Thomas Hardy: Difference between revisions
m →Later years: slight re-write |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|English novelist and poet (1840–1928)}} |
|||
{{redirect|Thomas Hardy}} |
|||
{{Use British English|date=November 2015}} |
|||
{{Use dmy dates|date=November 2022}} |
|||
{{Other uses}} |
|||
{{Infobox writer <!-- for more information see [[:Template:Infobox writer/doc]] --> |
|||
| name = Thomas Hardy |
|||
| honorific_suffix = {{post-nominals|country=GBR|size=100%|OM}} |
|||
| image = Thomashardy restored.jpg |
|||
| caption = Hardy between about 1910 and 1915 |
|||
| birth_date = {{birth date|df=yes|1840|6|2}} |
|||
| birth_place = [[Stinsford]], Dorset, England |
|||
| death_date = {{death date and age|df=yes |1928|1|11|1840|6|2}} |
|||
| death_place = [[Dorchester, Dorset]], England |
|||
| resting_place = {{unbulleted list | Stinsford parish church (heart) | [[Poets' Corner]], Westminster Abbey (ashes) }} |
|||
| occupation = {{cslist|Novelist|poet|short story writer}} |
|||
| alma_mater = [[King's College London]] |
|||
| genre = |
|||
| movement = {{cslist|[[Naturalism (literature)|Naturalism]]|[[Victorian literature]]}} |
|||
| notableworks = {{cslist|''[[Tess of the d'Urbervilles]]''|''[[Far from the Madding Crowd]]''|''[[The Mayor of Casterbridge]]''|''[[The Return of the Native]]''|''Collected Poems''|''[[Jude the Obscure]]''}} |
|||
| spouse = {{unbulleted list |{{marriage|[[Emma Gifford]]|1874|1912|end=her death}}| {{marriage|[[Florence Dugdale]]|1914}}}} |
|||
| signature = Thomas Hardy signature.svg |
|||
}} |
|||
'''Thomas Hardy''' {{post-nominals|country=GBR|size=100%|OM}} (2 June 1840 – 11 January 1928) was an English novelist and poet. A [[Literary realism|Victorian realist]] in the tradition of [[George Eliot]], he was influenced both in his novels and in his poetry by [[Romanticism]], including the poetry of [[William Wordsworth]].<ref>{{Citation |first=Dennis |last=Taylor |title=Hardy and Wordsworth |journal=Victorian Poetry |volume=24 |number=4 |date=Winter 1986}}.</ref> He was highly critical of much in [[Victorian era|Victorian]] society, especially on the declining status of rural people in Britain such as those from his native [[South West England]]. |
|||
While Hardy wrote poetry throughout his life and regarded himself primarily as a poet, his first collection was not published until 1898. Initially, he gained fame as the author of novels such as ''[[Far from the Madding Crowd]]'' (1874), ''[[The Mayor of Casterbridge]]'' (1886), ''[[Tess of the d'Urbervilles]]'' (1891) and ''[[Jude the Obscure]]'' (1895). During his lifetime, Hardy's poetry was acclaimed by younger poets (particularly the [[Georgian Poetry|Georgians]]) who viewed him as a mentor. After his death his poems were lauded by [[Ezra Pound]], [[W. H. Auden]] and [[Philip Larkin]].<ref>{{cite book|last=Watts|first=Cedric|title=Thomas Hardy: 'Tess of the d'Urbervilles'|date=2007|publisher=Humanities-Ebooks|pages=13, 14}}</ref> |
|||
[[Image:Thomas Hardy.jpg|thumb|right|Thomas Hardy]] |
|||
'''Thomas Hardy, [[Order of Merit|OM]]''' ([[2 June]], [[1840]] – [[11 January]], [[1928]]) — an [[England|English]] [[novelist]], [[short story]] writer, and [[poet]] of the [[naturalism (literature)|naturalist]] movement — delineated characters struggling against their passions and circumstances. The bulk of his work, set mainly in the semi-imaginary county of [[Thomas Hardy's Wessex|Wessex]], is marked by poetic descriptions and [[fatalism]]. |
|||
Many of his novels concern tragic characters struggling against their passions and social circumstances, and they are often set in the semi-fictional region of [[Wessex]]; initially based on the medieval Anglo-Saxon kingdom, [[Thomas Hardy's Wessex|Hardy's Wessex]] eventually came to include the counties of Dorset, Wiltshire, Somerset, Devon, Hampshire and much of Berkshire, in south-west and south central England. Two of his novels, ''Tess of the d'Urbervilles'' and ''Far from the Madding Crowd'', were listed in the top 50 on the [[BBC]]'s survey [[The Big Read]].<ref>[https://www.bbc.co.uk/arts/bigread/top100.shtml "BBC – The Big Read"] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121031065136/http://www.bbc.co.uk/arts/bigread/top100.shtml |date=31 October 2012 }}. BBC. April 2003, Retrieved 16 December 2016</ref> |
|||
==Biography== |
|||
==Life and career== |
|||
Thomas Hardy was born at Higher Bockhampton, a hamlet in the parish of [[Stinsford]] to the east of [[Dorchester, Dorset|Dorchester]] in [[Dorset]], [[England]]. His father worked as a stonemason and local builder. His mother was ambitious and well-read, supplementing his formal education, which ended at the age of 16 when he became apprenticed to John Hicks, a local architect. Hardy trained as an [[architect]] in Dorchester before moving to [[London]] in [[1862]]. Five years later he returned to Dorset to work as Hicks' assistant. He won prizes from the [[Royal Institute of British Architects]] and the [[Architectural Association School of Architecture|Architectural Association]]. |
|||
=== Early life === |
|||
[[File:2780theHardyTreeOldStPancrasChurchyard.jpg|thumb|"The Hardy Tree", a [[Great Trees of London|Great Tree of London]] in [[St Pancras Old Church|Old St Pancras]] churchyard in London, growing between gravestones moved while Hardy was working there. The tree fell in December 2022.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Brown |first=Matt |date=2022-12-28 |title=The Hardy Tree Of St Pancras Has Fallen |url=https://londonist.com/london/latest-news/the-hardy-tree-of-st-pancras-has-fallen |access-date=2022-12-28 |website=Londonist}}</ref>]] |
|||
Thomas Hardy was born on 2 June 1840 in Higher Bockhampton (then Upper Bockhampton), a hamlet in the parish of [[Stinsford]] to the east of [[Dorchester, Dorset|Dorchester]] in Dorset, England, where his father Thomas (1811–1892) worked as a stonemason and local builder. His parents had married at [[Melbury Osmond]] on 22 December 1839.<ref>Copy of marriage certificate in Melbury Osmond parish church.</ref> His mother, Jemima (née Hand; 1813–1904),<ref>{{cite web |date=13 October 2006 |title=Thomas Hardy: The Time-Torn Man |url=https://www.theguardian.com/books/2006/oct/13/thomashardy |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170729175642/https://www.theguardian.com/books/2006/oct/13/thomashardy |archive-date=29 July 2017 |access-date=13 December 2016 |work=The Guardian}}</ref> was well read, and she educated Thomas until he went to his first school at Bockhampton at the age of eight. For several years he attended Mr. Last's Academy for Young Gentlemen in Dorchester, where he learned Latin and demonstrated academic potential.<ref>{{Citation |first=Claire |last=Tomalin |title=Thomas Hardy: the Time-torn Man |publisher=Penguin |year=2007 |pages=30, 36}}.</ref> |
|||
Because Hardy's family lacked the means for a university education, his formal education ended at the age of sixteen, when he became apprenticed to James Hicks, a local architect.<ref>{{Citation |last=Walsh |first=Lauren |contribution=Introduction |title=The Return of the Native, by Thomas Hardy |place=New York |publisher=Barnes & Noble |series=Classics |year=2005 |type=print}}.</ref> He worked on the design of the new church at nearby Athelhampton, situated just opposite [[Athelhampton House]] where he painted a watercolour of the Tudor gatehouse while visiting his father, who was repairing the masonry of the dovecote. |
|||
In [[1870]], Hardy met [[Emma Lavinia Gifford]], whom he married in [[1874]].<ref>"Thomas Hardy - the Time-Torn Man", BBC Radio 4, 23 October 2006 (a reading of [[Claire Tomalin]]'s book of the same name).</ref> Although he later became estranged from his wife, her death in [[1912]] had a traumatic effect on him. He made a trip to [[Cornwall]] to revisit places linked with their courtship; his ''[[Poems 1912-13]]'' explore his grief. In [[1914]], Hardy married his secretary [[Florence Dugdale]], 40 years his junior, whom he had met in 1905. However, Hardy remained preoccupied with Emma's sudden death, and tried to overcome his remorse by writing poetry.<ref name="BBC-1">[http://www.bbc.co.uk/wiltshire/entertainment/days_out/thomas_hardy_stourhead.shtml bbc.co.uk] (accessed August 12, 2006)</ref> |
|||
He moved to London in 1862 where he enrolled as a student at [[King's College London]]. He won prizes from the [[Royal Institute of British Architects]] and the [[Architectural Association School of Architecture|Architectural Association]]. He joined [[Arthur Blomfield]]'s practice as assistant architect in April 1862 and worked with Blomfield on Christ Church, East Sheen [[Richmond, London]] where the tower collapsed in 1863, and All Saints' parish church in [[Windsor, Berkshire]], in 1862–64. A [[reredos]], possibly designed by Hardy, was discovered behind panelling at All Saints' in August 2016.<ref>{{cite news|last=Flood|first=Alison|title=Thomas Hardy altarpiece discovered in Windsor church|url=https://www.theguardian.com/books/2016/aug/16/thomas-hardy-altarpiece-discovered-in-windsor-church|access-date=17 August 2016|work=The Guardian|date=16 August 2016|archive-date=16 August 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160816234632/https://www.theguardian.com/books/2016/aug/16/thomas-hardy-altarpiece-discovered-in-windsor-church|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.windsorobserver.co.uk/news/14679029.Legendary_author_Thomas_Hardy_s_lost_contribution_to_Windsor_church_uncovered/|title=Legendary author Thomas Hardy's lost contribution to Windsor church uncovered|website=Royal Borough Observer|access-date=17 August 2016|archive-date=26 August 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160826151838/http://www.windsorobserver.co.uk/news/14679029.Legendary_author_Thomas_Hardy_s_lost_contribution_to_Windsor_church_uncovered/|url-status=live}}</ref> In the mid-1860s, Hardy was in charge of the excavation of part of the graveyard of [[St Pancras Old Church]] before its destruction when the [[Midland Railway]] was extended to a new terminus at [[St Pancras railway station|St Pancras]].<ref name="cornerstone">{{cite journal |last=Burley |first=Peter |year=2012 |title=When steam railroaded history |journal=Cornerstone |volume=33 |issue=1 |page=9 }}</ref> |
|||
[[Image:Egrac.jpg|thumbnail|right|Burial site of Thomas Hardy's heart]] |
|||
Hardy fell ill with [[pleurisy]] in December [[1927]] and died in January [[1928]], having dictated his final poem to his wife on his deathbed. His funeral, on [[16 January]] at [[Westminster Abbey]], proved a controversial occasion: Hardy, his family and friends had wished him to be buried at [[Stinsford]] in the same grave as his first wife, Emma. However, his executor, Sir [[Sydney Carlyle Cockerell]], insisted he be placed in the abbey's [[Poets' Corner]]. A compromise was reached whereby his heart was buried at Stinsford with Emma, and his ashes in Poets' Corner. |
|||
Hardy never felt at home in London, because he was acutely conscious of class divisions and his social inferiority. During this time he became interested in social reform and the works of [[John Stuart Mill]]. He was introduced by his Dorset friend [[Horatio Mosley Moule|Horace Moule]] to the works of [[Charles Fourier]] and [[Auguste Comte]]. Mill's essay ''[[On Liberty]]'' was one of Hardy's cures for despair, and in 1924 he declared that "my pages show harmony of view with" Mill.<ref>{{cite book |last=Wilson |first=Keith |title=A Companion to Thomas Hardy |date=2009 |publisher=John Wiley & Sons |page=55}}</ref> He was also attracted to [[Matthew Arnold]]'s and [[Leslie Stephen]]'s ideal of the urbane liberal freethinker.<ref>{{cite book |last=Widdowson |first=Peter |title=Thomas Hardy and Contemporary Literary Studies |date=2004 |publisher=Springer |page=132}}</ref> |
|||
Shortly after Hardy's death, the executors of his estate burnt his letters and notebooks. Twelve records survived, one of them containing notes and extracts of newspaper stories from the [[1820s]]. Research into these provided insight into how Hardy kept track of them and how he used them in his later work.<ref name="BBC-2">[http://www.bbc.co.uk/homeground/archive/2003/thomas_hardy.shtml bbc.co.uk], (accessed August 12, 2006)</ref> |
|||
After five years, concerned about his health, he returned to Dorset, settling in [[Weymouth, Dorset|Weymouth]], and decided to dedicate himself to writing. |
|||
Hardy's work was admired by many authors, amongst them [[D.H. Lawrence]] and [[Virginia Woolf]]. The writer [[Robert Graves]], in his autobiography ''[[Goodbye to All That]]'', recalls meeting Hardy in Dorset in the early [[1920s]]. Hardy received Graves and his newly married wife warmly, and was encouraging about the younger author's work. |
|||
=== Personal === |
|||
In [[1910]], Hardy was awarded the [[Order of Merit]]. |
|||
[[File:Max Gate.jpg|thumb|Max Gate in 2015]] |
|||
In 1870, while on an architectural mission to restore the [[St Julitta's Church, St Juliot|parish church of St Juliot]] in Cornwall,<ref>Gibson, James (ed.) (1975) Chosen Poems of Thomas Hardy, London: Macmillan Education; p.9.</ref> Hardy met and fell in love with [[Emma Gifford]], whom he married in Kensington in late 1874,<ref name="freebmd.org.uk">{{cite web |title=FreeBMD Home Page |url=http://www.freebmd.org.uk/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201211091910/https://www.freebmd.org.uk/ |archive-date=11 December 2020 |access-date=22 May 2016 |website=freebmd.org.uk}}</ref><ref>Hardy, Emma (1961) Some Recollections by Emma Hardy; with some relevant poems by Thomas Hardy; ed. by Evelyn Hardy & R. Gittings. London: Oxford University Press</ref><ref>"Thomas Hardy – the Time-Torn Man" (a reading of [[Claire Tomalin]]'s book of the same name), [[BBC Radio 4]], 23 October 2006</ref> renting St David's Villa, Southborough (now [[Surbiton]]) for a year. In 1885 Thomas and his wife moved into [[Max Gate]] in [[Dorchester, Dorset|Dorchester]], a house designed by Hardy and built by his brother. Although they became estranged, Emma's death in 1912 had a traumatic effect on him and after her death, Hardy made a trip to Cornwall to revisit places linked with their courtship; his ''[[Poems 1912–13]]'' reflect upon her death. In 1914, Hardy married his secretary [[Florence Dugdale|Florence Emily Dugdale]], who was 39 years his junior. He remained preoccupied with his first wife's death and tried to overcome his remorse by writing poetry. |
|||
In his later years, he kept a [[Wire Fox Terrier]] named Wessex, who was notoriously ill-tempered. Wessex's grave stone can be found on the Max Gate grounds.<ref>[https://www.theguardian.com/books/2006/sep/30/biography.thomashardy “At home with the wizard”] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180217082546/https://www.theguardian.com/books/2006/sep/30/biography.thomashardy |date=17 February 2018 }}. The Guardian, Retrieved 10 July 2019</ref><ref name="BBC100304">{{cite web |url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/wiltshire/entertainment/days_out/thomas_hardy_stourhead.shtml |title=Wiltshire Days Out – Thomas Hardy at Stourhead |publisher=BBC |access-date=19 May 2014 |archive-date=9 March 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120309014751/http://www.bbc.co.uk/wiltshire/entertainment/days_out/thomas_hardy_stourhead.shtml |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
Hardy's cottage at [[Bockhampton]] and Max Gate in [[Dorchester]] are owned by the [[National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty|National Trust]]. |
|||
In 1910, Hardy had been appointed a Member of the [[Order of Merit]] and was also for the first time nominated for the [[Nobel Prize in Literature]]. He was nominated again for the prize 11 years later and received a total of 25 nominations until 1927.<ref>{{London Gazette |issue=28393 |date=8 July 1910 |page=4857}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.nobelprize.org/nomination/archive/show_people.php?id=3892 |title=Nomination Database |date=April 2020 |access-date=14 June 2017 |archive-date=23 September 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170923194359/https://www.nobelprize.org/nomination/archive/show_people.php?id=3892 |url-status=live }}</ref> He was at least once, in 1923, one of the final candidates for the prize, but was not awarded.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Asaid |first=Alan |date=11 December 2012 |title=Yeats och Nobelpriset |url=https://www.kulturdelen.com/2012/12/11/yeats-och-nobelpriset/ |publisher=kulturdelen.com |language=sv}}</ref> |
|||
==Religious beliefs== |
|||
=== Hardy and the theatre === |
|||
Hardy's religious life seems to have mixed [[agnosticism]] and [[spiritism]]. Once, when asked in correspondence by a clergyman about the question of reconciling the horrors of pain with the goodness of a loving God, Hardy replied, |
|||
