid fuels, a distinction is made between dust firing , grate firing and fluidized bed firing .
Designs
In terms of design, a distinction is made between high-speed steam generators, shell boilers and water tube boilers. Electrically heated steam boilers are also used to generate small amounts of steam.
A distinction is made between land steam boilers and mobile steam boilers . The land steam boiler is at a permanent location. Movable steam boilers are z. B. Steam boilers on locomotives , locomobiles , ships or cranes , in order to drive a vehicle or a lifting device by means of a steam engine or steam turbine.
Locomotive steam boiler
The locomotive steam boiler was originally a riveted construction that has been optimized for mobile use. The highest possible steam output had to be generated in a limited space. The locomotive steam boiler has a water-cooled fire box . The walls of the fire box are stabilized with stud bolts to the outer jacket. At the exit of the fire box, the so-called long boiler connects , through which the flue gas is directed into smoke tubes. It usually consists of several boiler sections riveted or welded together. To increase the efficiency of the steam engine, superheater coils have been used in powerful locomotive steam boilers , which are led into the smoke tubes as U-tubes. The operating pressures of the locomotive steam boiler are usually 12 to 16 bar (Germany) or 14.1 to 21.8 bar (USA). Higher operating pressures have not prevailed.
New boilers that were used after the Second World War were mostly made as welded constructions due to the advancement of welding technology.
Steam output: up to 22 t / h (Germany, series 45 boilers, so-called splinter types are not taken into account); up to over 45 t / h (USA, boilers of various series)
Shell boiler
A distinction is made between:
- Flame tube smoke tube boiler
- Flame tube boiler
- Smoke tube boiler
- Roller bowl.
This type of boiler has a cylindrical shell. The flame tube boiler was developed from the shell-side heated roller boiler of the 19th century, which results in more effective heat transfer. With the introduction of welding technology, the flame tube smoke tube boiler was created. The flame tube received a reversing chamber through which the flue gas flow is directed into the downstream flue gas tubes. The design predominantly used today is the flame tube, smoke tube, three-pass boiler. It has a flame tube and two flue gas ducts and thus a front and rear turning chamber. The train denotes a continuous heating surface between two diversions of the flow path.
The smoke tube boiler is a waste heat boiler. The boiler is a furnace, z. B. upstream a fire box, a furnace or a gas turbine.
The shell boiler is used for small to medium steam outputs and steam pressures. The pressures are limited because the jacket with diameters up to 4 m must be designed for the pressure. Performance limits are:
Steam pressures: up to 30 bar.
Steam output: up to 55 t / h (two flame tubes).
All welding work on the boiler body is carried out by the manufacturer. In the case of small and medium-sized boilers, the insulation and the installation of the equipment can also be carried out by the manufacturer, so that only the connection to the components of the steam boiler system and to the steam consumer circuit has to be made at the installation site.
Water tube boiler
In contrast to shell boilers, water tube boilers contain the water in the tubes. This type of boiler is used for higher steam outputs and pressures. The water tube boiler is also used for solid fuel combustion, as the combustion chamber, in contrast to the flame tube, can be designed as desired by the arrangement of tube walls. Sootblowers can be inserted into the flue gas path in order to clean the heating surfaces when there is a lot of dust.
The following variants belong to the water tube boilers:
The heating surfaces are touched by the hot exhaust gas and absorb the heat. In the area of combustion (high heat flux density) and in areas at risk of thermal or abrasion / corrosion risk, refractory linings are placed in front of the pipe walls or the surfaces are pinned and lined with ramming compound. To improve the heat transfer, coil evaporators are attached to the flues. Since the steam generated by water tube boilers is often used for steam turbines, the steam has to be superheated. For this purpose, superheaters are hung in the flue gas path in the area of average flue gas temperatures . The feedwater preheater ( economiser ) is usually used in the last pass . The residual heat can still be used in the air preheater (LuVo) to heat the combustion air. The exhaust gas is then fed to the exhaust gas cleaning system.
