Zinc hexafluorosilicate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
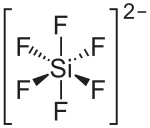
|
||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | Zinc hexafluorosilicate | |||||||||
| other names |
Zinc silicofluoride |
|||||||||
| Molecular formula | Zn [SiF 6 ] | |||||||||
| Brief description |
white odorless solid |
|||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 207.46 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||
| density |
2.104 g cm −3 |
|||||||||
| Melting point |
100 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||
| solubility |
easily soluble in water |
|||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
Zinc hexafluorosilicate with the empirical formula Zn [SiF 6 ] is an inorganic chemical compound of zinc from the group of hexafluorosilicates .
Extraction and presentation
Zinc hexafluorosilicate can be obtained by reacting zinc oxide with hexafluorosilicic acid.
properties
Zinc hexafluorosilicate is a crystalline white odorless solid that is readily soluble in water. It decomposes when heated above 100 ° C, producing hydrogen fluoride gas and silicon fluoride . The hexahydrate with the formula Zn [SiF 6 ] · 6 H 2 O forms colorless, hexagonal prisms and has a crystal structure with the space group R 3 (space group no. 148) . Here, zinc is octahedral surrounded by water molecules that form hydrogen bonds to the SF 6 octahedra. This creates a rhombohedral- distorted cesium chloride structure .
use
Zinc hexafluorosilicate is used to waterproof ( fluate ) cement , in combination with other fluorides to increase the corrosion resistance of the surfaces of aluminum and aluminum alloys , in the textile industry as a hardening accelerator for impregnating solutions based on melamine and urea resin and in wood protection as a fungicide . It is used as a component of so-called CKF and CKFZ salts (active ingredients for wood preservatives which, in addition to chromium or copper salts, also contain fluorine compounds such as copper hexafluorosilicate or zinc hexafluorosilicate).
safety instructions
Zinc hexafluorosilicate is poisonous and can be fatal if ingested by electrolyte imbalances and acidosis .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on zinc hexafluorosilicate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Nicholas P. Cheremisinoff: Handbook of Industrial Toxicology and Hazardous Materials . CRC Press, 1999, ISBN 978-0-8247-1935-7 , pp. 169 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Entry on zinc hexafluorosilicate in the Hazardous Substances Data Bank , accessed on November 23, 2016.
- ↑ Dietrich Breitinger, Wolfgang A. Herrmann, Wolfgang Hiller: Synthetic Methods of Organometallic and Inorganic Chemistry, Volume 5, 1999 Volume 5: Copper, Silver, Gold, Zinc, Cadmium and Mercury . Georg Thieme Verlag, 2014, ISBN 3-13-179211-6 , p. 134 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b Entry on zinc hexafluorosilicate. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on November 23, 2016.
- ^ A b S. Ray, A. Zalkin, DH Templeton: Crystal structures of the fluosilicate hexahydrates of cobalt, nickel and zinc. In: Acta Crystallographica Section B Structural Crystallography and Crystal Chemistry. 29, p. 2741, doi : 10.1107 / S056774087300748X .
- ↑ schadstoffberatung.de: Holzschutz , accessed on November 23, 2016
- ↑ C. Marx, S. Trautmann, M. Halank, M. Weise: Lethal intoxication with zinc hexafluorosilicate (hydrofluoric acid). In: Intensive Care Medicine and Emergency Medicine. 43, 2006, p. 209, doi : 10.1007 / s00390-006-0669-2 .


![{\ displaystyle \ mathrm {ZnO + H_ {2} [SiF_ {6}] + 5 \ H_ {2} O \ longrightarrow Zn [SiF_ {6}] \ cdot 6 \ H_ {2} O}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/af426b4628e6099e87928f1bed8559c1f8a11b7d)