Hardy's interest in the theatre dated from the 1860s. He corresponded with various would-be adapters over the years, including [[Robert Louis Stevenson]] in 1886 and [[Jack Grein]] and Charles Jarvis in the same decade.<ref>{{Cite book|title=Thomas Hardy on Stage|last=Wilson|first=Keith|publisher=The Macmillan Press|year=1995|isbn=9780333598856|pages=29}}</ref> Neither adaptation came to fruition, but Hardy showed he was potentially enthusiastic about such a project. One play that was performed, however, caused him a certain amount of pain. His experience of the controversy and lukewarm critical reception that had surrounded his and [[J. Comyns Carr|Comyns Carr]]'s adaptation of ''[[Far from the Madding Crowd]]'' in 1882 left him wary of the damage that adaptations could do to his literary reputation. So, in 1908, he so readily and enthusiastically became involved with a local amateur group, at the time known as the Dorchester Dramatic and Debating Society, but that would become [[the Hardy Players]]. His reservations about adaptations of his novels meant he was initially at some pains to disguise his involvement in the play.<ref>Wilson, Keith (1995). ''Thomas Hardy on Stage''. The Macmillan Press. p. 60. {{ISBN|9780333598856}}</ref> However, the international success<ref>Evans, Harold (1908). "A Souvenir of the Performances of the Play adapted from Mr. Thos. Hardy's Novel 'The Trumpet Major'". The Dorchester Debating and Dramatic Society.</ref> of the play, ''[[The Trumpet-Major|The Trumpet Major]]'', led to a long and successful collaboration between Hardy and the Players over the remaining years of his life. Indeed, his play ''The Famous Tragedy of the Queen of Cornwall at [[Tintagel]] in [[Lyonnesse]]'' (1923) was written to be performed by the Hardy Players.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Dean|first=Andrew R|date=February 1993|title=The Sources of The Famous Tragedy of the Queen of Cornwall|url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/45274094|journal=Thomas Hardy Journal, the|volume=9|issue=1|pages=76–89|jstor=45274094|via=JSTOR}}</ref> |
|||
<blockquote>"Mr. Hardy regrets that he is unable to offer any hypothesis which would reconcile the existence of such evils as Dr. Grosart describes with the idea of omnipotent goodness. Perhaps Dr. Grosart might be helped to a provisional view of the universe by the recently published Life of Darwin, and the works of Herbert Spencer, and other agnostics."<ref>Ellman, Richard & O'Clair, Robert (eds.) 1988. "Thomas Hardy" in The Norton Anthology of Modern Poetry, Norton, New York.</ref></blockquote> |
|||
=== Later years === |
|||
Nevertheless, Hardy frequently conceived of and wrote about supernatural forces that control the universe, more through indifference or caprice than any firm will. Also, Hardy showed in his writing some degree of fascination with ghosts and spirits.<ref>Ellman, Richard & O'Clair, Robert (eds.) 1988. "Thomas Hardy" in The Norton Anthology of Modern Poetry, Norton, New York.</ref> Despite these sentiments, Hardy retained a strong emotional attachment to the Christian liturgy and church rituals, particularly as manifested in rural communities, that had been such a formative influence in his early years. Some attributed the bleak outlook of many of his novels as reflecting his view of the absence of [[God]]. |
|||
[[File:Florence Hardy at the seaside 1915.jpg|thumb|200px|Florence Hardy at the seashore, 1915]] |
|||
From the 1880s, Hardy became increasingly involved in campaigns to save ancient buildings from destruction, or destructive modernisation, and he became an early member of the [[Society for the Protection of Ancient Buildings]]. His correspondence refers to his unsuccessful efforts to prevent major alterations to the parish church at Puddletown, close to his home at Max Gate. He became a frequent visitor at [[Athelhampton House]], which he knew from his teenage years, and in his letters he encouraged the owner, Alfred Cart de Lafontaine, to conduct the restoration of that building in a sensitive way. |
|||
== Novels== |
|||
Hardy's work takes place in the "partly-real, partly-dream" county of [[Thomas Hardy's Wessex|Wessex]], which preserves the name of the [[Anglo-Saxon England|Anglo-Saxon]] kingdom that existed in the area. The landscape was modelled on the real counties of [[Berkshire]], [[Devon]], [[Dorset]], [[Hampshire]], [[Somerset]] and [[Wiltshire]], with fictional places based on real locations. He captured the epoch just before the railways and the [[industrial revolution]] changed the English countryside. His works are pessimistic and bitterly [[irony|ironic]], and his writing is rough but capable of immense power. Hardy had an eye for poignant detail, such as the spreading bloodstain on the ceiling at the end of ''[[Tess of the d'Urbervilles]]'' and [[Jude the Obscure|little Jude's]] suicide note; he kept clippings from newspaper reports of real events and used them as details in his novels. |
|||
In 1914, Hardy was one of fifty-three leading British authors—including [[H. G. Wells]], [[Rudyard Kipling]] and Sir [[Arthur Conan Doyle]]—who signed their names to the "Authors' Declaration", justifying Britain's involvement in the [[First World War]]. This manifesto declared that the German invasion of Belgium had been a brutal crime, and that Britain "could not without dishonour have refused to take part in the present war."<ref>{{cite news |title=1914 Authors' Manifesto Defending Britain's Involvement in WWI, Signed by H.G. Wells and Arthur Conan Doyle |url=https://slate.com/human-interest/2014/10/british-authors-and-wwi-propaganda-manifesto-signed-by-h-g-wells-arthur-conan-doyle-rudyard-kipling.html |access-date=27 February 2020 |work=Slate |archive-date=27 February 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200227070407/https://slate.com/human-interest/2014/10/british-authors-and-wwi-propaganda-manifesto-signed-by-h-g-wells-arthur-conan-doyle-rudyard-kipling.html |url-status=live }}</ref> Hardy was horrified by the destruction caused by the war, pondering that "I do not think a world in which such fiendishness is possible to be worth the saving" and "better to let western 'civilization' perish, and let the black and yellow races have a chance."<ref name="Sherman">{{cite book |last=Sherman |first=George William |title=The Pessimism of Thomas Hardy |date=1976 |publisher=Fairleigh Dickinson Univ Press |page=447}}</ref> He wrote to [[John Galsworthy]] that "the exchange of international thought is the only possible salvation for the world."<ref name="Sherman"/> |
|||
Hardy's first [[novel]], ''[[The Poor Man and the Lady]]'', finished by [[1867]], failed to find a publisher and Hardy destroyed the manuscript. Only parts of the novel remain. He was encouraged to try again by his mentor and friend, Victorian poet and novelist [[George Meredith]]. ''[[Desperate Remedies]]'' ([[1871]]) and ''[[Under the Greenwood Tree]]'' ([[1872]]) were published anonymously. In [[1873]] ''[[A Pair of Blue Eyes]]'', a story drawing on Hardy's courtship of his first wife, was published under his own name. |
|||
Hardy became ill with [[pleurisy]] in December 1927 and died at [[Max Gate]] just after 9 pm on 11 January 1928, having dictated his final poem to his wife on his deathbed; the cause of death was cited, on his death certificate, as "cardiac syncope", with "old age" given as a contributory factor. His funeral was on 16 January at [[Westminster Abbey]], and it proved a controversial occasion because Hardy had wished for his body to be interred at Stinsford in the same grave as his first wife, Emma. His family and friends concurred; however, his executor, Sir [[Sydney Carlyle Cockerell]], insisted that he be placed in the abbey's famous [[Poets' Corner]]. A compromise was reached whereby his heart was buried at Stinsford with Emma, and his ashes in Poets' Corner.<ref>{{cite book |author=Bradford, Charles Angell |author-link=Charles Angell Bradford |title=Heart Burial |year=1933 |publisher=Allen & Unwin |location=London |isbn=978-1-162-77181-6 |page=246}}</ref> Hardy's estate at death was valued at [[Pound sterling|£]]95,418 ({{inflation|UK|95418|1928|fmt=eq|cursign=£|r=-5}}).<ref>From Probate Index for 1928: "Hardy O. M. Thomas of Max Gate Dorchester Dorsetshire died 11 January 1928 Probate London 22 February to Lloyds Bank Limited Effects £90707 14s 3d Resworn £95418 3s 1d."</ref> |
|||
Hardy said that he first introduced [[Thomas Hardy's Wessex|Wessex]] in ''[[Far from the Madding Crowd]]'' ([[1874]]), his next (and first important) novel. It was successful enough for Hardy to give up architectural work and pursue a literary career. Over the next twenty-five years Hardy produced ten more novels. He himself classified his finest prose work as "Novels of Character and Environment". Hardy was a gloomy [[pessimism|pessimist]] who emphasized the impersonal and, generally, negative powers of fate over the mainly working class people he represented in his novels. |
|||
Shortly after Hardy's death, the executors of his estate burnt his letters and notebooks, but twelve notebooks survived, one of them containing notes and extracts of newspaper stories from the 1820s, and research into these has provided insight into how Hardy used them in his works. The opening chapter of ''The Mayor of Casterbridge'', for example, written in 1886, was based on press reports of wife-selling.<ref name="BBC200803">{{cite web |url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/homeground/archive/2003/thomas_hardy.shtml |title=Homeground: Dead man talking |date=20 August 2003 |work=BBC Online |access-date=2006-08-12 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20040831225219/http://www.bbc.co.uk/homeground/archive/2003/thomas_hardy.shtml |archive-date=31 August 2004}}</ref> In the year of his death Mrs Hardy published ''The Early Life of Thomas Hardy, 1841–1891'', compiled largely from contemporary notes, letters, diaries and biographical memoranda, as well as from oral information in conversations extending over many years. |
|||
The Hardys moved from [[London]] to [[Yeovil]] and then to [[Sturminster Newton]], where he wrote ''[[The Return of the Native]]'' ([[1878]]). In [[1885]], they moved for a last time, to [[Max Gate]], a house outside Dorchester designed by Hardy and built by his brother. There he wrote ''[[The Mayor of Casterbridge]]'' ([[1886]]), ''[[The Woodlanders]]'' ([[1887]]) and ''[[Tess of the d'Urbervilles]]'' ([[1891]]), the last of which attracted criticism for its sympathetic portrayal of a "fallen woman" and was initially refused publication. Its subtitle, ''A Pure Woman: Faithfully Narrated'', was intended to raise the eyebrows of the [[Victorian era|Victorian]] [[middle-class]]es. |
|||
Hardy's work was admired by many younger writers, including [[D. H. Lawrence]],<ref>{{Citation |title=Study of Thomas Hardy and other essays |orig-year=1914 |editor-first=Bruce |editor-last=Steele |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=1985 |isbn=0-521-25252-0 |chapter=Literary criticism and metaphysics}}.</ref> [[John Cowper Powys]] and [[Virginia Woolf]].<ref>"The Novels of Thomas Hardy", ''The Common Reader'', 2nd series.</ref> In his autobiography ''[[Good-Bye to All That]]'' (1929), [[Robert Graves]] recalls meeting Hardy in Dorset in the early 1920s and how Hardy received him and his new wife warmly, and was encouraging about his work. |
|||
''[[Jude the Obscure]]'', published in [[1895]], met with even stronger negative outcries from the [[Victorian era|Victorian]] public for its frank treatment of sex, and was often referred to as "Jude the Obscene". Heavily criticized for its apparent attack on the institution of marriage, the book caused further strain on Hardy's already difficult marriage because Emma Hardy was concerned that ''Jude the Obscure'' would be read as being autobiographical. Some booksellers sold the novel in brown paper bags, and the [[Bishop of Wakefield]] is reputed to have burnt a copy.<ref name="BBC-2" /> |
|||
Hardy's [[Thomas Hardy's Cottage|birthplace in Bockhampton]] and his house [[Max Gate]], both in Dorchester, are owned by the [[National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty|National Trust]]. |
|||
Despite this criticism, Hardy had become a celebrity in English literature by the [[1900s]], with several blockbuster novels under his belt, yet he felt disgust at the public reception of two of his greatest works. He gave up writing novels altogether. Several critics have commented, however, that there was very little left for Hardy to write,{{Fact|date=February 2007}} having creatively exhausted the increasingly fatalistic tone of his novels. |
|||
== |
==Novels== |
||
[[File:Thomas Hardy's Cottage, Bockhampton, Dorset.jpg|thumb|Thomas Hardy's [[Thomas Hardy's Cottage|birthplace and cottage]] at Higher Bockhampton, where ''[[Under the Greenwood Tree]]'' and ''[[Far from the Madding Crowd]]'' were written]] |
|||
:''For the full text of several poems, see the [[Thomas Hardy#External links|External links]] section'' |
|||
[[File:Thomas Hardy Locations, Tess of the Durbervilles (1) - geograph.org.uk - 707277.jpg|thumb|View of the [[River Frome, Dorset|River Frome]] from the bridge at [[Lower Bockhampton]]. In ''[[Tess of the d'Urbervilles]]'' the lowland vale of the river is described as the Vale of the Great Dairies, in comparison to Tess's home, the fertile [[Vale of Blackmore]], which is the Vale of Little Dairies.]] |
|||
In [[1898]] Hardy published his first volume of poetry, ''[[Wessex Poems]]'', a collection of poems written over 30 years. Hardy claimed poetry as his first love, and published collections until his death in [[1928]]. Although not as well received by his contemporaries as his novels, Hardy's poetry has been applauded considerably in recent years, in part because of the influence on [[Philip Larkin]]. However, critically it is still not regarded as highly as his prose. |
|||
Hardy's first novel, ''[[The Poor Man and the Lady]]'', finished by 1867, failed to find a publisher. He then showed it to his mentor and friend, the Victorian poet and novelist [[George Meredith]], who felt that ''The Poor Man and the Lady'' would be too politically controversial and might damage Hardy's ability to publish in the future. So Hardy followed his advice and he did not try further to publish it. He subsequently destroyed the manuscript, but used some of the ideas in his later work.<ref name="Bullen2013">{{cite book|author=J. B. Bullen|title=Thomas Hardy: The World of his Novels|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=8aX0AgAAQBAJ&pg=PT143|date=24 June 2013|publisher=Frances Lincoln|isbn=978-1-78101-122-5|page=143}}</ref> In his recollections in ''Life and Work'', Hardy described the book as "socialistic, not to say revolutionary; yet not argumentatively so."<ref>{{cite book |last=Widdowson |first=Peter |title=Thomas Hardy |date=2018 |publisher=Oxford University Press |page=27}}</ref> |
|||
Most of his poems deal with themes of disappointment in love and life, and mankind's long struggle against indifference to human suffering. Some, like ''The Darkling Thrush'' and ''An August Midnight'', appear as poems about writing poetry, because the nature mentioned in them gives Hardy the inspiration to write those. A vein of regret tinges his often seemingly banal themes. His compositions range in style from the three-volume epic [[closet drama]] ''[[The Dynasts]]'' to smaller, and often hopeful or even cheerful ballads of the moment such as the little-known ''The Children and Sir Nameless'', a comic poem inspired by the tombs of the Martyns, builders of [[Athelhampton]]. |
|||
After he abandoned his first novel, Hardy wrote two new ones that he hoped would have more commercial appeal, ''[[Desperate Remedies]]'' (1871) and ''[[Under the Greenwood Tree]]'' (1872), both of which were published anonymously; it was while working on the latter that he met Emma Gifford, who would become his wife.<ref name="Bullen2013"/> In 1873 ''[[A Pair of Blue Eyes]]'', a novel drawing on Hardy's courtship of Emma, was published under his own name. A plot device popularised by [[Charles Dickens]], the term "[[cliffhanger]]" is considered to have originated with the serialised version of ''A Pair of Blue Eyes'' (published in ''[[William Tinsley (publisher)|Tinsley's Magazine]]'' between September 1872 and July 1873) in which Henry Knight, one of the protagonists, is left literally hanging off a cliff.<ref name="Hardy2013">{{cite book|author=Thomas Hardy|title=Delphi Complete Works of Thomas Hardy (Illustrated)|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=N1EbAgAAQBAJ&pg=PT570|date=17 November 2013|publisher=Delphi Classics|isbn=978-1-908909-17-6|pages=570–|access-date=16 October 2016|archive-date=19 August 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200819150410/https://books.google.com/books?id=N1EbAgAAQBAJ&pg=PT570|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>Emily Nussbaum. {{cite magazine |date=10 July 2019 |title=The curious staying power of the cliffhanger. |url=https://www.newyorker.com/magazine/2012/07/30/tune-in-next-week |magazine=The New Yorker}}</ref> Elements of Hardy's fiction reflect the influence of the commercially successful sensation fiction of the 1860s, particularly the legal complications in novels such as ''Desperate Remedies'' (1871), ''Far from the Madding Crowd'' (1874) and ''Two on a Tower'' (1882).<ref>Trish Ferguson, ''Thomas Hardy's Legal Fictions'', Edinburgh University Press, 2013.</ref> |
|||
Composer [[Lee Hoiby]]'s setting of "The Darkling Thrush" became the basis of the [[multimedia]] opera ''Darkling''. Other composers who set Hardy's text to music include [[Gerald Finzi]], who produced six song-cycles for poems by Hardy, and [[Benjamin Britten]], who based his song-cycle ''[[Winter Words (song cycle)|Winter Words]]'' on Hardy's poetry. [[Ralph Vaughan Williams]] and [[Gustav Holst]] also set texts by Hardy; Holst also based one of his last orchestral works, ''[[Egdon Heath]]'', on Hardy's work. It is said to be Holst's masterpiece. The poem was also set to music by Timothy Takach for a capella choir in 2005. |
|||
In ''[[Far from the Madding Crowd]]'', Hardy first introduced the idea of calling the region in the west of England, where his novels are set, [[Thomas Hardy's Wessex|Wessex]]. Wessex had been the name of an early [[Saxon]] kingdom, in approximately the same part of England. ''Far from the Madding Crowd'' was successful enough for Hardy to give up architectural work and pursue a literary career. Over the next 25 years, Hardy produced 10 more novels. |
|||
==Works== |
|||
