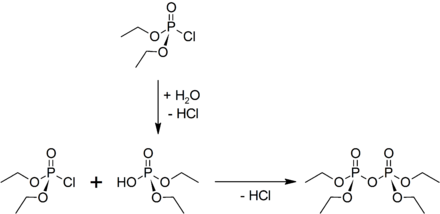Tetraethyl pyrophosphate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Tetraethyl pyrophosphate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 20 O 7 P 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
hygroscopic colorless liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 290.19 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.18 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
0 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
124 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
2.0664 Pa (° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
miscible with water (decomposes)
|
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4071 |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
Switzerland: 0.005 ml m −3 or 0.05 mg m −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Tetraethyl pyrophosphate , abbreviated TEPP, is a chemical compound from the group of phosphoric acid esters . Its toxicity is based on the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase in nerve cells .
history
TEPP was first synthesized in the mid-19th century by the Russian chemist Vladimir Petrovich Moschnin, a student of Charles Adolphe Wurtz , in his Paris laboratory. The synthesis was repeated by Philippe de Clermont and reported to the Académie des sciences . It was not until 1932 that the enormous toxicity of the substance was reported. In 1938, Gerhard Schrader developed TEPP into one of the first organic insecticides .
presentation
TEPP can be made from diethyl chlorophosphate and water in the presence of pyridine to scavenge the hydrogen chloride .
Admission
There was never an EU approval, in Germany, Austria and Switzerland no pesticides with this active substance are approved.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Entry on tetraethyl pyrophosphate in ChemicalBook , accessed January 20, 2014.
- ↑ a b c data sheet TEPP, PESTANAL at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 19, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ International Chemical Safety Card (ICSC) for TEPP at the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), accessed January 18, 2016.
- ↑ a b c Entry on TEPP in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 13, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ VI Boiko, LN Onikiichuk, AV Yakovenko, VI Kal'chenko: New Syntheses of 1,1-Dichloro-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl Isocyanate and Its Reaction with Triethyl Phosphite . In: Russian Journal of General Chemistry . tape 72 , no. 8 , August 2002, p. 1313-1314 , doi : 10.1023 / A: 1020816905116 .
- ↑ Entry on TEPP in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 107-49-3 or tetraethyl pyrophosphate ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ Ladislaus Szinicz: History of chemical and biological warfare agents . In: Toxicology . tape 214 , no. 3 , October 30, 2005, p. 167-181 , doi : 10.1016 / j.tox.2005.06.011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ George Petroianu: History of organophosphorus cholinesterase inhibitor & Reactivators . In: Military Medical Science Letters . tape 84 , no. 4 , 2015, p. 182-185 ( PDF ).
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Tetraethyl pyrophosphate (TEPP) in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on February 22, 2016.