The static stability of this construction is achieved by welding the pipes with flat iron (picture), which at the same time is sealed against the flue gases .
Rapid steam generator
The high-speed steam generator is a water tube boiler for smaller capacities to generate wet or saturated steam . The heating surfaces only consist of a spiral-shaped arrangement of tubes. The burner is arranged on the axis of the heating coil. The fuel quantity and the delivery quantity of the pump are coordinated in such a way that wet steam with a low residual water content is generated. A water separator is often arranged in the steam line in order to achieve almost saturated steam conditions. Since the high-speed steam generator has no storage volume, only those steam consumers that require an even amount of steam should be connected. The advantage of the high-speed steam generator is based on the lower price compared to the flame tube / smoke tube boiler and the short start-up time from cold to operating condition. The performance limits are steam pressures: up to 32 bar with a steam output of up to 2 t / h.
Electric steam boiler
the generation of steam in electric steam boilers can be done in two ways:
- Use of heating rods immersed in the water space. The heating takes place through the ohmic resistance of the heating windings.
- Three electrodes ( three-phase current ) insulated from the jacket are immersed in the water space . The boiler water acts as an electrolyte and it is heated by the ohmic resistance of the water. In this case, salty boiler water must be used in order to achieve sufficient conductivity. However, this arrangement is rarely used.
Electric steam boilers are used when only small amounts of steam are required or when steam is only required irregularly (e.g. for test systems). Another reason for the use of electric steam boilers can be official requirements regarding emissions.
The electrically generated steam output of a boiler is usually well below 1 t / h. The kettles usually consist of cylindrical jackets with a dished bottom . The heating rods are inserted into a blind flange and sealed and are screwed to a flange socket of the boiler.
Sterilizers in hospitals or laboratories are often supplied with steam from electric boilers, which are integrated into the system housing to save space. The electric steam boilers can also include steam irons or steam-heated devices for cleaning purposes or for removing wallpaper .
Nuclear power plants
In nuclear power plants with boiling water reactors , the steam is generated in the reactor pressure vessel .
In nuclear power plants with pressurized water reactors , the steam is generated in heat exchangers in which the feed water is evaporated in the secondary circuit by means of the forced flow of the primary water heated in the reactor pressure vessel . In nuclear power plants of Siemens AG / Kraftwerk Union there are steam generators with vertical U-tubes, in the nuclear power plant Mülheim-Kärlich (BBC / BBR- Babcock-Brown Boveri Reaktor GmbH ) vertical straight-tube steam generators were in use.
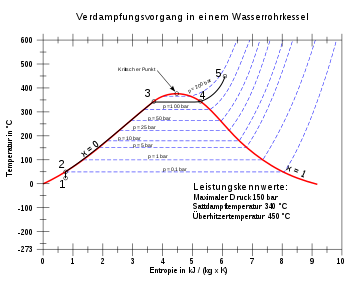
Steam generation in the Ts diagram
The Ts diagram shows the typical changes in the state of water and water vapor in a steam generator with superheater (pressure losses were neglected):
- 1–2 : Pressure increase of the water to the boiler pressure of the feed pump
- 2–3 : Isobars (at constant pressure) heat input up to the evaporation temperature corresponding to the pressure
- 3–4 : Isothermal complete evaporation of the water
- 4–5 : Isobaric overheating of the resulting water vapor
(Energetic considerations: see steam power plant )
Use of steam boilers
Steam boilers are used in particular where steam and superheated steam are required. Steam boilers are used in the energy industry in the form of power plant steam generators to generate electricity. In addition to the various areas of application in industry, for example in heating systems or in production, steam boilers are also used in agriculture for steaming (soil disinfection) for soil disinfection .
Safety of steam boilers
Desalination and boiler water monitoring
In the boiler, especially in the steam generator, salts accumulate over time , since only chemically pure water escapes from the boiler through evaporation or evaporation and water that is loaded with salts has to be replenished. These salts have to be removed again by blowdown. Otherwise there is a risk of corrosion and deposit formation.