Subsequently, Hardy moved from London to [[Yeovil]], and then to [[Sturminster Newton]], where he wrote ''[[The Return of the Native]]'' (1878).<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.dorsetlife.co.uk/2013/06/curiosities-of-sturminster-newton/|title=Curiosities of Sturminster Newton – Dorset Life – The Dorset Magazine|website=dorsetlife.co.uk|access-date=9 November 2017|archive-date=10 November 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171110061814/http://www.dorsetlife.co.uk/2013/06/curiosities-of-sturminster-newton/|url-status=live}}</ref> In 1880, Hardy published his only historical novel, ''[[The Trumpet-Major]]''. A further move to Wimborne saw Hardy write ''[[Two on a Tower]]'', published in 1882, a romance story set in the world of astronomy. Then in 1885, they moved for the last time, to [[Max Gate]], a house outside Dorchester designed by Hardy and built by his brother. There he wrote ''[[The Mayor of Casterbridge]]'' (1886), ''[[The Woodlanders]]'' (1887) and ''[[Tess of the d'Urbervilles]]'' (1891), the last of which attracted criticism for its sympathetic portrayal of a "fallen woman", and initially it was refused publication. Its subtitle, ''A Pure Woman: Faithfully Presented'', was intended to raise the eyebrows of the Victorian middle classes. |
|||
'''Prose''' |
|||
[[File:Thomas Hardy Locations, Return of the Native - geograph.org.uk - 786542.jpg|thumb|A major location of ''[[The Return of the Native]]'' as part of Hardy's fictional [[Egdon Heath]]]] |
|||
''[[Jude the Obscure]]'', published in 1895, met with an even stronger negative response from the Victorian public because of its controversial treatment of sex, religion and marriage. Its apparent attack on the institution of marriage caused strain on Hardy's already difficult marriage because Emma Hardy was concerned that ''Jude the Obscure'' would be read as autobiographical. Some booksellers sold the novel in brown paper bags, and [[Walsham How]], the [[Bishop of Wakefield (diocese)|Bishop of Wakefield]], is reputed to have burnt his copy.<ref name="BBC200803"/> In his postscript of 1912, Hardy humorously referred to this incident as part of the career of the book: "After these [hostile] verdicts from the press its next misfortune was to be burnt by a bishop – probably in his despair at not being able to burn me".<ref>{{cite book |title= Jude the Obscure |last= Hardy |first= Thomas |year= 1998 |publisher= Penguin Classics |isbn= 0-14-043538-7 |page= 466 |url= https://books.google.com/books?id=txZevBW0iX0C |access-date= 16 October 2016 |archive-date= 15 September 2022 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20220915014720/https://books.google.com/books?id=txZevBW0iX0C |url-status= live }}</ref> Despite this, Hardy had become a celebrity by the 1900s, but some argue that he gave up writing novels because of the criticism of both ''Tess of the d'Urbervilles'' and ''Jude the Obscure''.<ref name="English Literature 2000">"Thomas Hardy", ''The Norton Anthology of English Literature'', 7th edition, vol. 2. New York: W.W. Norton, 2000, p.1916.</ref> ''[[The Well-Beloved]]'', first serialised in 1892, was published in 1897. |
|||
Hardy divided his novels and collected short stories into three classes: |
|||
==Literary themes== |
|||
'''Novels of Character and Environment''' |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
| align = left |
|||
| direction = vertical |
|||
| header = |
|||
| width = 156 |
|||
| image1 = Thomas Hardy Vanity Fair 1892-06-04.jpg |
|||
| width1 = |
|||
| alt1 = |
|||
| caption1 = Caricature of Hardy in ''[[Vanity Fair (British magazine)|Vanity Fair]]'', 4 June 1892 |
|||
| image2 = Thomas Hardy by William Strang 1893.jpg |
|||
| width2 = |
|||
| alt2 = |
|||
| caption2 = Hardy painted by [[William Strang]], 1893 |
|||
}} |
|||
Considered a Victorian realist, Hardy examines the social constraints on the lives of those living in [[Victorian England]], and criticises those beliefs, especially those relating to marriage, education and religion, that limited people's lives and caused unhappiness. Such unhappiness, and the suffering it brings, is seen by poet [[Philip Larkin]] as central in Hardy's works: |
|||
{{quote|What is the intensely maturing experience of which Hardy's modern man is most sensible? In my view it is suffering, or sadness, and extended consideration of the centrality of suffering in Hardy's work should be the first duty of the true critic for which the work is still waiting [...] Any approach to his work, as to any writer's work, must seek first of all to determine what element is peculiarly his, which imaginative note he strikes most plangently, and to deny that in this case it is the sometimes gentle, sometimes ironic, sometimes bitter but always passive apprehension of suffering is, I think, wrong-headed.<ref>Larkin, Philip 1983, "Wanted: Good Hardy Critic" in ''Required Writing'', London: [[Faber and Faber]].</ref>}} |
|||
*''[[The Poor Man and the Lady]]'' ([[1867]], unpublished and lost) |
|||
*''[[Under the Greenwood Tree]]'' ([[1872]]) |
|||
*''[[Far from the Madding Crowd]]'' ([[1874]]) |
|||
*''[[The Return of the Native]]'' ([[1878]]) |
|||
*''[[The Mayor of Casterbridge]]'' ([[1886]]) |
|||
*''[[The Woodlanders]]'' ([[1887]]) |
|||
*''[[Wessex Tales]]'' ([[1888]], a collection of short stories) |
|||
*''[[Tess of the d'Urbervilles]]'' ([[1891]]) |
|||
*''[[Life's Little Ironies]]'' ([[1894]], a collection of short stories) |
|||
*''[[Jude the Obscure]]'' ([[1895]]) |
|||
In ''Two on a Tower'', for example, Hardy takes a stand against these rules of society with a story of love that crosses the boundaries of class. The reader is forced to reconsider the conventions set up by society for the relationships between men and women. Nineteenth-century society had conventions, which were enforced. In this novel Swithin St Cleeve's idealism pits him against such contemporary social constraints. |
|||
'''Romances and Fantasies''' |
|||
{{quote|In a novel structured around contrasts, the main opposition is between Swithin St Cleeve and Lady Viviette Constantine, who are presented as binary figures in a series of ways: aristocratic and lower class, youthful and mature, single and married, fair and dark, religious and agnostic...she [Lady Viviette Constantine] is also deeply conventional, absurdly wishing to conceal their marriage until Swithin has achieved social status through his scientific work, which gives rise to uncontrolled ironies and tragic-comic misunderstandings.<ref>Geoffrey Harvey, ''Thomas Hardy: The Complete Critical Guide to Thomas Hardy.'' New York: Routledge, 2003, p.108.</ref>}} |
|||
*''[[A Pair of Blue Eyes]]'' ([[1873]]) |
|||
*''[[The Trumpet-Major]]'' ([[1880]]) |
|||
*''[[Two on a Tower]]'' ([[1882]]) |
|||
*''[[A Group of Noble Dames]]'' ([[1891]], a collection of short stories) |
|||
*''[[The Well-Beloved]]'' ([[1897]]) (first published as a serial from [[1892]]). |
|||
Fate or chance is another important theme. Hardy's characters often encounter crossroads on a journey, a junction that offers alternative physical destinations but which is also symbolic of a point of opportunity and transition, further suggesting that fate is at work. ''Far from the Madding Crowd'' is an example of a novel in which chance has a major role: "Had Bathsheba not sent the valentine, had Fanny not missed her wedding, for example, the story would have taken an entirely different path."<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.enotes.com/twentieth-century-criticism/far-from-madding-crowd-thomas-hardy |title=Far from the Madding Crowd, Thomas Hardy – Introduction (Twentieth-Century Literary Criticism. Ed. Linda Pavlovski. Vol. 153. Gale Group, Inc.,) |publisher=Enotes.com |access-date=7 September 2009 |archive-date=15 January 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100115210245/http://www.enotes.com/twentieth-century-criticism/far-from-madding-crowd-thomas-hardy |url-status=live }}</ref> Indeed, Hardy's main characters often seem to be held in fate's overwhelming grip. |
|||
'''Novels of Ingenuity''' |
|||
==Poetry== |
|||
*''[[Desperate Remedies]]'' ([[1871]]) |
|||
[[File:Thomas Hardy by Walter William Ouless.jpg|thumb|upright|Thomas Hardy by [[Walter William Ouless]], 1922]] |
|||
*''[[The Hand of Ethelberta]]'' ([[1876]]) |
|||
In 1898, Hardy published his first volume of poetry, ''[[Wessex Poems]]'', a collection of poems written over 30 years. While some suggest that Hardy gave up writing novels following the harsh criticism of ''Jude the Obscure'' in 1896, the poet [[C. H. Sisson]] calls this "hypothesis" "superficial and absurd".<ref name="English Literature 2000"/><ref>"Introduction" to the Penguin edition of ''Jude the Obscure'' (1978). Harmondsworth: Penguin Books, 1984, p.13.</ref> In the twentieth century Hardy published only poetry. |
|||
*''[[A Laodicean]]'' ([[1881]]) |
|||
Thomas Hardy published ''[[Poems of the Past and the Present]]'' in 1901, which contains "[[The Darkling Thrush]]" (originally titled "The Century's End"), one of his best known poems about the [[turn of the century]].<ref>{{Cite news |last=Rumens |first=Carol |date=2009-12-28 |title=Poem of the week: The Darkling Thrush, by Thomas Hardy |language=en-GB |work=The Guardian |url=https://www.theguardian.com/books/booksblog/2009/dec/28/poem-of-the-week-the-darkling-thrush-thomas-hardy |access-date=2023-08-09 |issn=0261-3077}}</ref> |
|||
Hardy also produced a number of minor tales and a collaborative novel, ''The Spectre of the Real'' ([[1894]]). An additional short-story collection, beyond the ones mentioned above, is ''A Changed Man and Other Tales'' ([[1913]]). His works have been collected as the 24-volume Wessex Edition (1912-1913) and the 37-volume Mellstock Edition (1919-1920). His largely self-written biography appears under his second wife's name in two volumes from 1928-1930, as ''The Early Life of Thomas Hardy, 1840-1891'' and ''The Later Years of Thomas Hardy, 1892-1928'', now published in a critical one-volume edition as ''The Life and Work of Thomas Hardy'', edited by Michael Millgate (1984). |
|||
Thomas Hardy wrote in a great variety of poetic forms, including [[lyric poetry|lyrics]], [[ballad]]s, satire, [[dramatic monologue]]s and dialogue, as well as a three-volume epic closet drama ''[[The Dynasts]]'' (1904–08),<ref name="britannica1">{{cite encyclopedia|url=http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/255167/Thomas-Hardy |title=Thomas Hardy (British writer) – Encyclopædia Britannica |encyclopedia=Britannica.com |date=6 November 2013 |access-date=19 May 2014}}</ref> and though in some ways a very traditional poet, because he was influenced by folksong and ballads,<ref>"Thomas Hardy", ''The Bloomsbury Guide to English Literature'', ed. Marion Wynne Davies. New York: Prentice Hall, 1990, p.583.</ref> he "was never conventional," and "persistently experiment[ed] with different, often invented, stanza forms and metres,"<ref>''The Bloomsbury Guide'', p. 583.</ref> and made use of "rough-hewn rhythms and colloquial diction".<ref name="poets1">{{cite web |url=http://www.poets.org/poet.php/prmPID/110#sthash.STdc5gsw.dpuf |title=Thomas Hardy | Academy of American Poets |publisher=Poets.org |date=11 January 1928 |access-date=19 May 2014 |archive-date=14 April 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140414084147/http://www.poets.org/poet.php/prmPID/110#sthash.STdc5gsw.dpuf |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
'''Poetry''' (not a comprehensive list) |
|||
Hardy wrote a number of significant war poems that relate to both the [[Boer War]]s and [[World War I]], including "Drummer Hodge", "In Time of 'The Breaking of Nations'" and "[[The Man He Killed]]"; his work had a profound influence on other war poets such as [[Rupert Brooke]] and [[Siegfried Sassoon]].<ref name="Axelrod">{{cite web |last=Axelrod |first=Jeremy |url=http://www.poetryfoundation.org/bio/thomas-hardy |title=Thomas Hardy |publisher=The Poetry Foundation |access-date=19 May 2014 |archive-date=27 May 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140527112937/http://www.poetryfoundation.org/bio/thomas-hardy |url-status=live }}</ref> Hardy in these poems often used the viewpoint of ordinary soldiers and their colloquial speech.<ref name="Axelrod"/> A theme in the ''Wessex Poems'' is the long shadow that the [[Napoleonic Wars]] cast over the 19th century, as seen, for example, in "The Sergeant's Song" and "Leipzig".<ref name="Katherine Kearney Maynard 1991, pp. 8">Katherine Kearney Maynard, ''Thomas Hardy's Tragic Poetry: The Lyrics and The Dynasts''. Iowa City: University of Iowa Press, 1991, pp. 8–12.</ref> The Napoleonic War is the subject of ''The Dynasts''. |
|||
*''[[Wessex Poems and Other Verses]]'' ([[1898 in poetry|1898]]) |
|||
*''[[Poems of the Past and Present]]'' ([[1901 in poetry|1901]]) |
|||
*''[[The Dynasts|The Dynasts, Part 1]]'' ([[1904 in poetry|1904]]) |
|||
*''[[The Dynasts|The Dynasts, Part 2]]'' ([[1906 in poetry|1906]]) |
|||
*''[[The Dynasts|The Dynasts, Part 3]]'' ([[1908 in poetry|1908]]) |
|||
*''[[Time's Laughingstocks and Other Verses]]'' ([[1909 in poetry|1909]]) |
|||
*''[[Satires of Circumstance]]'' ([[1914 in poetry|1914]]) |
|||
*''[[Collected Poems (Thomas Hardy)|Collected Poems]]'' ([[1919 in poetry|1919]], part of the Mellstock Edition of his novels and poems) |
|||
*''[[Late Lyrics and Earlier with Many Other Verses]]'' ([[1921 in poetry|1922]]) |
|||
*''[[Human Shows, Far Phantasies, Songs and Trifles]]'' ([[1925 in poetry|1925]]) |
|||
*''[[Winter Words in Various Moods and Metres]]'' ([[1928 in poetry|1928]], published posthumously) |
|||
Some of Hardy's more famous poems are from ''[[Poems 1912–13]]'', which later became part of ''Satires of Circumstance'' (1914), written following the death of his wife Emma in 1912. They had been estranged for 20 years, and these lyric poems express deeply felt "regret and remorse".<ref name="Axelrod"/> Poems like "After a Journey", "The Voice" and others from this collection "are by general consent regarded as the peak of his poetic achievement".<ref name="britannica1"/> In a 2007 biography on Hardy, [[Claire Tomalin]] argues that Hardy became a truly great English poet after the death of his first wife Emma, beginning with these elegies, which she describes as among "the finest and strangest celebrations of the dead in English poetry."<ref>Tomalin, Claire. "Thomas Hardy." New York: Penguin, 2007.</ref> |
|||
'''Drama''' |
|||
*[[The Famous Tragedy of the Queen of Cornwall]] ([[1923 in literature|1923]]) |
|||
[[File:Thomas Hardy (1923 portrait).jpg|thumb|left|upright|A portrait of Thomas Hardy in 1923 by [[Reginald Eves]]]] |
|||
== Locations in novels == |
|||
Many of Hardy's poems deal with themes of disappointment in love and life, and "the perversity of fate", but the best of them present these themes with "a carefully controlled elegiac feeling".<ref>''The Norton Anthology of English Literature'', 7th edition, vol. 2, p. 1916.</ref> [[Irony]] is an important element in a number of Hardy's poems, including "The Man He Killed" and "Are You Digging on My Grave".<ref name="Katherine Kearney Maynard 1991, pp. 8"/> A few of Hardy's poems, such as "[[The Blinded Bird]]", a melancholy polemic against the sport of {{lang|nl|[[Vinkensport|vinkenzetting]]}}, reflect his firm stance against animal cruelty, exhibited in his [[Vivisection|antivivisectionist]] views and his membership in the [[Royal Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals]].<ref>{{cite book| url=https://archive.org/details/wakinggiantspres00schn_0 |
|||
[[Berkshire]] is ''North Wessex'', |
|||
| url-access=registration |
|||
[[Devon]] is ''Lower Wessex'', |
|||
| page=[https://archive.org/details/wakinggiantspres00schn_0/page/35 35] |
|||
[[Dorset]] is ''South Wessex'', |
|||
| quote=the blinded bird. |
|||
[[Somerset]] is ''Outer'' or ''Nether Wessex'', |
|||
|title=Waking Giants: The Presence of the Past in Modernism| year=1991 |
|||
[[Wiltshire]] is ''Mid-Wessex'', |
|||
| publisher=Oxford University Press |
|||
|author=Herbert N. Schneidau| isbn=978-0-19-506862-7 |
|||
|access-date=16 April 2008 }} (Google Books)</ref> |
|||
A number of notable English composers, including [[Gerald Finzi]],<ref>Song cycle ''[[Earth and Air and Rain]]'' (1936)</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.geraldfinzi.com/biography/ |title=Biography " Gerald Finzi Official Site |publisher=Geraldfinzi.com |date=27 September 1956 |access-date=19 May 2014 |archive-date=10 November 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171110023001/http://www.geraldfinzi.com/biography/ |url-status=live }}</ref> [[Benjamin Britten]],<ref>Song cycle ''[[Winter Words (song cycle)|Winter Words]]'' (1953)</ref> [[Ralph Vaughan Williams]],<ref>Cantata ''[[Hodie#VII: Song|Hodie]]'' (1954)</ref> and [[Gustav Holst]],<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.lieder.net/get_settings.html?ComposerId=1237 |title=Gustav Holst (Vocal Texts and Translations for Composer Gustav Holst) |publisher=LiederNet Archive |access-date=19 May 2014 |archive-date=14 September 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180914203708/http://www.lieder.net/get_settings.html?ComposerId=1237 |url-status=live }}</ref> set poems by Hardy to music. Holst also wrote the orchestral tone poem ''[[Egdon Heath (Holst)|Egdon Heath: A Homage to Thomas Hardy]]'' in 1927. |
|||
[[Bere Regis]] is ''King's-Bere'' of ''Tess'', |
|||
[[Bincombe|Bincombe Down]] cross roads is the scene of the military execution in ''A Melancholy Hussar''. It is a true story, the deserters from the German Legion were shot in [[1801]] and are recorded in the parish register. |
|||
[[Wool, Dorset|Bindon Abbey]] is where Clare carried her. |
|||
[[Bournemouth]] is ''Sandbourne'' of ''Hand of Ethelberta'' and ''[[Tess of the D'Urbervilles]]'', |
