Streptozocin
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
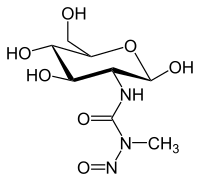
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Streptozocin | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 15 N 3 O 7 | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class |
Cytostatic |
||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 265.22 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
115 ° C (decomposition) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water (5.07 g l −1 at 25 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Streptozocin , also streptozotocin (STZ) [trade name: Zanosar ® (CH)], is to the substance classes of Glucosamine and the nitrosoureas belonging and naturally-occurring chemical compound which specifically toxic for the insulin-producing beta cells in the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas is. It is used therapeutically as a cytostatic agent for the treatment of beta cell tumors known as insulinomas . In experimental medicine, it is used in diabetes research to trigger diabetes mellitus in laboratory animals .
Properties and effects
Streptozocin is a white to light yellow powder. In terms of its chemical structure, it contains methylnitrosourea bound to the C 2 position of glucose . It belongs to the substance class of the nitrosoureas and, like some other comparable substances, has an alkylating effect . This means that there is an installation of alkyl groups in the DNA effected, whereby the cell division is inhibited. Damage to the DNA by the generation of free radicals is also discussed as a mechanism of action. Streptozocin is therefore mutagenic (mutagenic) and carcinogenic .
The selective effect on the beta cells is based on the fact that streptozocin is transported into the cell interior due to the glucose structure by the glucose transporter GLUT2, which occurs in high density in the membrane of beta cells. In the cell there is a split between the glucose content and the methylnitrosourea, which is responsible for the DNA-damaging effects.
application
The therapeutic use of streptozocin is limited to the treatment of insulinomas that cannot be surgically removed because of the risks involved . In affected patients, the treatment can reduce the tumor size and thus the symptoms associated with the excessive production of insulin by the tumor, such as the recurrence of hypoglycaemia . It is used by intravenous injection over several days, with repetition as necessary after four to six weeks.
As part of the experimental application to induce diabetes mellitus in test animals, streptozocin has largely prevailed over previously used substances such as alloxan or steroids . However, its use has also decreased due to the availability of various spontaneous diabetic animal models such as the BB rat or NOD mouse . Depending on the question to be investigated, acute insulin-dependent diabetes can be triggered by a single administration of a corresponding dose, as can an autoimmune process similar to human type 1 diabetes due to multiple administration of subacute doses. Treatment of test animals immediately after birth can also induce diabetes mellitus that does not require insulin.
Historical information
Streptozocin was found in 1956 as an antibiotic substance by scientists from Upjohn in a strain of the soil bacterium Streptomyces achromogenes . A patent was applied for in 1959 and granted in March 1962. In the mid-1960s, the selective toxic effect against the beta cells in the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas was discovered. Shortly thereafter, this led to its use in experimental diabetes research in order to specifically induce diabetes mellitus in test animals.
At the same time, the first investigations into the clinical application for the treatment of insulin-producing tumors of the pancreas began. Further research at the National Cancer Institute led to approval as a drug by the American Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1982 . Upjohn, which later became the property of Pfizer as part of several takeovers , marketed streptozocin under the trade name Zanosar ® . It has been available as a generic since its patent protection expired .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry on streptozocin in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM)
- ↑ a b sheet streptozocin at Sigma-Aldrich retrieved on May 13, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ^ S. Lenzen: The mechanisms of alloxan- and streptozotocin-induced diabetes. In: Diabetologia . Volume 51, Number 2, February 2008, pp. 216-226, doi : 10.1007 / s00125-007-0886-7 . PMID 18087688 . (Review).
- ↑ IF Federiuk, HM Casey u. a .: Induction of type-1 diabetes mellitus in laboratory rats by use of alloxan: route of administration, pitfalls, and insulin treatment. In: Comparative Medicine. Volume 54, Number 3, June 2004, pp. 252-257, PMID 15253270 . (Review).
- ↑ JJ Vavra et al. (1959): Streptozotocin, a new antibacterial antibiotic. In: Antibiotics Annual. Vol. 7, pp. 230-235. PMID 13841501
- ↑ Patent US3027300 : Streptozotocin and its production. Filed August 1, 1958 , published March 27, 1962 , Applicant: Upjohn Co., Inventors: Malcolm E. Bergy, Clarence Deboer, Alma Dietz, Thomas E. Eble, Ross R. Herr, Leroy E. Johnson.
- ↑ KR Mans Ford & Opie L. (1968): Comparison of metabolic abnormalities in diabetes mellitus induced by streptozotocin or alloxan by. In: Lancet. Vol. 30, pp. 670-671. PMID 4170654 .
- ^ IM Murray-Lyon et al. (1968): Treatment of multiple-hormone-producing malignant islet-cell tumor with streptozotocin. In: Lancet. Vol. 26, pp. 895-898. PMID 4176152 .
literature
- Renier Brentjens, Leonard Saltz: ISLET CELL TUMORS OF THE PANCREAS: The Medical Oncologist's Perspective . In: Surgical Clinics of North America . tape 81 , no. 3 , June 2001, p. 527-542 , doi : 10.1016 / S0039-6109 (05) 70141-9 .
- DA Rees, JC Alcolado: Animal models of diabetes mellitus . In: Diabetic Medicine . tape 22 , no. 4 , April 2005, p. 359-370 , doi : 10.1111 / j.1464-5491.2005.01499.x .