If the deposits on the smoke tubes or flame tubes initially lead to poor heat transfer and the associated energy losses, the excessively high salt content in the kettle leads to "foaming", comparable to cooking potatoes. In other words, salty boiler water can be carried away with the steam and lead to corrosion in the downstream steam lines and system components. If the deposits build up to such an extent that the heat transfer from the heating surfaces to the boiler water is hindered, the heating surfaces will overheat, which can lead to a burn through and thus to a boiler explosion. The consequences are similar to those of water deficiency damage.
The boiler is preventively protected against such damage by using automatic blowdown controls. Conductive conductivity measuring systems permanently monitor the electrical conductivity of the boiler water. If the defined limits are exceeded, water is discharged using a blowdown valve . A distinction is made between two- and four-electrode systems, analogous to two- wire and four-wire circuits . If the two-electrode measurement is suitable for monitoring clean boiler water in a preferred conductivity range of 0.5 to 1000 µS / cm, the four-electrode measurement is used primarily where deposits and deposits are to be expected, depending on the boiler water constituents. With the two-electrode measurement, deposits increasing the resistance are directly included in the measurement result, i.e. That is, a lower conductivity is simulated. Component-tested systems recognize this fact and issue a fault report. Simple systems simply show a lower conductivity. With the four-electrode measurement method, however, the separation of current-carrying electrodes and electrodes used for measurement excludes polarization effects on the measurement result and also largely compensates for soiling or the formation of deposits. The component-tested systems have automatic temperature compensation, i. This means that the increase in conductivity as a result of an increase in temperature is automatically and permanently compensated.
In the boiler sedimented particles by means of blowdown be removed.
Quality regulations
Steam boilers are pressure equipment at risk of overheating within the meaning of the Pressure Equipment Directive 2014/68 / EU (up to 07-2016 RL 97/23 / EC) and may only be placed on the market if the manufacturer has demonstrated through a conformity assessment procedure with the participation of a notified body that the basic Safety requirements of the guideline have been met. The manufacturer affixes the CE mark and issues an EC declaration of conformity .
Harmonized product standards for steam boilers are:
- EN 12952-1 to 17: water tube boilers
- EN 12953-1 to 14: Shell boilers
- EN 14222: Stainless steel shell boiler
When applying these standards, the manufacturer can assume that he meets the basic safety requirements of the directive (presumption of conformity).
The basis for the requirement for reliable conductivity measuring systems can be found in TRD regulations 604. The requirements that are a prerequisite for a type examination can be found e.g. B. in the VdTÜV leaflet "Water monitoring devices 100".
However, other standards and regulations can also be used. However, the manufacturer has to prove that he fulfills the basic safety requirements of the Pressure Equipment Directive.
Operating rules
Steam boilers or steam boiler systems have a high risk potential due to their high stored energy and their high internal pressure. They therefore belong to the systems requiring monitoring according to the industrial safety regulations . Because of these provisions are
- to have the steam boiler checked by an approved monitoring body prior to commissioning
- Obtain permission from the competent authority to operate this system
- Carry out recurring tests (internal and external tests, strength tests, functional tests of the safety devices) by an approved monitoring body within certain periods.
In most cases, the systems mentioned may only be operated by qualified specialists, heating plant operators, boiler operators or heaters.
See also
literature
- Resch, Fritz Mayr Published by Kesselbetriebstechnik.
- Wolfgang Noot: From suitcase boilers to large power plants - the development in boiler construction. Basics, construction, applications . Vulkan-Verlag, Essen 2011, ISBN 978-3-8027-2558-6 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Picture of welded pipes. Retrieved February 8, 2019 .
- ↑ a b c boiler water monitoring. (No longer available online.) IGEMA GmbH, formerly in the original ; Retrieved October 22, 2012 . ( Page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.