|||
[[Bridport]] is ''Port Bredy'', |
|||
[[Charborough House]] and its [[folly]] tower at {{coor dms|50|46|38.75|N|2|6|7.09|W|}} is the model for ''Welland House'' in the novel ''[[Two on a Tower]]''. |
|||
[[Corfe Castle]] is the ''Corvsgate-Castle'' of ''Hand of Ethelberta''. |
|||
[[Cranborne Chase]] is ''The Chase'' scene of Tess's seduction. (Note - [[Bowerchalke]] on Cranborne Chase at {{coor dms|51|0|30.75|N|1|59|18.30|W|}} was the film location for the great fire in [[John Schlesinger]]'s 1967 film [[Far from the Madding Crowd (1967 film)|Far from the Madding Crowd]].) |
|||
Although his poems were initially not as well received as his novels had been, Hardy is now recognised as one of the great poets of the 20th century, and his verse had a profound influence on later writers, including [[Robert Frost]], [[W. H. Auden]], [[Dylan Thomas]] and [[Philip Larkin]].<ref name="poets1"/> Larkin included 27 poems by Hardy compared with only nine by [[T. S. Eliot]] in his edition of ''[[The Oxford Book of Twentieth Century English Verse]]'' in 1973.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.poets.org/poet.php/prmPID/110 |title=Poetry.org |publisher=Poets.org |date=11 January 1928 |access-date=19 May 2014 |archive-date=14 April 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140414084147/http://www.poets.org/poet.php/prmPID/110 |url-status=live }}</ref> There were fewer poems by [[W. B. Yeats]].<ref>"Thomas Hardy", ''The Norton Anthology of English Literature'', 7th edition, vol.2, p. 1916.</ref> Poet-critic [[Donald Davie]]'s ''Thomas Hardy and English Poetry'' considers Hardy's contribution to ongoing poetic tradition at length and in creative depth. Davie's friend [[Thom Gunn]] also wrote on Hardy and acknowledged his stature and example. |
|||
[[Dorchester]] is ''[[Casterbridge]]'', the scene of ''[[Mayor of Casterbridge]]''. |
|||
[[Dunster Castle]] in [[Somerset]] is ''Castle De Stancy'' of ''A Laodicean''. |
|||
[[Fordington (liberty)|Fordington moor]] is ''Durnover moor'' and ''fields''. |
|||
[[Bere Regis|Greenhill Fair]] near [[Bere Regis]] is ''Woodbury Hill Fair'', |
|||
[[Lulworth Cove]] is ''Lulstead Cove'', |
|||
[[Marnhull]] is ''Marlott'' of ''[[Tess of the D'Urbervilles]]'', |
|||
[[Evershot|Melbury House]] near [[Evershot]] is ''Great Hintock Court'' in ''A Group of Noble Dames.'' |
|||
[[Minterne Magna|Minterne]] is ''Little Hintock'', |
|||
[[Owermoigne]] is ''Nether Moynton'' in ''Wessex Tales''. |
|||
==Religious beliefs== |
|||
[[Piddlehinton]] and [[River Piddle|Piddle Trenthide]] are the ''Longpuddle'' of ''A Few Crusted Characters''. |
|||
[[File:Thomas Hardy aged 70, by William Strang.jpg|thumb|upright|Thomas Hardy aged 70, by [[William Strang]]]]<!-- the source given at the uploaded page by [[User:Stephencdickson]] is "own work", which is obviously not so. The image medium and the current collection would be useful to know. Looks like an etching. --> |
|||
[[Puddletown]] Heath, [[Moreton]] Heath, [[Tincleton]] Heath and [[Bere Regis|Bere]] Heath are ''Egdon Heath''. |
|||
Hardy's family was [[Anglican]], but not especially devout. He was baptised at the age of five weeks and attended church, where his father and uncle contributed to music. He did not attend the local [[Church of England]] school, instead being sent to Mr Last's school, three miles away. As a young adult, he befriended [[Henry R. Bastow]] (a [[Plymouth Brethren]] man), who also worked as a pupil architect, and who was preparing for [[adult baptism]] in the [[Baptist Church]]. Hardy flirted with conversion, but decided against it.<ref>Claire Tomalin. ''Thomas Hardy, The Time Torn Man'' (Penguin, 2007), pp. 46–47.</ref> Bastow went to Australia and maintained a long correspondence with Hardy, but eventually Hardy tired of these exchanges and the correspondence ceased. This concluded Hardy's links with the Baptists. |
|||
[[Poole]] is ''Havenpool'' in ''Life's Little Ironies''. |
|||
[[Portland]] is the scene of ''The Pursuit of the Well-Beloved''. |
|||
[[Puddletown]] is ''Weatherbury'' in ''Far from the Madding Crowd'', |
|||
[[River Frome]] valley is the scene of ''Talbothays dairy'' in ''Tess''. |
|||
[[Salisbury]] is ''Melchester'' in ''On the Western Circuit'', ''Life's Little Ironies'' and ''Jude the Obscure'' etc. |
|||
[[Shaftesbury]] is ''Shaston'' in ''[[Tess of the D'Urbervilles]]'' and ''[[Jude the Obscure]]''. |
|||
[[Sherborne]] is ''Sherton-Abbas'', |
|||
[[Sherborne Castle]] is home of ''Lady Baxby'' in ''A Group of Noble Dames''. |
|||
[[Stonehenge]] is the scene of Tess's apprehension. |
|||
[[Sutton Poyntz]] is ''Overcombe''. |
|||
[[Swanage]] is the ''Knollsea'' of ''Hand of Ethelberta''. |
|||
[[Wantage]] is ''Alfredston'', of Jude the Obscure. [[Fawley, Berkshire]] is ''Marygreen'' of ''[[Jude the Obscure]]''. |
|||
[[Andover, Hampshire|Weyhill]] is ''Weydon Priors'', |
|||
[[Weymouth]] is ''Budmouth Regis'', the scene of ''Trumpet Major'' & portions of other novels; |
|||
[[Winchester]] is ''Wintoncester'' where Tess was executed. [[Wimborne]] is ''Warborne'' of ''[[Two on a Tower]]''. |
|||
[[Charminster|Wolfeton House]], near Dorchester is the scene of ''The Lady Penelope'' in ''a Group of Noble Dames''. |
|||
[[Wool, Dorset|Woolbridge]] old Manor House, close to Wool station, is the scene of Tess's confession and |
|||
The irony and struggles of life, coupled with his naturally curious mind, led him to question the traditional Christian view of God: |
|||
==Notes== |
|||
{{quote|The Christian God – the external personality – has been replaced by the intelligence of the First Cause...the replacement of the old concept of God as all-powerful by a new concept of universal consciousness. The 'tribal god, man-shaped, fiery-faced and tyrannous' is replaced by the 'unconscious will of the Universe' which progressively grows aware of itself and 'ultimately, it is to be hoped, sympathetic'.<ref>Wotton, G. (1985), ''Thomas Hardy: Towards A Materialist Criticism'', Lanham: [[Rowman & Littlefield]], p.36</ref>}} |
|||
Scholars have debated Hardy's religious leanings for years, often unable to reach a consensus. Once, when asked in correspondence by a clergyman, Dr. [[Alexander Balloch Grosart|A. B. Grosart]], about the question of reconciling the horrors of human and animal life with "the absolute goodness and non-limitation of God",<ref>Florence Emily Hardy, ''The Early Life of Thomas Hardy, 1840–1891'', p. 269</ref> Hardy replied, |
|||
<references/> |
|||
{{quote|Mr. Hardy regrets that he is unable to offer any hypothesis which would reconcile the existence of such evils as Dr. Grosart describes with the idea of omnipotent goodness. Perhaps Dr. Grosart might be helped to a provisional view of the universe by the recently published ''Life of Darwin'' and the works of [[Herbert Spencer]] and other agnostics.<ref name=norton/>}} |
|||
==References== |
|||
Hardy frequently conceived of, and wrote about, supernatural forces, particularly those that control the universe through indifference or caprice, a force he called The Immanent Will. He also showed in his writing some degree of fascination with ghosts and spirits.<ref name="norton">Ellman, Richard, & O'Clair, Robert (eds.) 1988. "Thomas Hardy" in ''The Norton Anthology of Modern Poetry'', Norton, New York.</ref> Even so, he retained a strong emotional attachment to the Christian liturgy and church rituals, particularly as manifested in rural communities, that had been such a formative influence in his early years, and Biblical references can be found woven throughout many of Hardy's novels. |
|||
* Armstrong, Tim. "Player Piano: Poetry and Sonic Modernity" in [http://www.press.jhu.edu/journals/modernism_modernity/index.html'' Modernism/Modernity''] 14.1 (January 2007), 1-19. |
|||
Hardy's friends during his apprenticeship to John Hicks included [[Horatio Mosley Moule|Horace Moule]] (one of the eight sons of [[Henry Moule]]) and the poet [[William Barnes]], both ministers of religion. Moule remained a close friend of Hardy's for the rest of his life, and introduced him to new scientific findings that cast doubt on literal interpretations of the Bible,<ref>{{cite web|title=Pearson Literature: Biography: Thomas Hardy|url=http://wps.ablongman.com/long_kennedy_lfpd_9/0,9130,1489987-,00.html|access-date=15 April 2008|archive-date=22 June 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130622162641/http://wps.ablongman.com/long_kennedy_lfpd_9/0,9130,1489987-,00.html|url-status=dead}}</ref> such as those of [[Gideon Mantell]]. Moule gave Hardy a copy of Mantell's book ''The Wonders of Geology'' (1848) in 1858, and Adelene Buckland has suggested that there are "compelling similarities" between the "cliffhanger" section from ''A Pair of Blue Eyes'' and Mantell's geological descriptions. It has also been suggested that the character of Henry Knight in ''A Pair of Blue Eyes'' was based on Horace Moule.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.19.bbk.ac.uk/index.php/19/article/viewFile/469/329 |title=Adelene Buckland: ''Thomas Hardy, Provincial Geology and the Material Imagination'' |access-date=10 December 2011 |archive-date=1 April 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110401090850/http://www.19.bbk.ac.uk/index.php/19/article/viewFile/469/329 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
{{multiple image |
|||
* Blunden, Edmund. ''Thomas Hardy.'' New York: St. Martin's, 1942. |
|||
| align = right |
|||
| direction = vertical |
|||
| width = 200 |
|||
| image1 = Kipling's grave in Poets Corner.png |
|||
| caption1 = Grave of Thomas Hardy's ashes in [[Westminster Abbey]] (foreground, next to that of [[Rudyard Kipling]]) |
|||
| image2 = Thomas Hardy's heart.JPG |
|||
| caption2 = Grave of Thomas Hardy's heart at [[Stinsford]] parish church |
|||
}} |
|||
Throughout his life, Hardy sought a rationale for believing in an afterlife or a timeless existence, turning first to spiritualists, such as [[Henri Bergson]], and then to [[Albert Einstein]] and [[J. M. E. McTaggart]], considering their philosophy on time and space in relation to immortality.<ref>Trish Ferguson. "Time's Renewal": Death and Immortality in Thomas Hardy's ''Emma poems'', ''Literature and Modern Time: Technological Modernity, Glimpses of Eternity, Experiments with Time'', Palgrave, 2020.</ref> |
|||
* Brennecke, Jr., Ernest. ''The Life of Thomas Hardy.'' New York: Greenberg, 1925. |
|||
==Locations in novels== |
|||
* Deacon, Lois and Terry Coleman. ''Providence and Mr. Hardy.'' London: Hutchinson, 1966. |
|||
Sites associated with Hardy's own life and which inspired the settings of his novels continue to attract literary tourists and casual visitors. For locations in Hardy's novels see: [[Thomas Hardy's Wessex]], and the Thomas Hardy's Wessex<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.st-andrews.ac.uk/~bp10/wessex/index.shtml |title=Thomas Hardy's Wessex |publisher=St-andrews.ac.uk |access-date=19 May 2014 |archive-date=28 February 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130228192011/http://www.st-andrews.ac.uk/~bp10/wessex/index.shtml |url-status=live }}</ref> research site, which includes maps.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.st-andrews.ac.uk/~bp10/wessex/evolution/maps/index.shtml |title=Thomas Hardy's Wessex: The Evolution of Wessex |publisher=St-andrews.ac.uk |access-date=19 May 2014 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130502070810/http://www.st-andrews.ac.uk/~bp10/wessex/evolution/maps/index.shtml |archive-date=2 May 2013}}</ref> |
|||
==Influence== |
|||
* Draper, Jo. ''Thomas Hardy: A Life in Pictures.'' Wimborne, Dorset: The Dovecote Press. |
|||
Hardy corresponded with and visited [[Charles George Milnes Gaskell|Lady Catherine Milnes Gaskell]] at [[Wenlock Abbey]] and many of Lady Catherine's books are inspired by Hardy, who was very fond of her.<ref>Gamble, Cynthia, 2015 Wenlock Abbey 1857–1919: A Shropshire Country House and the Milnes Gaskell Family, Ellingham Press.</ref> |
|||
[[D. H. Lawrence]]'s ''Study of Thomas Hardy'' (1914, first published 1936) indicates the importance of Hardy for him, even though this work is a platform for Lawrence's own developing philosophy rather than a more standard literary study. The influence of Hardy's treatment of character, and Lawrence's own response to the central [[metaphysic]] behind many of Hardy's novels, helped significantly in the development of ''[[The Rainbow]]'' (1915) and ''[[Women in Love]]'' (1920).<ref>Terry R. Wright. "Hardy's Heirs: D. H. Lawrence and John Cowper Powys" in ''A Companion to Thomas Hardy''. Chichester, Sussex: John Wiley, 2012.[https://books.google.com/books?id=xLP3sa-bnkoC&pg=PA1925] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210411132913/https://books.google.com/books?id=xLP3sa-bnkoC&pg=PA1925|date=11 April 2021}}</ref> |
|||
* Ellman, Richard & O'Clair, Robert (eds.) 1988. "Thomas Hardy" in ''The Norton Anthology of Modern Poetry'', Norton, New York. |
|||
''Wood and Stone'' (1915), the first novel by [[John Cowper Powys]], who was a contemporary of Lawrence, was "Dedicated with devoted admiration to the greatest poet and novelist of our age Thomas Hardy".<ref>Terry R. Wright. "Hardy's Heirs: D. H. Lawrence and John Cowper Powys"</ref> Powys's later novel ''[[Maiden Castle (novel)|Maiden Castle]]'' (1936) is set in [[Dorchester, Dorset|Dorchester]], which was Hardy's [[Casterbridge]], and was intended by Powys to be a "rival" to Hardy's ''[[The Mayor of Casterbridge]]''.<ref>Morine Krissdottir, ''Descents of Memory: The Life of John Cowper Powys''. (New York: Overlook Duckworth, 2007), p. 312.</ref> ''Maiden Castle'' is the last of Powys's so-called Wessex novels, ''[[Wolf Solent]]'' (1929), ''[[A Glastonbury Romance]]'' (1932) and ''[[Weymouth Sands]]'' (1934), which are set in Somerset and Dorset.<ref>Herbert Williams, ''John Cowper Powys''. (Bridgend, Wales: Seren, 1997), p. 94.</ref> |
|||
* Gatrell, Simon. ''Hardy the Creator: A Textual Biography.'' Oxford: Clarendon, 1988. |
|||
Hardy was clearly the starting point for the character of the novelist Edward Driffield in [[W. Somerset Maugham]]'s novel ''[[Cakes and Ale]]'' (1930).<ref>{{cite encyclopedia|title=Cakes and Ale|encyclopedia= Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online Academic Edition. Encyclopædia Britannica Inc.|year= 2015|access-date= 26 April 2015|url= http://academic.eb.com/EBchecked/topic/88658/Cakes-and-Ale}}</ref> Thomas Hardy's works also feature prominently in the American playwright [[Christopher Durang]]'s ''The Marriage of Bette and Boo'' (1985), in which a graduate thesis analysing ''[[Tess of the d'Urbervilles]]'' is interspersed with analysis of Matt's family's neuroses.<ref>Christopher Durang. ''The Marriage of Bette and Boo''. New York: Grove Press, 1987.[https://books.google.com/books?id=-z-ns9m7hTIC&pg=PA18] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220915014720/https://books.google.com/books?id=-z-ns9m7hTIC&pg=PA18|date=15 September 2022}}</ref> |
|||
* Gibson, James. ''Thomas Hardy: A Literary Life.'' London: Macmillan, 1996. |
|||
The [[symphonic poem]]s ''[[Mai-Dun]]'' by [[John Ireland (composer)|John Ireland]] (1921) and ''[[Egdon Heath (Holst)|Egdon Heath]]'' by [[Gustav Holst]] (1927) evoke the landscape of Hardy's novels. |
|||
* Gittings, Robert. ''Thomas Hardy's Later Years.'' Boston : Little, Brown, 1978. |
|||
Hardy has been a significant influence on Nigel Blackwell, frontman of the [[post-punk]] British rock band [[Half Man Half Biscuit]], who has often incorporated phrases (some obscure) by or about Hardy into his song lyrics.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.theguardian.com/theguardian/2001/jul/21/weekend7.weekend6 |title=Taking the biscuit |first=Kevin |last=Sampson |author-link=Kevin Sampson (writer) |newspaper=[[The Guardian]] |date=21 July 2001 |access-date=27 December 2019 |archive-date=27 December 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191227114855/https://www.theguardian.com/theguardian/2001/jul/21/weekend7.weekend6 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>See for example the song title "[[Thy Damnation Slumbereth Not]]", which is a quotation from Thomas Hardy's novel ''[[Tess of the d'Urbervilles]]'',{{cite book|url=http://www.victorianlondon.org/etexts/hardy/tess-0012.shtml|last=Hardy|first=Thomas|title=Tess of the d'Urbervilles|at=Chapter 12|year=1891|access-date=21 February 2015|archive-date=21 February 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150221154951/http://www.victorianlondon.org/etexts/hardy/tess-0012.shtml|url-status=live}} which is itself an adaptation of the [[Second Epistle of Peter]] at [[s:Bible (King James)/2 Peter#Chapter 2|2:3]]: "Their damnation slumbereth not".</ref> |
|||
* Gittings, Robert. ''Young Thomas Hardy.'' Boston : Little, Brown, 1975. |
|||
==Works== |
|||
* Gittings, Robert and Jo Manton. ''The Second Mrs Hardy.'' London: Heinemann, 1979. |
|||
[[File:Far-From-The-Madding-Crowd-1874-Title-Page.jpg|thumb|upright|The title page from a [[first edition]] of ''[[Far from the Madding Crowd]]'' (1874)]] |
|||
===Prose=== |
|||
* Halliday, F. E. ''Thomas Hardy: His Life and Work.'' Bath: Adams & Dart, 1972. |
|||
In 1912, Hardy divided his novels and collected short stories into three classes:<ref>{{cite book |last=Gilmore |first=Dehn |title=The Victorian Novel and the Space of Art: Fictional Form on Display |date=2014 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |page=207}}</ref> |
|||
====Novels of character and environment==== |
|||
* Hands, Timothy. ''Thomas Hardy : Distracted Preacher? : Hardy's religious biography and its influence on his novels.'' New York: St. Martin's Press, 1989. |
|||
* ''[[The Poor Man and the Lady]]'' (1867, unpublished and lost) |
|||
