Triphenyl phosphate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
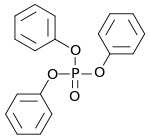
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Triphenyl phosphate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 18 H 15 O 4 P | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless crystals with a phenolic odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 326.29 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.18 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
49.4 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
400 ° C (220 ° C at 5 hPa) |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
8.8 m Pa (100 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
Switzerland: 3 mg m −3 (measured as inhalable dust ) |
|||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Triphenyl phosphate ( TPP or TPHP ) with the constitutional formula (C 6 H 5 ) 3 PO 4 is a chemical compound which, in its pure state, consists of colorless to white, odorless platelets. It is mainly used as a plasticizer and flame retardant . Triphenyl phosphate is a fish poison; it inhibits the enzyme acetylcholinesterase . It is made from phosphorus oxychloride and phenol .
properties
TPP hydrolyzes in an alkaline solution to diphenyl phosphate and phenol . Thermal decomposition begins at 600 ° C, but is not yet complete at 1000 ° C. Traces of TPP in the environment come from hydraulic oil leaks and the burning of plastics and can be detected everywhere.
use
TPP is mainly used as a flame retardant in electrical and automotive components. It is also used as a plasticizer for cellulose acetate plastics ( celluloid ), with a deliberate side effect being that it is less flammable. TPP is also a component of hydraulic oils and lubricants.
Risk assessment
In 2012, triphenyl phosphate was included in the EU's ongoing action plan ( CoRAP ) in accordance with Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH) as part of substance evaluation . The effects of the substance on human health and the environment are re-evaluated and, if necessary, follow-up measures are initiated. Triphenyl phosphate uptake was driven by concerns about consumer use , high (aggregated) tonnage and widespread use, and as a potential endocrine disruptor . The re-evaluation has been running since 2017 and is carried out by France . In order to be able to reach a final assessment, further information was requested.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Entry on triphenyl phosphate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b entry on triphenyl phosphate. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on December 28, 2014.
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 115-86-6 or triphenyl phosphate ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ Åke Bergman , Andreas Rydén, Robin J. Law, Jacob de Boer, Adrian Covaci, Mehran Alaee, Linda Birnbaum, Myrto Petreas, Martin Rose, Shinichi Sakai, Nele Van den Eede, Ike van der Veen: A novel abbreviation standard for organobromine , organochlorine and organophosphorus flame retardants and some characteristics of the chemicals . In: Environment International . tape 49 , 2012, p. 57–82 , doi : 10.1016 / j.envint.2012.08.003 , PMC 3483428 (free full text).
- ↑ Environmental Health Criteria (EHC) for Triphenyl Phosphate , accessed November 29, 2014.
- ↑ Community rolling action plan ( CoRAP ) of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA): Triphenyl phosphate , accessed on March 26, 2019.
