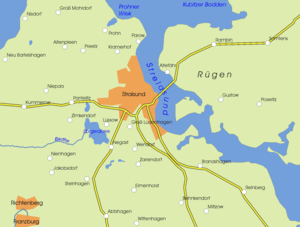
Strelasund
| Strelasund | ||
|---|---|---|
| View over the Strelasund from the air | ||
| Connects waters | Prohner Wiek , Kubitzer Bodden | |
| with water | Greifswalder Bodden | |
| Separates land mass | to reprimand | |
| of land mass | Western Pomerania | |
| Data | ||
| Geographical location | 54 ° 17 ' N , 13 ° 7' E | |
|
|
||
| length | 25 km | |
| Smallest width | 1 km | |
| Greatest depth | 16 m | |
| Coastal towns | Altefähr , Brandshagen , Glewitz on the Zudar (Garz) , Gustow , Parow , Stahlbrode , Stralsund | |
| Islands | Dänholm , Gustower Werder | |
| Peninsulas | Devin , Drigge , Zudar | |
| bridges | Rügen Bridge , Ziegelgraben Bridge | |
| Dams | Rügenamm | |
| Site plan of the Strelasund | ||
The Strelasund is an arm of the Baltic Sea in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania . It separates the island of Rügen from the mainland near the Hanseatic city of Stralsund . The elongated and with more than ten meters unusually deep strait for an inner Western Pomeranian coastal water has an area of 64 square kilometers.
Emergence
The last ice age and its ice masses that melted in this region 13,000 years ago left a gently undulating marl landscape. Until at least 7000 years ago there was probably still a wooded valley with a river that had been cut by the meltwater from the ice age ice sheet . With the post-glacial sea level rise in the Baltic Sea ( Littorina Transgression ), the sea penetrated this valley from both sides and the Strelasund was created in its present form.
The banks of the Strelasund on the Rügen side are characterized by both steep banks and flat banks with a belt of reeds, while the mainland bank is mostly flat.
Information about the formation of the Strelasund is shown in the German Sea Museum in Stralsund.
history
In Stralsund found in 1362 and 1369 battles between the Danish King Waldemar IV. And Navy of the Hanseatic instead. As a result of the second battle, the Peace of Stralsund was concluded in 1370 . In 1678 and 1715, the Strelasund was the scene of battles between the Prussians, allied with Denmark , against the Swedes , as a result of which Swedish rule in this part of Swedish Pomerania was briefly interrupted. Both times the Swedes were pushed back over the Strelasund to Stralsund after the landing of Danish, Brandenburg and Prussian troops on Rügen.
Strelasund crossing
The island of Rügen has been accessible from Stralsund - apart from ferry connections - via a combined road and rail connection since the mid-1930s. This connection leads over the small island of Dänholm and consists of the Ziegelgraben bascule bridge between Stralsund and Dänholm and the Rügen dam between Dänholm and Rügen. Since 2007, this compound is of the immediately to the north parallel, as Hochbrücke executed Rügenbrücke relieved. This has a ship passage height of 40 meters above the Ziegelgraben. Above the Strelasund proper, however, the passage height for ships is only 8 meters at the designated point.
additional
A sporting event that takes place once a year is Sundschwimmen , a swimming competition over a distance of 2.3 kilometers between Altefähr and Stralsund.
The Strelasund is well known as a good fishing ground for pike and zander anglers. In brackish water , there is a great variety of food, so the predatory fish grow up fast. Angling and professional fishing, however, consume a lot of the population.
In 2002, builders came across Stralsund's dugout canoes in Stralsund , three 6000 to 7000 year old dugout canoes .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ Southern Strelasund and Greifswald. ( Memento from September 28, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) Description of the Strelasund (as a sailing area) on the state portal Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania
- ↑ The Strelasund. Description in the online port manual Germany (European Sailing Information System ESYS), private website of O. Walter
- ↑ Official charts for small and sport shipping, set 3006, sheet 22 (2017/2018 edition of January 13, 2017) and official nautical charts 1579 (5th edition of May 27, 2016) and 1622 (11th edition of November 13th 2015), BSH , Hamburg and Rostock