* ''[[Under the Greenwood Tree]]: A Rural Painting of the Dutch School'' (1872) |
|||
* ''[[Far from the Madding Crowd]]'' (1874) |
|||
* ''[[The Return of the Native]]'' (1878) |
|||
* ''[[The Mayor of Casterbridge]]: The Life and Death of a Man of Character'' (1886) |
|||
* ''[[The Woodlanders]]'' (1887) |
|||
* ''[[Wessex Tales]]'' (1888, a collection of short stories) |
|||
* ''[[Tess of the d'Urbervilles]]: A Pure Woman Faithfully Presented'' (1891) |
|||
* ''[[Life's Little Ironies]]'' (1894, a collection of short stories) |
|||
* ''[[Jude the Obscure]]'' (1895) |
|||
====Romances and fantasies==== |
|||
* Hardy, Evelyn. ''Thomas Hardy: A Critical Biography.'' London: Hogarth Press, 1954. |
|||
{{See|Romance (literary fiction)}} |
|||
* ''[[A Pair of Blue Eyes]]: A Novel'' (1873) |
|||
* Hardy, Florence Emily. ''The Early Life of Thomas Hardy, 1840-1891.'' London: Macmillan, 1928. |
|||
* ''[[The Trumpet-Major]]'' (1880) |
|||
* ''[[Two on a Tower]]: A Romance'' (1882) |
|||
* ''[[A Group of Noble Dames]]'' (1891, a collection of short stories) |
|||
* ''[[The Well-Beloved]]: A Sketch of a Temperament'' (1897) (first published as a serial from 1892) |
|||
====Novels of ingenuity==== |
|||
* Hardy, Florence Emily. ''The Later Years of Thomas Hardy, 1892-1928.'' London: Macmillan, 1930. |
|||
* ''[[Desperate Remedies]]: A Novel'' (1871) |
|||
* ''[[The Hand of Ethelberta]]: A Comedy in Chapters'' (1876) |
|||
* ''[[A Laodicean]]: A Story of To-day'' (1881) |
|||
====Other==== |
|||
Hardy also produced minor tales; one story, ''The Spectre of the Real'' (1894) was written in collaboration with [[Florence Henniker]].<ref>{{cite journal|title=Thomas Hardy And Florence Henniker: The Writing Of "The Spectre of the Real|first=Richard|last=Purdy|journal=Colby Library Quarterly|volume=1|issue=8|date=October 1944|pages=122–6|url=http://digitalcommons.colby.edu/cq/vol1/iss8/4/|access-date=7 September 2013|archive-date=24 May 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140524022702/http://digitalcommons.colby.edu/cq/vol1/iss8/4/|url-status=live}}</ref> An additional short-story collection, beyond the ones mentioned above, is ''[[A Changed Man and Other Tales]]'' (1913). His works have been collected as the 24-volume Wessex Edition (1912–13) and the 37-volume Mellstock Edition (1919–20). His largely self-written biography appears under his second wife's name in two volumes from 1928 to 1930, as ''The Early Life of Thomas Hardy, 1840–91'' and ''The Later Years of Thomas Hardy, 1892–1928'', now published in a critical one-volume edition as ''The Life and Work of Thomas Hardy'', edited by Michael Millgate (1984). |
|||
====Short stories==== |
|||
(with date of first publication) |
|||
* "How I Built Myself a House" (1865) |
|||
* "Destiny and a Blue Cloak" (1874) |
|||
* "The Thieves Who Couldn't Stop Sneezing" (1877) |
|||
* "The Duchess of Hamptonshire" (1878) (collected in ''A Group of Noble Dames'') |
|||
* "The Distracted Preacher" (1879) (collected in ''Wessex Tales'') |
|||
* "Fellow-Townsmen" (1880) (collected in ''Wessex Tales'') |
|||
* "The Honourable Laura" (1881) (collected in ''A Group of Noble Dames'') |
|||
* "What the Shepherd Saw" (1881) (collected in ''A Changed Man and Other Stories'') |
|||
* "A Tradition of Eighteen Hundred and Four" (1882) (collected in ''Life's Little Ironies'') |
|||
* "[[The Three Strangers]]" (1883) (collected in ''Wessex Tales'') |
|||
* "The Romantic Adventures of a Milkmaid" (1883) (collected in ''A Changed Man and Other Stories'') |
|||
* "Interlopers at the Knap" (1884) (collected in ''Wessex Tales'') |
|||
* "[[A Mere Interlude]]" (1885) (collected in ''A Changed Man and Other Stories'') |
|||
* "A Tryst at an Ancient Earthwork" (1885) (collected in ''A Changed Man and Other Stories'') |
|||
* "[[Alicia's Diary]]" (1887) (collected in ''A Changed Man and Other Stories'') |
|||
* "The Waiting Supper" (1887–88) (collected in ''A Changed Man and Other Stories'') |
|||
* "The Withered Arm" (1888) (collected in ''Wessex Tales'') |
|||
* "[[A Tragedy of Two Ambitions]]" (1888) (collected in ''Life's Little Ironies'') |
|||
* "The First Countess of Wessex" (1889) (collected in ''A Group of Noble Dames'') |
|||
* "Anna, Lady Baxby" (1890) (collected in ''A Group of Noble Dames'') |
|||
* "The Lady Icenway" (1890) (collected in ''A Group of Noble Dames'') |
|||
* "Lady Mottisfont" (1890) (collected in ''A Group of Noble Dames'') |
|||
* "The Lady Penelope" (1890) (collected in ''A Group of Noble Dames'') |
|||
* "The Marchioness of Stonehenge" (1890) (collected in ''A Group of Noble Dames'') |
|||
* "Squire Petrick's Lady" (1890) (collected in ''A Group of Noble Dames'') |
|||
* "Barbara of the House of Grebe" (1890) (collected in ''A Group of Noble Dames'') |
|||
* "The Melancholy Hussar of The German Legion" (1890) (collected in ''Life's Little Ironies'') |
|||
* "Absent-Mindedness in a Parish Choir" (1891) (collected in ''Life's Little Ironies'') |
|||
* "The Winters and the Palmleys" (1891) (collected in ''Life's Little Ironies'') |
|||
* "For Conscience' Sake" (1891) (collected in ''Life's Little Ironies'') |
|||
* "Incident in the Life of Mr. George Crookhill" (1891) (collected in ''Life's Little Ironies'') |
|||
* "The Doctor's Legend" (1891) |
|||
* "Andrey Satchel and the Parson and Clerk" (1891) (collected in ''Life's Little Ironies'') |
|||
* "The History of the Hardcomes" (1891) (collected in ''Life's Little Ironies'') |
|||
* "Netty Sargent's Copyhold" (1891) (collected in ''Life's Little Ironies'') |
|||
* "On the Western Circuit" (1891) (collected in ''Life's Little Ironies'') |
|||
* "A Few Crusted Characters: Introduction" (1891) (collected in ''Life's Little Ironies'') |
|||
* "The Superstitious Man's Story" (1891) (collected in ''Life's Little Ironies'') |
|||
* "Tony Kytes, the Arch-Deceiver" (1891) (collected in ''Life's Little Ironies'') |
|||
* "To Please His Wife" (1891) (collected in ''Life's Little Ironies'') |
|||
* "The Son's Veto" (1891) (collected in ''Life's Little Ironies'') |
|||
* "Old Andrey's Experience as a Musician" (1891) (collected in ''Life's Little Ironies'') |
|||
* "[[Our Exploits At West Poley]]" (1892–93) |
|||
* "Master John Horseleigh, Knight" (1893) (collected in ''A Changed Man and Other Stories'') |
|||
* "[[The Fiddler of the Reels]]" (1893) (collected in ''Life's Little Ironies'') |
|||
* "An Imaginative Woman" (1894) (collected in ''Wessex Tales'', 1896 edition) |
|||
* "The Spectre of the Real" (1894) |
|||
* "A Committee-Man of 'The Terror'" (1896) (collected in ''A Changed Man and Other Stories'') |
|||
* "The Duke's Reappearance" (1896) (collected in ''A Changed Man and Other Stories'') |
|||
* "The Grave by the Handpost" (1897) (collected in ''A Changed Man and Other Stories'') |
|||
* "A Changed Man" (1900) (collected in ''A Changed Man and Other Stories'') |
|||
* "Enter a Dragoon" (1900) (collected in ''A Changed Man and Other Stories'') |
|||
* "Blue Jimmy: The Horse Stealer" (1911) |
|||
* "Old Mrs. Chundle" (1929) |
|||
* "[[The Unconquerable]]"(1992) |
|||
===Poetry collections=== |
|||
* ''[[Wessex Poems and Other Verses]]'' (1898) |
|||
* ''[[Poems of the Past and the Present]]'' (1901) |
|||
* ''[[Time's Laughingstocks and Other Verses]]'' (1909) |
|||
* ''[[Satires of Circumstance]]'' (1914) |
|||
* ''[[Moments of Vision]]'' (1917) |
|||
* ''Collected Poems'' (1919) |
|||
* ''[[Late Lyrics and Earlier with Many Other Verses]]'' (1922) |
|||
* ''[[Human Shows, Far Phantasies, Songs and Trifles]]'' (1925) |
|||
* ''[[Winter Words in Various Moods and Metres]]'' (1928) |
|||
* ''The Complete Poems'' (Macmillan, 1976) |
|||
* ''Selected Poems'' (Edited by Harry Thomas, Penguin, 1993) |
|||
* ''Hardy: Poems'' (Everyman's Library Pocket Poets, 1995) |
|||
* ''Thomas Hardy: Selected Poetry and Nonfictional Prose'' ([[St. Martin's Press]], 1996) |
|||
* ''Selected Poems'' (Edited by Robert Mezey, Penguin, 1998) |
|||
* ''Thomas Hardy: The Complete Poems'' (Edited by James Gibson, Palgrave, 2001) |
|||
Online poems: Poems by Thomas Hardy<ref>{{cite web |last=Axelrod |first=Jeremy |url=http://www.poetryfoundation.org/archive/poet.html?id=2926 |title=Thomas Hardy |publisher=The Poetry Foundation |access-date=19 May 2014 |archive-date=10 July 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100710005620/http://www.poetryfoundation.org/archive/poet.html?id=2926 |url-status=live }}</ref> at [[Poetry Foundation]] and Poems by Thomas Hardy at poemhunter.com<ref>[http://www.poemhunter.com/i/ebooks/pdf/thomas_hardy_2004_9.pdf “Thomas Hardy poems”] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100622035642/http://www.poemhunter.com/i/ebooks/pdf/thomas_hardy_2004_9.pdf |date=22 June 2010 }}.</ref> |
|||
===Drama=== |
|||
* ''[[The Dynasts]]: An Epic-Drama of the War with Napoleon'' (verse drama) |
|||
** ''The Dynasts, Part 1'' (1904) |
|||
** ''The Dynasts, Part 2'' (1906) |
|||
** ''The Dynasts, Part 3'' (1908) |
|||
* ''The Famous Tragedy of the Queen of Cornwall at [[Tintagel]] in Lyonnesse'' (1923) (one-act play) |
|||
==References== |
|||
{{Reflist|30em}} |
|||
==Biographies and criticism== |
|||
{{Refbegin|35em}} |
|||
* Armstrong, Tim. "Player Piano: Poetry and Sonic Modernity" in ''Modernism/Modernity'' 14.1 (January 2007), 1–19. |
|||
* Beatty, Claudius J.P. ''Thomas Hardy: Conservation Architect. His Work for the Society for the Protection of Ancient Buildings''. Dorset Natural History and Archaeological Society 1995. {{ISBN|0-900341-44-0}} |
|||
* Blunden, Edmund. ''Thomas Hardy.'' New York: St. Martin's, 1942. |
|||
* Brady, Kristen. ''The Short Stories of Thomas Hardy.'' London: Macmillan, 1982. |
|||
* Boumelha, Penny. ''Thomas Hardy and Women.'' New Jersey: Barnes and Noble, 1982. |
|||
* Brennecke, Jr., Ernest. ''The Life of Thomas Hardy.'' New York: Greenberg, 1925. |
|||
* Cecil, Lord David. ''Hardy the Novelist.'' London: Constable, 1943. |
|||
* D'Agnillo, Renzo, "Music and Metaphor in ''Under the Greenwood Tree'', in ''The Thomas Hardy Journal'', 9, 2 (May 1993), pp.39–50. |
|||
* D'Agnillo, Renzo, "Between Belief and Non-Belief: Thomas Hardy’s 'The Shadow on the Stone'”, in Thomas Hardy, Francesco Marroni and Norman Page (eds), Pescara, Edizioni Tracce, 1995, pp. 197–222. |
|||
* Deacon, Lois and Terry Coleman. ''Providence and Mr. Hardy.'' London: Hutchinson, 1966. |
|||
* Draper, Jo. ''Thomas Hardy: A Life in Pictures.'' Wimborne, Dorset: The Dovecote Press. |
|||
* Ellman, Richard & O'Clair, Robert (eds.) 1988. "Thomas Hardy" in ''The Norton Anthology of Modern Poetry'', Norton, New York. |
|||
* Gatrell, Simon. ''Hardy the Creator: A Textual Biography.'' Oxford: Clarendon, 1988. |
|||
* Gibson, James. ''Thomas Hardy: A Literary Life.'' London: Macmillan, 1996. |
|||
* Gibson, James. ''Thomas Hardy: Interviews and Recollections.'' London: Macmillan, 1999; New York: St Martin's Press, 1999. |
|||
* Gittings, Robert. ''Thomas Hardy's Later Years.'' Boston : Little, Brown, 1978. |
|||
* Gittings, Robert. ''Young Thomas Hardy.'' Boston : Little, Brown, 1975. |
|||
* Gittings, Robert and Jo Manton. ''The Second Mrs Hardy.'' London: Heinemann, 1979. |
|||
* Gossin, P. ''Thomas Hardy's Novel Universe: Astronomy, Cosmology, and Gender in the Post-Darwinian World''. Aldershot, Ashgate, 2007 (The Nineteenth Century Series). |
|||
* [[F. E. Halliday|Halliday, F. E.]] ''Thomas Hardy: His Life and Work.'' Bath: Adams & Dart, 1972. |
|||
* Hands, Timothy. ''Thomas Hardy : Distracted Preacher? : Hardy's religious biography and its influence on his novels.'' New York: St. Martin's Press, 1989. |
|||
* Hardy, Evelyn. ''Thomas Hardy: A Critical Biography.'' London: Hogarth Press, 1954. |
|||
* Hardy, Florence Emily. ''The Early Life of Thomas Hardy, 1840–1891.'' London: Macmillan, 1928. |
|||
* Hardy, Florence Emily. ''The Later Years of Thomas Hardy, 1892–1928'' London: Macmillan, 1930. |
|||
* Harvey, Geoffrey. ''Thomas Hardy: The Complete Critical Guide to Thomas Hardy.'' New York: Routledge (Taylor & Francis Group), 2003. |
|||
* [[Desmond Hawkins|Hawkins, Desmond]]. ''Thomas Hardy.'' London: Arthur Barker, 1950. (The English Novelists series) |
|||
* Hedgcock, F. A., ''Thomas Hardy: penseur et artiste.'' Paris: Librairie Hachette, 1911. |
* Hedgcock, F. A., ''Thomas Hardy: penseur et artiste.'' Paris: Librairie Hachette, 1911. |
||
* Holland, Clive. ''Thomas Hardy O.M.: The Man, His Works and the Land of Wessex.'' London: Herbert Jenkins, 1933. |
* Holland, Clive. ''Thomas Hardy O.M.: The Man, His Works and the Land of Wessex.'' London: Herbert Jenkins, 1933. |
||
* Jedrzejewski, Jan. ''Thomas Hardy and the Church.'' London: Macmillan, 1996. |
* Jedrzejewski, Jan. ''Thomas Hardy and the Church.'' London: Macmillan, 1996. |
||
* Johnson, Lionel Pigot. ''The Art of Thomas Hardy'' (London: E. Mathews, 1894). |
|||
* Kay-Robinson, Denys. ''The First Mrs Thomas Hardy.'' London: Macmillan, 1979. |
* Kay-Robinson, Denys. ''The First Mrs Thomas Hardy.'' London: Macmillan, 1979. |
||
* [[Robert Langbaum|Langbaum, Robert]]. "Thomas Hardy in Our Time." New York: St. Martin's Press, 1995, London: Macmillan, 1997. |
|||
* Marroni, Francesco, "The Negation of Eros in 'Barbara of the House of Grebe' ", in "Thomas Hardy Journal", 10, 1 (February 1994) pp. 33–41 |
|||
* Marroni, Francesco and Norman Page (eds.), ''Thomas Hardy''. Pescara: Edizioni Tracce, 1995. |
|||
* Marroni, Francesco, ''La poesia di Thomas Hardy''. Bari: Adriatica Editrice, 1997. |
|||
* Marroni, Francesco, "The Poetry of Ornithology in Keats, Leopardi, and Hardy: A Dialogic Analysis", in "Thomas Hardy Journal", 14, 2 (May 1998) pp. 35–44 |
|||
* Millgate, Michael (ed.). ''The Life and Work of Thomas Hardy by Thomas Hardy.'' London: Macmillan, 1984. |
* Millgate, Michael (ed.). ''The Life and Work of Thomas Hardy by Thomas Hardy.'' London: Macmillan, 1984. |
||
* Millgate, Michael. ''Thomas Hardy: A Biography.'' New York: Random House, 1982. |
* Millgate, Michael. ''Thomas Hardy: A Biography.'' New York: Random House, 1982. |
||
* Millgate, Michael. ''Thomas Hardy: A Biography Revisited.'' Oxford: [[Oxford University Press]], 2004. |
|||
* Morgan, Rosemarie, (ed) The Ashgate Research Companion to Thomas Hardy, (Ashgate publishing), 2010. |
|||
* Millgate, Michael. ''Thomas Hardy: A Biography Revisited.'' Oxford: Oxford UP, 2004. |
|||
* Morgan, Rosemarie, (ed) The Hardy Review,(Maney Publishing), 1999–. |
|||
* Morgan, Rosemarie, Student Companion to Thomas Hardy (Greenwood Press), 2006. |
|||
* Morgan, Rosemarie, Cancelled Words: Rediscovering Thomas Hardy (Routledge, Chapman & Hall),1992 |
|||
* Morgan, Rosemarie, Women and Sexuality in the Novels of Thomas Hardy (Routledge & Kegan Paul), 1988; paperback: 1990. |
|||
* [[David Musselwhite|Musselwhite, David]], Social Transformations in Hardy's Tragic Novels: Megamachines and Phantasms, Palgrave Macmillan, 2003. |
|||
* Norman, Andrew. ''Behind the Mask'', History Press, 2011. {{ISBN|978-0-7524-5630-0}} |
|||
* O'Sullivan, Timothy. ''Thomas Hardy: An Illustrated Biography.'' London: Macmillan, 1975. |
* O'Sullivan, Timothy. ''Thomas Hardy: An Illustrated Biography.'' London: Macmillan, 1975. |
||
* Orel, Harold. ''The Final Years of Thomas Hardy, 1912–1928.'' Lawrence: [[University Press of Kansas]], 1976. |
|||
* Orel, Harold. ''The Final Years of Thomas Hardy, 1912-1928.'' Lawrence: University Press of Kansas, 1976. |
|||
* Orel, Harold. ''The Unknown Thomas Hardy.'' New York: St. Martin's, 1987. |
* Orel, Harold. ''The Unknown Thomas Hardy.'' New York: St. Martin's, 1987. |
||
* Page, Norman, ed. ''Thomas Hardy Annual.'' No.1: 1982; No.2: 1984; No.3: 1985; No.4:1986; No.5; 1987. London: Macmillan, 1982–1987. |
|||
* Phelps, Kenneth. ''The Wormwood Cup: Thomas Hardy in Cornwall.'' Padstow: Lodenek Press, 1975. |
* Phelps, Kenneth. ''The Wormwood Cup: Thomas Hardy in Cornwall.'' Padstow: Lodenek Press, 1975. |
||
* Pinion, F. B. ''Thomas Hardy: His Life and Friends.'' London: Palgrave, 1992. |
* Pinion, F. B. ''Thomas Hardy: His Life and Friends.'' London: Palgrave, 1992. |
||
* Pite, Ralph. ''Thomas Hardy: The Guarded Life.'' London: Picador, 2006. |
* Pite, Ralph. ''Thomas Hardy: The Guarded Life.'' London: Picador, 2006. |
||
* Saxelby, F. Outwin. ''A Thomas Hardy dictionary : the characters and scenes of the novels and poems alphabetically arranged and described'' (London: G. Routledge, 1911). |
|||
* Seymour-Smith, Martin. ''Hardy.'' London: Bloomsbury, 1994. |
* Seymour-Smith, Martin. ''Hardy.'' London: Bloomsbury, 1994. |
||
* Stevens-Cox, J. ''Thomas Hardy: Materials for a Study of his Life, Times, and Works.'' St. Peter Port, Guernsey: Toucan Press, 1968. |
* Stevens-Cox, J. ''Thomas Hardy: Materials for a Study of his Life, Times, and Works.'' St. Peter Port, Guernsey: Toucan Press, 1968. |
||
* Stevens-Cox, J. ''Thomas Hardy: More Materials for a Study of his Life, Times, and Works.'' St. Peter Port, Guernsey: Toucan Press, 1971. |
* Stevens-Cox, J. ''Thomas Hardy: More Materials for a Study of his Life, Times, and Works.'' St. Peter Port, Guernsey: Toucan Press, 1971. |
||
* Stewart, J. I. M. ''Thomas Hardy: A Critical Biography.'' New York: Dodd, Mead & Co., 1971. |
* Stewart, J. I. M. ''Thomas Hardy: A Critical Biography.'' New York: Dodd, Mead & Co., 1971. |
||
* Taylor, Richard H. ''The Neglected Hardy: Thomas Hardy's Lesser Novels.'' London: Macmillan; New York: St Martin's Press, 1982. |
|||
* Taylor, Richard H., ed. ''The Personal Notebooks of Thomas Hardy.'' London: Macmillan, 1979. |
|||
* Tomalin, Claire. ''Thomas Hardy.'' New York: Penguin Press, 2006. |
|||
* Turner, Paul. ''The Life of Thomas Hardy: A Critical Biography.'' Oxford: Blackwell, 1998. |
* Turner, Paul. ''The Life of Thomas Hardy: A Critical Biography.'' Oxford: Blackwell, 1998. |
||
* Weber, Carl J. ''Hardy of Wessex, His Life and Literary Career.'' New York: [[Columbia University Press]], 1940. |
|||
* Wilson, Keith. ''Thomas Hardy on Stage.'' London: Macmillan, 1995. |
|||
* Wilson, Keith, ed. ''Thomas Hardy Reappraised: Essays in Honour of Michael Millgate.'' Toronto: [[University of Toronto Press]], 2006. |
|||
* Wilson, Keith, ed. ''A Companion to Thomas Hardy.'' Wiley-Blackwell, 2009. |
|||
* Wotton, George. Thomas Hardy: Towards A Materialist Criticism. Lanham: Rowman & Littlefield, 1985. |
|||
{{refend}} |
|||
==External links== |
|||
* Weber, Carl J. ''Hardy of Wessex, his Life and Literary Career.'' New York: Columbia University Press, 1940. |
|||
{{Library resources box}} |
|||
{{Wikiquote}} |
|||
{{wikisource author}} |
|||
{{Wikisource1911Enc|Hardy, Thomas}} |
|||
{{Commons category}} |
|||
;Digital collections |
|||
* {{StandardEbooks|Standard Ebooks URL=https://standardebooks.org/ebooks/thomas-hardy}} |
|||
* {{Gutenberg author |id=23| name=Thomas Hardy}} |
|||
* {{Internet Archive author |sname=Thomas Hardy}} |
|||
* {{Librivox author |id=92}} |
|||
* [https://www.poetryfoundation.org/poets/thomas-hardy Thomas Hardy] at the [[Poetry Foundation]] |
|||
* [http://victorian-studies.net/concordance/hardy/ A Hyper-Concordance to the Works of Thomas Hardy] at the Victorian Literary Studies Archive, Nagoya University, Japan |
|||
;Physical collections |
|||
* Wilson, Keith. ''Thomas Hardy on Stage.'' London: Macmillan, 1995. |
|||
* [http://www.dorsetmuseum.org/ Dorset Museum], Dorchester, Dorset, contains the largest Hardy collections in the world, donated directly to the Museum by the Hardy family and inscribed on the UNESCO Memory of the World register for the United Kingdom. |
|||
* [https://norman.hrc.utexas.edu/fasearch/findingAid.cfm?eadID=00532 Thomas Hardy Collection] at the [[Harry Ransom Center]] at the [[University of Texas at Austin]] |
|||
* [http://www.bl.uk/people/thomas-hardy Thomas Hardy] at the British Library |
|||
* [http://thethomashardyassociation.org/images/maps/windle.htm Letter from Hardy to Bertram Windle, transcribed by Birgit Plietzsch, from ''Collected Letters'', vol 2, pp.131–133]. Retrieved 25 May 2015. |
|||
;Biographical information |
|||
* [http://www.yale.edu/hardysoc/images/maps/windle.htm Letter from Hardy to Bertram Windle, transcribed by Birgit Plietzsch, from CL, vol 2, pp 131-133] |
|||
* [https://www.parliament.uk/about/living-heritage/transformingsociety/private-lives/relationships/collections1/1968-theatre-censorship/1909-censorship-committee/ Thomas Hardy & 1909 Theatre Censorship Committee - UK Parliament Living Heritage] |
|||
;Geographic information |
|||
==External links== |
|||
* [http://www.nationaltrust.org.uk/hardys-cottage/ Hardy's Cottage] National Trust visitor information for Hardy's birthplace. |
|||
* [http://www.hardycountry.org/ Hardy Country] A visitor guide for 'Hardy Country' in Dorset (sites of interest). |
|||
* [http://www.nationaltrust.org.uk/max-gate/ Max Gate] National Trust visitor information for Max Gate (the home Hardy designed, lived and died in). |
|||
;Other links |
|||
{{wikiquote}} |
|||
* [http://thethomashardyassociation.org/ The Thomas Hardy Association] (TTHA) |
|||
{{wikisource author}} |
|||
{{commons}} |
|||
* [http://www.poetryfoundation.org/archive/poet.html?id=2926 Poems by Thomas Hardy at PoetryFoundation.org] |
|||
* [http://poetry.lastpromise.com/content/hardy_thomas/ Selected Poems by Thomas Hardy at Inspired Poetry] |
|||
* {{gutenberg author|id=Thomas_Hardy|name=Thomas Hardy}} |
|||
* [http://www.st-andrews.ac.uk/~bp10/wessex/index.shtml Thomas Hardy's Wessex] Research site, including [http://www.st-andrews.ac.uk/~bp10/wessex/evolution/maps/index.shtml maps], by Dr Birgit Plietzsch |
|||
* [http://www.cosmoetica.com/TOP6-DES5.htm Essay on Hardy's ''Afterwards''] |
|||
* [http://www.hardysociety.org/ The Thomas Hardy Society] |
* [http://www.hardysociety.org/ The Thomas Hardy Society] |
||
* [http://hardyonline.org The New Hardy Players] Theatrical group specialising in the works of Thomas Hardy. |
|||
* [http://www.yale.edu/hardysoc/Welcome/welcomet.htm The Thomas Hardy Association] |
|||
* {{PM20|FID=pe/007130}} |
|||
* [http://www.classicistranieri.com/english/indexes/authh.htm Works by Thomas Hardy] in e-book version |
|||
* {{Curlie|Arts/Literature/Authors/H/Hardy,_Thomas}} |
|||
* [http://www.findagrave.com/cgi-bin/fg.cgi?page=gr&GRid=4112 Thomas Hardy's ashes at Westminster Abbey] |
|||
* [https://www.greatwartheatre.org.uk/db/person/128/ ''The Dynasts'' on Great War Theatre] |
|||
* [http://www.isleofportlandpictures.org.uk/Surnames/Stopes/ Pictures of Thomas Hardy visiting Marie Stopes at her lighthouse home on Portland, Dorset] |
|||
* [http://www.yale.edu/hardysoc/images/maps/windle.htm Letter from Hardy to Bertram Windle, transcribed by Birgit Plietzsch, from CL, vol 2, pp 131-133] |
|||
{{Thomas Hardy|state=expanded}} |
|||
* [http://www.wardsbookofdays.com/11january.htm The Life and Death of Thomas Hardy @ ''Ward's Book of Days''] |
|||
{{Far from the Madding Crowd}} |
|||
===Individual poems=== |
|||
{{Tess of the d'Urbervilles}} |
|||
* [http://www.poetsgraves.co.uk/Classic%20Poems/Hardy/The%20Dead%20Man%20Walking.htm The Dead Man Walking] |
|||
{{The Mayor of Casterbridge}} |
|||
* [http://www.poetsgraves.co.uk/Classic%20Poems/Hardy/At%20Castle%20Boterel.htm At Castle Boterel] |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
* [http://www.poetsgraves.co.uk/Classic%20Poems/Hardy/afterwards.htm Afterwards] |
|||
* [http://www.poetsgraves.co.uk/Classic%20Poems/Hardy/On%20the%20departure_platform.htm On the Departure Platform] |
|||
* [http://www.poetsgraves.co.uk/Classic%20Poems/Hardy/The_Robin.htm The Robin] |
|||
* [http://www.poemtree.com/poems/Oxen.htm The Oxen] |
|||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hardy, Thomas}} |
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hardy, Thomas}} |
||
[[Category:Thomas Hardy| ]] |
[[Category:Thomas Hardy| ]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:1840 births]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:1928 deaths]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:19th-century British short story writers]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:19th-century English novelists]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:19th-century English poets]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:20th-century English writers]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Alumni of King's College London]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Anti-vivisectionists]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:British male poets]] |
||
[[Category:Burials at Westminster Abbey]] |
|||
[[Category:English male novelists]] |
|||
[[ar:توماس هاردي]] |
|||
[[Category:English male short story writers]] |
|||
[[bs:Thomas Hardy]] |
|||
[[Category:English short story writers]] |
|||
[[cs:Thomas Hardy]] |
|||
[[Category:Fellows of the Royal Society of Literature]] |
|||
[[cy:Thomas Hardy]] |
|||
[[Category:Members of the Order of Merit]] |
|||
[[de:Thomas Hardy (Schriftsteller)]] |
|||
[[Category:Pantheists]] |
|||
[[el:Τόμας Χάρντι]] |
|||
[[Category:People from Dorchester, Dorset]] |
|||
[[es:Thomas Hardy]] |
|||
[[Category:Philosophers of pessimism]] |
|||
[[eo:Thomas Hardy]] |
|||
[[Category:Victorian novelists]] |
|||
[[fa:توماس هاردی]] |
|||
[[ |
[[Category:Victorian poets]] |
||
[[Category:Presidents of the Society of Authors]] |
|||
[[hr:Thomas Hardy]] |
|||
[[id:Thomas Hardy]] |
|||
[[it:Thomas Hardy]] |
|||
[[he:תומס הרדי]] |
|||
[[ka:ჰარდი, ტომას]] |
|||
[[nl:Thomas Hardy]] |
|||
[[ja:トーマス・ハーディ]] |
|||
[[no:Thomas Hardy]] |
|||
[[pl:Thomas Hardy]] |
|||
[[pt:Thomas Hardy]] |
|||
[[ro:Thomas Hardy]] |
|||
[[ru:Харди, Томас]] |
|||
[[simple:Thomas Hardy]] |
|||
[[sr:Томас Харди]] |
|||
[[sv:Thomas Hardy]] |
|||
[[zh:托马斯·哈代]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 08:41, 13 May 2024
Thomas Hardy | |
|---|---|
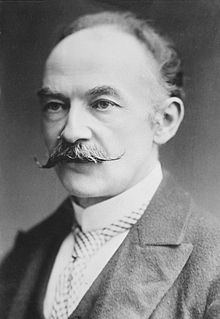 Hardy between about 1910 and 1915 | |
| Born | 2 June 1840 Stinsford, Dorset, England |
| Died | 11 January 1928 (aged 87) Dorchester, Dorset, England |
| Resting place |
|
| Occupation |
|
| Alma mater | King's College London |
| Literary movement | |
| Notable works | |
| Spouse | |
| Signature | |
 | |
Thomas Hardy OM (2 June 1840 – 11 January 1928) was an English novelist and poet. A Victorian realist in the tradition of George Eliot, he was influenced both in his novels and in his poetry by Romanticism, including the poetry of William Wordsworth.[1] He was highly critical of much in Victorian society, especially on the declining status of rural people in Britain such as those from his native South West England.
While Hardy wrote poetry throughout his life and regarded himself primarily as a poet, his first collection was not published until 1898. Initially, he gained fame as the author of novels such as Far from the Madding Crowd (1874), The Mayor of Casterbridge (1886), Tess of the d'Urbervilles (1891) and Jude the Obscure (1895). During his lifetime, Hardy's poetry was acclaimed by younger poets (particularly the Georgians) who viewed him as a mentor. After his death his poems were lauded by Ezra Pound, W. H. Auden and Philip Larkin.[2]
Many of his novels concern tragic characters struggling against their passions and social circumstances, and they are often set in the semi-fictional region of Wessex; initially based on the medieval Anglo-Saxon kingdom, Hardy's Wessex eventually came to include the counties of Dorset, Wiltshire, Somerset, Devon, Hampshire and much of Berkshire, in south-west and south central England. Two of his novels, Tess of the d'Urbervilles and Far from the Madding Crowd, were listed in the top 50 on the BBC's survey The Big Read.[3]
Life and career[edit]
Early life[edit]

Thomas Hardy was born on 2 June 1840 in Higher Bockhampton (then Upper Bockhampton), a hamlet in the parish of Stinsford to the east of Dorchester in Dorset, England, where his father Thomas (1811–1892) worked as a stonemason and local builder. His parents had married at Melbury Osmond on 22 December 1839.[5] His mother, Jemima (née Hand; 1813–1904),[6] was well read, and she educated Thomas until he went to his first school at Bockhampton at the age of eight. For several years he attended Mr. Last's Academy for Young Gentlemen in Dorchester, where he learned Latin and demonstrated academic potential.[7]
Because Hardy's family lacked the means for a university education, his formal education ended at the age of sixteen, when he became apprenticed to James Hicks, a local architect.[8] He worked on the design of the new church at nearby Athelhampton, situated just opposite Athelhampton House where he painted a watercolour of the Tudor gatehouse while visiting his father, who was repairing the masonry of the dovecote.
He moved to London in 1862 where he enrolled as a student at King's College London. He won prizes from the Royal Institute of British Architects and the Architectural Association. He joined Arthur Blomfield's practice as assistant architect in April 1862 and worked with Blomfield on Christ Church, East Sheen Richmond, London where the tower collapsed in 1863, and All Saints' parish church in Windsor, Berkshire, in 1862–64. A reredos, possibly designed by Hardy, was discovered behind panelling at All Saints' in August 2016.[9][10] In the mid-1860s, Hardy was in charge of the excavation of part of the graveyard of St Pancras Old Church before its destruction when the Midland Railway was extended to a new terminus at St Pancras.[11]
Hardy never felt at home in London, because he was acutely conscious of class divisions and his social inferiority. During this time he became interested in social reform and the works of John Stuart Mill. He was introduced by his Dorset friend Horace Moule to the works of Charles Fourier and Auguste Comte. Mill's essay On Liberty was one of Hardy's cures for despair, and in 1924 he declared that "my pages show harmony of view with" Mill.[12] He was also attracted to Matthew Arnold's and Leslie Stephen's ideal of the urbane liberal freethinker.[13]
After five years, concerned about his health, he returned to Dorset, settling in Weymouth, and decided to dedicate himself to writing.
Personal[edit]

In 1870, while on an architectural mission to restore the parish church of St Juliot in Cornwall,[14] Hardy met and fell in love with Emma Gifford, whom he married in Kensington in late 1874,[15][16][17] renting St David's Villa, Southborough (now Surbiton) for a year. In 1885 Thomas and his wife moved into Max Gate in Dorchester, a house designed by Hardy and built by his brother. Although they became estranged, Emma's death in 1912 had a traumatic effect on him and after her death, Hardy made a trip to Cornwall to revisit places linked with their courtship; his Poems 1912–13 reflect upon her death. In 1914, Hardy married his secretary Florence Emily Dugdale, who was 39 years his junior. He remained preoccupied with his first wife's death and tried to overcome his remorse by writing poetry.
In his later years, he kept a Wire Fox Terrier named Wessex, who was notoriously ill-tempered. Wessex's grave stone can be found on the Max Gate grounds.[18][19]
In 1910, Hardy had been appointed a Member of the Order of Merit and was also for the first time nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature. He was nominated again for the prize 11 years later and received a total of 25 nominations until 1927.[20][21] He was at least once, in 1923, one of the final candidates for the prize, but was not awarded.[22]
Hardy and the theatre[edit]
Hardy's interest in the theatre dated from the 1860s. He corresponded with various would-be adapters over the years, including Robert Louis Stevenson in 1886 and Jack Grein and Charles Jarvis in the same decade.[23] Neither adaptation came to fruition, but Hardy showed he was potentially enthusiastic about such a project. One play that was performed, however, caused him a certain amount of pain. His experience of the controversy and lukewarm critical reception that had surrounded his and Comyns Carr's adaptation of Far from the Madding Crowd in 1882 left him wary of the damage that adaptations could do to his literary reputation. So, in 1908, he so readily and enthusiastically became involved with a local amateur group, at the time known as the Dorchester Dramatic and Debating Society, but that would become the Hardy Players. His reservations about adaptations of his novels meant he was initially at some pains to disguise his involvement in the play.[24] However, the international success[25] of the play, The Trumpet Major, led to a long and successful collaboration between Hardy and the Players over the remaining years of his life. Indeed, his play The Famous Tragedy of the Queen of Cornwall at Tintagel in Lyonnesse (1923) was written to be performed by the Hardy Players.[26]
Later years[edit]

From the 1880s, Hardy became increasingly involved in campaigns to save ancient buildings from destruction, or destructive modernisation, and he became an early member of the Society for the Protection of Ancient Buildings. His correspondence refers to his unsuccessful efforts to prevent major alterations to the parish church at Puddletown, close to his home at Max Gate. He became a frequent visitor at Athelhampton House, which he knew from his teenage years, and in his letters he encouraged the owner, Alfred Cart de Lafontaine, to conduct the restoration of that building in a sensitive way.
In 1914, Hardy was one of fifty-three leading British authors—including H. G. Wells, Rudyard Kipling and Sir Arthur Conan Doyle—who signed their names to the "Authors' Declaration", justifying Britain's involvement in the First World War. This manifesto declared that the German invasion of Belgium had been a brutal crime, and that Britain "could not without dishonour have refused to take part in the present war."[27] Hardy was horrified by the destruction caused by the war, pondering that "I do not think a world in which such fiendishness is possible to be worth the saving" and "better to let western 'civilization' perish, and let the black and yellow races have a chance."[28] He wrote to John Galsworthy that "the exchange of international thought is the only possible salvation for the world."[28]
Hardy became ill with pleurisy in December 1927 and died at Max Gate just after 9 pm on 11 January 1928, having dictated his final poem to his wife on his deathbed; the cause of death was cited, on his death certificate, as "cardiac syncope", with "old age" given as a contributory factor. His funeral was on 16 January at Westminster Abbey, and it proved a controversial occasion because Hardy had wished for his body to be interred at Stinsford in the same grave as his first wife, Emma. His family and friends concurred; however, his executor, Sir Sydney Carlyle Cockerell, insisted that he be placed in the abbey's famous Poets' Corner. A compromise was reached whereby his heart was buried at Stinsford with Emma, and his ashes in Poets' Corner.[29] Hardy's estate at death was valued at £95,418 (equivalent to £7,300,000 in 2023).[30]
Shortly after Hardy's death, the executors of his estate burnt his letters and notebooks, but twelve notebooks survived, one of them containing notes and extracts of newspaper stories from the 1820s, and research into these has provided insight into how Hardy used them in his works. The opening chapter of The Mayor of Casterbridge, for example, written in 1886, was based on press reports of wife-selling.[31] In the year of his death Mrs Hardy published The Early Life of Thomas Hardy, 1841–1891, compiled largely from contemporary notes, letters, diaries and biographical memoranda, as well as from oral information in conversations extending over many years.
Hardy's work was admired by many younger writers, including D. H. Lawrence,[32] John Cowper Powys and Virginia Woolf.[33] In his autobiography Good-Bye to All That (1929), Robert Graves recalls meeting Hardy in Dorset in the early 1920s and how Hardy received him and his new wife warmly, and was encouraging about his work.
Hardy's birthplace in Bockhampton and his house Max Gate, both in Dorchester, are owned by the National Trust.
Novels[edit]


Hardy's first novel, The Poor Man and the Lady, finished by 1867, failed to find a publisher. He then showed it to his mentor and friend, the Victorian poet and novelist George Meredith, who felt that The Poor Man and the Lady would be too politically controversial and might damage Hardy's ability to publish in the future. So Hardy followed his advice and he did not try further to publish it. He subsequently destroyed the manuscript, but used some of the ideas in his later work.[34] In his recollections in Life and Work, Hardy described the book as "socialistic, not to say revolutionary; yet not argumentatively so."[35]
After he abandoned his first novel, Hardy wrote two new ones that he hoped would have more commercial appeal, Desperate Remedies (1871) and Under the Greenwood Tree (1872), both of which were published anonymously; it was while working on the latter that he met Emma Gifford, who would become his wife.[34] In 1873 A Pair of Blue Eyes, a novel drawing on Hardy's courtship of Emma, was published under his own name. A plot device popularised by Charles Dickens, the term "cliffhanger" is considered to have originated with the serialised version of A Pair of Blue Eyes (published in Tinsley's Magazine between September 1872 and July 1873) in which Henry Knight, one of the protagonists, is left literally hanging off a cliff.[36][37] Elements of Hardy's fiction reflect the influence of the commercially successful sensation fiction of the 1860s, particularly the legal complications in novels such as Desperate Remedies (1871), Far from the Madding Crowd (1874) and Two on a Tower (1882).[38]
In Far from the Madding Crowd, Hardy first introduced the idea of calling the region in the west of England, where his novels are set, Wessex. Wessex had been the name of an early Saxon kingdom, in approximately the same part of England. Far from the Madding Crowd was successful enough for Hardy to give up architectural work and pursue a literary career. Over the next 25 years, Hardy produced 10 more novels.
Subsequently, Hardy moved from London to Yeovil, and then to Sturminster Newton, where he wrote The Return of the Native (1878).[39] In 1880, Hardy published his only historical novel, The Trumpet-Major. A further move to Wimborne saw Hardy write Two on a Tower, published in 1882, a romance story set in the world of astronomy. Then in 1885, they moved for the last time, to Max Gate, a house outside Dorchester designed by Hardy and built by his brother. There he wrote The Mayor of Casterbridge (1886), The Woodlanders (1887) and Tess of the d'Urbervilles (1891), the last of which attracted criticism for its sympathetic portrayal of a "fallen woman", and initially it was refused publication. Its subtitle, A Pure Woman: Faithfully Presented, was intended to raise the eyebrows of the Victorian middle classes.

Jude the Obscure, published in 1895, met with an even stronger negative response from the Victorian public because of its controversial treatment of sex, religion and marriage. Its apparent attack on the institution of marriage caused strain on Hardy's already difficult marriage because Emma Hardy was concerned that Jude the Obscure would be read as autobiographical. Some booksellers sold the novel in brown paper bags, and Walsham How, the Bishop of Wakefield, is reputed to have burnt his copy.[31] In his postscript of 1912, Hardy humorously referred to this incident as part of the career of the book: "After these [hostile] verdicts from the press its next misfortune was to be burnt by a bishop – probably in his despair at not being able to burn me".[40] Despite this, Hardy had become a celebrity by the 1900s, but some argue that he gave up writing novels because of the criticism of both Tess of the d'Urbervilles and Jude the Obscure.[41] The Well-Beloved, first serialised in 1892, was published in 1897.
Literary themes[edit]
Considered a Victorian realist, Hardy examines the social constraints on the lives of those living in Victorian England, and criticises those beliefs, especially those relating to marriage, education and religion, that limited people's lives and caused unhappiness. Such unhappiness, and the suffering it brings, is seen by poet Philip Larkin as central in Hardy's works:
What is the intensely maturing experience of which Hardy's modern man is most sensible? In my view it is suffering, or sadness, and extended consideration of the centrality of suffering in Hardy's work should be the first duty of the true critic for which the work is still waiting [...] Any approach to his work, as to any writer's work, must seek first of all to determine what element is peculiarly his, which imaginative note he strikes most plangently, and to deny that in this case it is the sometimes gentle, sometimes ironic, sometimes bitter but always passive apprehension of suffering is, I think, wrong-headed.[42]
In Two on a Tower, for example, Hardy takes a stand against these rules of society with a story of love that crosses the boundaries of class. The reader is forced to reconsider the conventions set up by society for the relationships between men and women. Nineteenth-century society had conventions, which were enforced. In this novel Swithin St Cleeve's idealism pits him against such contemporary social constraints.
In a novel structured around contrasts, the main opposition is between Swithin St Cleeve and Lady Viviette Constantine, who are presented as binary figures in a series of ways: aristocratic and lower class, youthful and mature, single and married, fair and dark, religious and agnostic...she [Lady Viviette Constantine] is also deeply conventional, absurdly wishing to conceal their marriage until Swithin has achieved social status through his scientific work, which gives rise to uncontrolled ironies and tragic-comic misunderstandings.[43]
Fate or chance is another important theme. Hardy's characters often encounter crossroads on a journey, a junction that offers alternative physical destinations but which is also symbolic of a point of opportunity and transition, further suggesting that fate is at work. Far from the Madding Crowd is an example of a novel in which chance has a major role: "Had Bathsheba not sent the valentine, had Fanny not missed her wedding, for example, the story would have taken an entirely different path."[44] Indeed, Hardy's main characters often seem to be held in fate's overwhelming grip.
Poetry[edit]

In 1898, Hardy published his first volume of poetry, Wessex Poems, a collection of poems written over 30 years. While some suggest that Hardy gave up writing novels following the harsh criticism of Jude the Obscure in 1896, the poet C. H. Sisson calls this "hypothesis" "superficial and absurd".[41][45] In the twentieth century Hardy published only poetry.
Thomas Hardy published Poems of the Past and the Present in 1901, which contains "The Darkling Thrush" (originally titled "The Century's End"), one of his best known poems about the turn of the century.[46]
Thomas Hardy wrote in a great variety of poetic forms, including lyrics, ballads, satire, dramatic monologues and dialogue, as well as a three-volume epic closet drama The Dynasts (1904–08),[47] and though in some ways a very traditional poet, because he was influenced by folksong and ballads,[48] he "was never conventional," and "persistently experiment[ed] with different, often invented, stanza forms and metres,"[49] and made use of "rough-hewn rhythms and colloquial diction".[50]
Hardy wrote a number of significant war poems that relate to both the Boer Wars and World War I, including "Drummer Hodge", "In Time of 'The Breaking of Nations'" and "The Man He Killed"; his work had a profound influence on other war poets such as Rupert Brooke and Siegfried Sassoon.[51] Hardy in these poems often used the viewpoint of ordinary soldiers and their colloquial speech.[51] A theme in the Wessex Poems is the long shadow that the Napoleonic Wars cast over the 19th century, as seen, for example, in "The Sergeant's Song" and "Leipzig".[52] The Napoleonic War is the subject of The Dynasts.
Some of Hardy's more famous poems are from Poems 1912–13, which later became part of Satires of Circumstance (1914), written following the death of his wife Emma in 1912. They had been estranged for 20 years, and these lyric poems express deeply felt "regret and remorse".[51] Poems like "After a Journey", "The Voice" and others from this collection "are by general consent regarded as the peak of his poetic achievement".[47] In a 2007 biography on Hardy, Claire Tomalin argues that Hardy became a truly great English poet after the death of his first wife Emma, beginning with these elegies, which she describes as among "the finest and strangest celebrations of the dead in English poetry."[53]

Many of Hardy's poems deal with themes of disappointment in love and life, and "the perversity of fate", but the best of them present these themes with "a carefully controlled elegiac feeling".[54] Irony is an important element in a number of Hardy's poems, including "The Man He Killed" and "Are You Digging on My Grave".[52] A few of Hardy's poems, such as "The Blinded Bird", a melancholy polemic against the sport of vinkenzetting, reflect his firm stance against animal cruelty, exhibited in his antivivisectionist views and his membership in the Royal Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals.[55]
A number of notable English composers, including Gerald Finzi,[56][57] Benjamin Britten,[58] Ralph Vaughan Williams,[59] and Gustav Holst,[60] set poems by Hardy to music. Holst also wrote the orchestral tone poem Egdon Heath: A Homage to Thomas Hardy in 1927.
Although his poems were initially not as well received as his novels had been, Hardy is now recognised as one of the great poets of the 20th century, and his verse had a profound influence on later writers, including Robert Frost, W. H. Auden, Dylan Thomas and Philip Larkin.[50] Larkin included 27 poems by Hardy compared with only nine by T. S. Eliot in his edition of The Oxford Book of Twentieth Century English Verse in 1973.[61] There were fewer poems by W. B. Yeats.[62] Poet-critic Donald Davie's Thomas Hardy and English Poetry considers Hardy's contribution to ongoing poetic tradition at length and in creative depth. Davie's friend Thom Gunn also wrote on Hardy and acknowledged his stature and example.
Religious beliefs[edit]

Hardy's family was Anglican, but not especially devout. He was baptised at the age of five weeks and attended church, where his father and uncle contributed to music. He did not attend the local Church of England school, instead being sent to Mr Last's school, three miles away. As a young adult, he befriended Henry R. Bastow (a Plymouth Brethren man), who also worked as a pupil architect, and who was preparing for adult baptism in the Baptist Church. Hardy flirted with conversion, but decided against it.[63] Bastow went to Australia and maintained a long correspondence with Hardy, but eventually Hardy tired of these exchanges and the correspondence ceased. This concluded Hardy's links with the Baptists.
The irony and struggles of life, coupled with his naturally curious mind, led him to question the traditional Christian view of God:
The Christian God – the external personality – has been replaced by the intelligence of the First Cause...the replacement of the old concept of God as all-powerful by a new concept of universal consciousness. The 'tribal god, man-shaped, fiery-faced and tyrannous' is replaced by the 'unconscious will of the Universe' which progressively grows aware of itself and 'ultimately, it is to be hoped, sympathetic'.[64]
Scholars have debated Hardy's religious leanings for years, often unable to reach a consensus. Once, when asked in correspondence by a clergyman, Dr. A. B. Grosart, about the question of reconciling the horrors of human and animal life with "the absolute goodness and non-limitation of God",[65] Hardy replied,
Mr. Hardy regrets that he is unable to offer any hypothesis which would reconcile the existence of such evils as Dr. Grosart describes with the idea of omnipotent goodness. Perhaps Dr. Grosart might be helped to a provisional view of the universe by the recently published Life of Darwin and the works of Herbert Spencer and other agnostics.[66]
Hardy frequently conceived of, and wrote about, supernatural forces, particularly those that control the universe through indifference or caprice, a force he called The Immanent Will. He also showed in his writing some degree of fascination with ghosts and spirits.[66] Even so, he retained a strong emotional attachment to the Christian liturgy and church rituals, particularly as manifested in rural communities, that had been such a formative influence in his early years, and Biblical references can be found woven throughout many of Hardy's novels. Hardy's friends during his apprenticeship to John Hicks included Horace Moule (one of the eight sons of Henry Moule) and the poet William Barnes, both ministers of religion. Moule remained a close friend of Hardy's for the rest of his life, and introduced him to new scientific findings that cast doubt on literal interpretations of the Bible,[67] such as those of Gideon Mantell. Moule gave Hardy a copy of Mantell's book The Wonders of Geology (1848) in 1858, and Adelene Buckland has suggested that there are "compelling similarities" between the "cliffhanger" section from A Pair of Blue Eyes and Mantell's geological descriptions. It has also been suggested that the character of Henry Knight in A Pair of Blue Eyes was based on Horace Moule.[68]
Throughout his life, Hardy sought a rationale for believing in an afterlife or a timeless existence, turning first to spiritualists, such as Henri Bergson, and then to Albert Einstein and J. M. E. McTaggart, considering their philosophy on time and space in relation to immortality.[69]
Locations in novels[edit]
Sites associated with Hardy's own life and which inspired the settings of his novels continue to attract literary tourists and casual visitors. For locations in Hardy's novels see: Thomas Hardy's Wessex, and the Thomas Hardy's Wessex[70] research site, which includes maps.[71]
Influence[edit]
Hardy corresponded with and visited Lady Catherine Milnes Gaskell at Wenlock Abbey and many of Lady Catherine's books are inspired by Hardy, who was very fond of her.[72]
D. H. Lawrence's Study of Thomas Hardy (1914, first published 1936) indicates the importance of Hardy for him, even though this work is a platform for Lawrence's own developing philosophy rather than a more standard literary study. The influence of Hardy's treatment of character, and Lawrence's own response to the central metaphysic behind many of Hardy's novels, helped significantly in the development of The Rainbow (1915) and Women in Love (1920).[73]
Wood and Stone (1915), the first novel by John Cowper Powys, who was a contemporary of Lawrence, was "Dedicated with devoted admiration to the greatest poet and novelist of our age Thomas Hardy".[74] Powys's later novel Maiden Castle (1936) is set in Dorchester, which was Hardy's Casterbridge, and was intended by Powys to be a "rival" to Hardy's The Mayor of Casterbridge.[75] Maiden Castle is the last of Powys's so-called Wessex novels, Wolf Solent (1929), A Glastonbury Romance (1932) and Weymouth Sands (1934), which are set in Somerset and Dorset.[76]
Hardy was clearly the starting point for the character of the novelist Edward Driffield in W. Somerset Maugham's novel Cakes and Ale (1930).[77] Thomas Hardy's works also feature prominently in the American playwright Christopher Durang's The Marriage of Bette and Boo (1985), in which a graduate thesis analysing Tess of the d'Urbervilles is interspersed with analysis of Matt's family's neuroses.[78]
The symphonic poems Mai-Dun by John Ireland (1921) and Egdon Heath by Gustav Holst (1927) evoke the landscape of Hardy's novels.
Hardy has been a significant influence on Nigel Blackwell, frontman of the post-punk British rock band Half Man Half Biscuit, who has often incorporated phrases (some obscure) by or about Hardy into his song lyrics.[79][80]
Works[edit]

Prose[edit]
In 1912, Hardy divided his novels and collected short stories into three classes:[81]
Novels of character and environment[edit]
- The Poor Man and the Lady (1867, unpublished and lost)
- Under the Greenwood Tree: A Rural Painting of the Dutch School (1872)
- Far from the Madding Crowd (1874)
- The Return of the Native (1878)
- The Mayor of Casterbridge: The Life and Death of a Man of Character (1886)
- The Woodlanders (1887)
- Wessex Tales (1888, a collection of short stories)
- Tess of the d'Urbervilles: A Pure Woman Faithfully Presented (1891)
- Life's Little Ironies (1894, a collection of short stories)
- Jude the Obscure (1895)
Romances and fantasies[edit]
- A Pair of Blue Eyes: A Novel (1873)
- The Trumpet-Major (1880)
- Two on a Tower: A Romance (1882)
- A Group of Noble Dames (1891, a collection of short stories)
- The Well-Beloved: A Sketch of a Temperament (1897) (first published as a serial from 1892)
Novels of ingenuity[edit]
- Desperate Remedies: A Novel (1871)
- The Hand of Ethelberta: A Comedy in Chapters (1876)
- A Laodicean: A Story of To-day (1881)
Other[edit]
Hardy also produced minor tales; one story, The Spectre of the Real (1894) was written in collaboration with Florence Henniker.[82] An additional short-story collection, beyond the ones mentioned above, is A Changed Man and Other Tales (1913). His works have been collected as the 24-volume Wessex Edition (1912–13) and the 37-volume Mellstock Edition (1919–20). His largely self-written biography appears under his second wife's name in two volumes from 1928 to 1930, as The Early Life of Thomas Hardy, 1840–91 and The Later Years of Thomas Hardy, 1892–1928, now published in a critical one-volume edition as The Life and Work of Thomas Hardy, edited by Michael Millgate (1984).
Short stories[edit]
(with date of first publication)
- "How I Built Myself a House" (1865)
- "Destiny and a Blue Cloak" (1874)
- "The Thieves Who Couldn't Stop Sneezing" (1877)
- "The Duchess of Hamptonshire" (1878) (collected in A Group of Noble Dames)
- "The Distracted Preacher" (1879) (collected in Wessex Tales)
- "Fellow-Townsmen" (1880) (collected in Wessex Tales)
- "The Honourable Laura" (1881) (collected in A Group of Noble Dames)
- "What the Shepherd Saw" (1881) (collected in A Changed Man and Other Stories)
- "A Tradition of Eighteen Hundred and Four" (1882) (collected in Life's Little Ironies)
- "The Three Strangers" (1883) (collected in Wessex Tales)
- "The Romantic Adventures of a Milkmaid" (1883) (collected in A Changed Man and Other Stories)
- "Interlopers at the Knap" (1884) (collected in Wessex Tales)
- "A Mere Interlude" (1885) (collected in A Changed Man and Other Stories)
- "A Tryst at an Ancient Earthwork" (1885) (collected in A Changed Man and Other Stories)
- "Alicia's Diary" (1887) (collected in A Changed Man and Other Stories)
- "The Waiting Supper" (1887–88) (collected in A Changed Man and Other Stories)
- "The Withered Arm" (1888) (collected in Wessex Tales)
- "A Tragedy of Two Ambitions" (1888) (collected in Life's Little Ironies)
- "The First Countess of Wessex" (1889) (collected in A Group of Noble Dames)
- "Anna, Lady Baxby" (1890) (collected in A Group of Noble Dames)
- "The Lady Icenway" (1890) (collected in A Group of Noble Dames)
- "Lady Mottisfont" (1890) (collected in A Group of Noble Dames)
- "The Lady Penelope" (1890) (collected in A Group of Noble Dames)
- "The Marchioness of Stonehenge" (1890) (collected in A Group of Noble Dames)
- "Squire Petrick's Lady" (1890) (collected in A Group of Noble Dames)
- "Barbara of the House of Grebe" (1890) (collected in A Group of Noble Dames)
- "The Melancholy Hussar of The German Legion" (1890) (collected in Life's Little Ironies)
- "Absent-Mindedness in a Parish Choir" (1891) (collected in Life's Little Ironies)
- "The Winters and the Palmleys" (1891) (collected in Life's Little Ironies)
- "For Conscience' Sake" (1891) (collected in Life's Little Ironies)
- "Incident in the Life of Mr. George Crookhill" (1891) (collected in Life's Little Ironies)
- "The Doctor's Legend" (1891)
- "Andrey Satchel and the Parson and Clerk" (1891) (collected in Life's Little Ironies)
- "The History of the Hardcomes" (1891) (collected in Life's Little Ironies)
- "Netty Sargent's Copyhold" (1891) (collected in Life's Little Ironies)
- "On the Western Circuit" (1891) (collected in Life's Little Ironies)
- "A Few Crusted Characters: Introduction" (1891) (collected in Life's Little Ironies)
- "The Superstitious Man's Story" (1891) (collected in Life's Little Ironies)
- "Tony Kytes, the Arch-Deceiver" (1891) (collected in Life's Little Ironies)
- "To Please His Wife" (1891) (collected in Life's Little Ironies)
- "The Son's Veto" (1891) (collected in Life's Little Ironies)
- "Old Andrey's Experience as a Musician" (1891) (collected in Life's Little Ironies)
- "Our Exploits At West Poley" (1892–93)
- "Master John Horseleigh, Knight" (1893) (collected in A Changed Man and Other Stories)
- "The Fiddler of the Reels" (1893) (collected in Life's Little Ironies)
- "An Imaginative Woman" (1894) (collected in Wessex Tales, 1896 edition)
- "The Spectre of the Real" (1894)
- "A Committee-Man of 'The Terror'" (1896) (collected in A Changed Man and Other Stories)
- "The Duke's Reappearance" (1896) (collected in A Changed Man and Other Stories)
- "The Grave by the Handpost" (1897) (collected in A Changed Man and Other Stories)
- "A Changed Man" (1900) (collected in A Changed Man and Other Stories)
- "Enter a Dragoon" (1900) (collected in A Changed Man and Other Stories)
- "Blue Jimmy: The Horse Stealer" (1911)
- "Old Mrs. Chundle" (1929)
- "The Unconquerable"(1992)
Poetry collections[edit]
- Wessex Poems and Other Verses (1898)
- Poems of the Past and the Present (1901)
- Time's Laughingstocks and Other Verses (1909)
- Satires of Circumstance (1914)
- Moments of Vision (1917)
- Collected Poems (1919)
- Late Lyrics and Earlier with Many Other Verses (1922)
- Human Shows, Far Phantasies, Songs and Trifles (1925)
- Winter Words in Various Moods and Metres (1928)
- The Complete Poems (Macmillan, 1976)
- Selected Poems (Edited by Harry Thomas, Penguin, 1993)
- Hardy: Poems (Everyman's Library Pocket Poets, 1995)
- Thomas Hardy: Selected Poetry and Nonfictional Prose (St. Martin's Press, 1996)
- Selected Poems (Edited by Robert Mezey, Penguin, 1998)
- Thomas Hardy: The Complete Poems (Edited by James Gibson, Palgrave, 2001)
Online poems: Poems by Thomas Hardy[83] at Poetry Foundation and Poems by Thomas Hardy at poemhunter.com[84]
Drama[edit]
- The Dynasts: An Epic-Drama of the War with Napoleon (verse drama)
- The Dynasts, Part 1 (1904)
- The Dynasts, Part 2 (1906)
- The Dynasts, Part 3 (1908)
- The Famous Tragedy of the Queen of Cornwall at Tintagel in Lyonnesse (1923) (one-act play)
References[edit]
- ^ Taylor, Dennis (Winter 1986), "Hardy and Wordsworth", Victorian Poetry, 24 (4).
- ^ Watts, Cedric (2007). Thomas Hardy: 'Tess of the d'Urbervilles'. Humanities-Ebooks. pp. 13, 14.
- ^ "BBC – The Big Read" Archived 31 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine. BBC. April 2003, Retrieved 16 December 2016
- ^ Brown, Matt (28 December 2022). "The Hardy Tree Of St Pancras Has Fallen". Londonist. Retrieved 28 December 2022.
- ^ Copy of marriage certificate in Melbury Osmond parish church.
- ^ "Thomas Hardy: The Time-Torn Man". The Guardian. 13 October 2006. Archived from the original on 29 July 2017. Retrieved 13 December 2016.
- ^ Tomalin, Claire (2007), Thomas Hardy: the Time-torn Man, Penguin, pp. 30, 36.
- ^ Walsh, Lauren (2005), "Introduction", The Return of the Native, by Thomas Hardy (print), Classics, New York: Barnes & Noble.
- ^ Flood, Alison (16 August 2016). "Thomas Hardy altarpiece discovered in Windsor church". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 16 August 2016. Retrieved 17 August 2016.
- ^ "Legendary author Thomas Hardy's lost contribution to Windsor church uncovered". Royal Borough Observer. Archived from the original on 26 August 2016. Retrieved 17 August 2016.
- ^ Burley, Peter (2012). "When steam railroaded history". Cornerstone. 33 (1): 9.
- ^ Wilson, Keith (2009). A Companion to Thomas Hardy. John Wiley & Sons. p. 55.
- ^ Widdowson, Peter (2004). Thomas Hardy and Contemporary Literary Studies. Springer. p. 132.
- ^ Gibson, James (ed.) (1975) Chosen Poems of Thomas Hardy, London: Macmillan Education; p.9.
- ^ "FreeBMD Home Page". freebmd.org.uk. Archived from the original on 11 December 2020. Retrieved 22 May 2016.
- ^ Hardy, Emma (1961) Some Recollections by Emma Hardy; with some relevant poems by Thomas Hardy; ed. by Evelyn Hardy & R. Gittings. London: Oxford University Press
- ^ "Thomas Hardy – the Time-Torn Man" (a reading of Claire Tomalin's book of the same name), BBC Radio 4, 23 October 2006
- ^ “At home with the wizard” Archived 17 February 2018 at the Wayback Machine. The Guardian, Retrieved 10 July 2019
- ^ "Wiltshire Days Out – Thomas Hardy at Stourhead". BBC. Archived from the original on 9 March 2012. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ "No. 28393". The London Gazette. 8 July 1910. p. 4857.
- ^ "Nomination Database". April 2020. Archived from the original on 23 September 2017. Retrieved 14 June 2017.
- ^ Asaid, Alan (11 December 2012). "Yeats och Nobelpriset" (in Swedish). kulturdelen.com.
- ^ Wilson, Keith (1995). Thomas Hardy on Stage. The Macmillan Press. p. 29. ISBN 9780333598856.
- ^ Wilson, Keith (1995). Thomas Hardy on Stage. The Macmillan Press. p. 60. ISBN 9780333598856
- ^ Evans, Harold (1908). "A Souvenir of the Performances of the Play adapted from Mr. Thos. Hardy's Novel 'The Trumpet Major'". The Dorchester Debating and Dramatic Society.
- ^ Dean, Andrew R (February 1993). "The Sources of The Famous Tragedy of the Queen of Cornwall". Thomas Hardy Journal, the. 9 (1): 76–89. JSTOR 45274094 – via JSTOR.
- ^ "1914 Authors' Manifesto Defending Britain's Involvement in WWI, Signed by H.G. Wells and Arthur Conan Doyle". Slate. Archived from the original on 27 February 2020. Retrieved 27 February 2020.
- ^ a b Sherman, George William (1976). The Pessimism of Thomas Hardy. Fairleigh Dickinson Univ Press. p. 447.
- ^ Bradford, Charles Angell (1933). Heart Burial. London: Allen & Unwin. p. 246. ISBN 978-1-162-77181-6.
- ^ From Probate Index for 1928: "Hardy O. M. Thomas of Max Gate Dorchester Dorsetshire died 11 January 1928 Probate London 22 February to Lloyds Bank Limited Effects £90707 14s 3d Resworn £95418 3s 1d."
- ^ a b "Homeground: Dead man talking". BBC Online. 20 August 2003. Archived from the original on 31 August 2004. Retrieved 12 August 2006.
- ^ Steele, Bruce, ed. (1985) [1914], "Literary criticism and metaphysics", Study of Thomas Hardy and other essays, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-25252-0.
- ^ "The Novels of Thomas Hardy", The Common Reader, 2nd series.
- ^ a b J. B. Bullen (24 June 2013). Thomas Hardy: The World of his Novels. Frances Lincoln. p. 143. ISBN 978-1-78101-122-5.
- ^ Widdowson, Peter (2018). Thomas Hardy. Oxford University Press. p. 27.
- ^ Thomas Hardy (17 November 2013). Delphi Complete Works of Thomas Hardy (Illustrated). Delphi Classics. pp. 570–. ISBN 978-1-908909-17-6. Archived from the original on 19 August 2020. Retrieved 16 October 2016.
- ^ Emily Nussbaum. "The curious staying power of the cliffhanger". The New Yorker. 10 July 2019.
- ^ Trish Ferguson, Thomas Hardy's Legal Fictions, Edinburgh University Press, 2013.
- ^ "Curiosities of Sturminster Newton – Dorset Life – The Dorset Magazine". dorsetlife.co.uk. Archived from the original on 10 November 2017. Retrieved 9 November 2017.
- ^ Hardy, Thomas (1998). Jude the Obscure. Penguin Classics. p. 466. ISBN 0-14-043538-7. Archived from the original on 15 September 2022. Retrieved 16 October 2016.
- ^ a b "Thomas Hardy", The Norton Anthology of English Literature, 7th edition, vol. 2. New York: W.W. Norton, 2000, p.1916.
- ^ Larkin, Philip 1983, "Wanted: Good Hardy Critic" in Required Writing, London: Faber and Faber.
- ^ Geoffrey Harvey, Thomas Hardy: The Complete Critical Guide to Thomas Hardy. New York: Routledge, 2003, p.108.
- ^ "Far from the Madding Crowd, Thomas Hardy – Introduction (Twentieth-Century Literary Criticism. Ed. Linda Pavlovski. Vol. 153. Gale Group, Inc.,)". Enotes.com. Archived from the original on 15 January 2010. Retrieved 7 September 2009.
- ^ "Introduction" to the Penguin edition of Jude the Obscure (1978). Harmondsworth: Penguin Books, 1984, p.13.
- ^ Rumens, Carol (28 December 2009). "Poem of the week: The Darkling Thrush, by Thomas Hardy". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 9 August 2023.
- ^ a b "Thomas Hardy (British writer) – Encyclopædia Britannica". Britannica.com. 6 November 2013. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ "Thomas Hardy", The Bloomsbury Guide to English Literature, ed. Marion Wynne Davies. New York: Prentice Hall, 1990, p.583.
- ^ The Bloomsbury Guide, p. 583.
- ^ a b "Thomas Hardy | Academy of American Poets". Poets.org. 11 January 1928. Archived from the original on 14 April 2014. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ a b c Axelrod, Jeremy. "Thomas Hardy". The Poetry Foundation. Archived from the original on 27 May 2014. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ a b Katherine Kearney Maynard, Thomas Hardy's Tragic Poetry: The Lyrics and The Dynasts. Iowa City: University of Iowa Press, 1991, pp. 8–12.
- ^ Tomalin, Claire. "Thomas Hardy." New York: Penguin, 2007.
- ^ The Norton Anthology of English Literature, 7th edition, vol. 2, p. 1916.
- ^ Herbert N. Schneidau (1991). Waking Giants: The Presence of the Past in Modernism. Oxford University Press. p. 35. ISBN 978-0-19-506862-7. Retrieved 16 April 2008.
the blinded bird.
(Google Books) - ^ Song cycle Earth and Air and Rain (1936)
- ^ "Biography " Gerald Finzi Official Site". Geraldfinzi.com. 27 September 1956. Archived from the original on 10 November 2017. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ Song cycle Winter Words (1953)
- ^ Cantata Hodie (1954)
- ^ "Gustav Holst (Vocal Texts and Translations for Composer Gustav Holst)". LiederNet Archive. Archived from the original on 14 September 2018. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ "Poetry.org". Poets.org. 11 January 1928. Archived from the original on 14 April 2014. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ "Thomas Hardy", The Norton Anthology of English Literature, 7th edition, vol.2, p. 1916.
- ^ Claire Tomalin. Thomas Hardy, The Time Torn Man (Penguin, 2007), pp. 46–47.
- ^ Wotton, G. (1985), Thomas Hardy: Towards A Materialist Criticism, Lanham: Rowman & Littlefield, p.36
- ^ Florence Emily Hardy, The Early Life of Thomas Hardy, 1840–1891, p. 269
- ^ a b Ellman, Richard, & O'Clair, Robert (eds.) 1988. "Thomas Hardy" in The Norton Anthology of Modern Poetry, Norton, New York.
- ^ "Pearson Literature: Biography: Thomas Hardy". Archived from the original on 22 June 2013. Retrieved 15 April 2008.
- ^ "Adelene Buckland: Thomas Hardy, Provincial Geology and the Material Imagination". Archived from the original on 1 April 2011. Retrieved 10 December 2011.
- ^ Trish Ferguson. "Time's Renewal": Death and Immortality in Thomas Hardy's Emma poems, Literature and Modern Time: Technological Modernity, Glimpses of Eternity, Experiments with Time, Palgrave, 2020.
- ^ "Thomas Hardy's Wessex". St-andrews.ac.uk. Archived from the original on 28 February 2013. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ "Thomas Hardy's Wessex: The Evolution of Wessex". St-andrews.ac.uk. Archived from the original on 2 May 2013. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ Gamble, Cynthia, 2015 Wenlock Abbey 1857–1919: A Shropshire Country House and the Milnes Gaskell Family, Ellingham Press.
- ^ Terry R. Wright. "Hardy's Heirs: D. H. Lawrence and John Cowper Powys" in A Companion to Thomas Hardy. Chichester, Sussex: John Wiley, 2012.[1] Archived 11 April 2021 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Terry R. Wright. "Hardy's Heirs: D. H. Lawrence and John Cowper Powys"
- ^ Morine Krissdottir, Descents of Memory: The Life of John Cowper Powys. (New York: Overlook Duckworth, 2007), p. 312.
- ^ Herbert Williams, John Cowper Powys. (Bridgend, Wales: Seren, 1997), p. 94.
- ^ "Cakes and Ale". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online Academic Edition. Encyclopædia Britannica Inc. 2015. Retrieved 26 April 2015.
- ^ Christopher Durang. The Marriage of Bette and Boo. New York: Grove Press, 1987.[2] Archived 15 September 2022 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Sampson, Kevin (21 July 2001). "Taking the biscuit". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 27 December 2019. Retrieved 27 December 2019.
- ^ See for example the song title "Thy Damnation Slumbereth Not", which is a quotation from Thomas Hardy's novel Tess of the d'Urbervilles,Hardy, Thomas (1891). Tess of the d'Urbervilles. Chapter 12. Archived from the original on 21 February 2015. Retrieved 21 February 2015. which is itself an adaptation of the Second Epistle of Peter at 2:3: "Their damnation slumbereth not".
- ^ Gilmore, Dehn (2014). The Victorian Novel and the Space of Art: Fictional Form on Display. Cambridge University Press. p. 207.
- ^ Purdy, Richard (October 1944). "Thomas Hardy And Florence Henniker: The Writing Of "The Spectre of the Real". Colby Library Quarterly. 1 (8): 122–6. Archived from the original on 24 May 2014. Retrieved 7 September 2013.
- ^ Axelrod, Jeremy. "Thomas Hardy". The Poetry Foundation. Archived from the original on 10 July 2010. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ “Thomas Hardy poems” Archived 22 June 2010 at the Wayback Machine.
Biographies and criticism[edit]
- Armstrong, Tim. "Player Piano: Poetry and Sonic Modernity" in Modernism/Modernity 14.1 (January 2007), 1–19.
- Beatty, Claudius J.P. Thomas Hardy: Conservation Architect. His Work for the Society for the Protection of Ancient Buildings. Dorset Natural History and Archaeological Society 1995. ISBN 0-900341-44-0
- Blunden, Edmund. Thomas Hardy. New York: St. Martin's, 1942.
- Brady, Kristen. The Short Stories of Thomas Hardy. London: Macmillan, 1982.
- Boumelha, Penny. Thomas Hardy and Women. New Jersey: Barnes and Noble, 1982.
- Brennecke, Jr., Ernest. The Life of Thomas Hardy. New York: Greenberg, 1925.
- Cecil, Lord David. Hardy the Novelist. London: Constable, 1943.
- D'Agnillo, Renzo, "Music and Metaphor in Under the Greenwood Tree, in The Thomas Hardy Journal, 9, 2 (May 1993), pp.39–50.
- D'Agnillo, Renzo, "Between Belief and Non-Belief: Thomas Hardy’s 'The Shadow on the Stone'”, in Thomas Hardy, Francesco Marroni and Norman Page (eds), Pescara, Edizioni Tracce, 1995, pp. 197–222.
- Deacon, Lois and Terry Coleman. Providence and Mr. Hardy. London: Hutchinson, 1966.
- Draper, Jo. Thomas Hardy: A Life in Pictures. Wimborne, Dorset: The Dovecote Press.
- Ellman, Richard & O'Clair, Robert (eds.) 1988. "Thomas Hardy" in The Norton Anthology of Modern Poetry, Norton, New York.
- Gatrell, Simon. Hardy the Creator: A Textual Biography. Oxford: Clarendon, 1988.
- Gibson, James. Thomas Hardy: A Literary Life. London: Macmillan, 1996.
- Gibson, James. Thomas Hardy: Interviews and Recollections. London: Macmillan, 1999; New York: St Martin's Press, 1999.
- Gittings, Robert. Thomas Hardy's Later Years. Boston : Little, Brown, 1978.
- Gittings, Robert. Young Thomas Hardy. Boston : Little, Brown, 1975.
- Gittings, Robert and Jo Manton. The Second Mrs Hardy. London: Heinemann, 1979.
- Gossin, P. Thomas Hardy's Novel Universe: Astronomy, Cosmology, and Gender in the Post-Darwinian World. Aldershot, Ashgate, 2007 (The Nineteenth Century Series).
- Halliday, F. E. Thomas Hardy: His Life and Work. Bath: Adams & Dart, 1972.
- Hands, Timothy. Thomas Hardy : Distracted Preacher? : Hardy's religious biography and its influence on his novels. New York: St. Martin's Press, 1989.
- Hardy, Evelyn. Thomas Hardy: A Critical Biography. London: Hogarth Press, 1954.
- Hardy, Florence Emily. The Early Life of Thomas Hardy, 1840–1891. London: Macmillan, 1928.
- Hardy, Florence Emily. The Later Years of Thomas Hardy, 1892–1928 London: Macmillan, 1930.
- Harvey, Geoffrey. Thomas Hardy: The Complete Critical Guide to Thomas Hardy. New York: Routledge (Taylor & Francis Group), 2003.
- Hawkins, Desmond. Thomas Hardy. London: Arthur Barker, 1950. (The English Novelists series)
- Hedgcock, F. A., Thomas Hardy: penseur et artiste. Paris: Librairie Hachette, 1911.
- Holland, Clive. Thomas Hardy O.M.: The Man, His Works and the Land of Wessex. London: Herbert Jenkins, 1933.
- Jedrzejewski, Jan. Thomas Hardy and the Church. London: Macmillan, 1996.
- Johnson, Lionel Pigot. The Art of Thomas Hardy (London: E. Mathews, 1894).
- Kay-Robinson, Denys. The First Mrs Thomas Hardy. London: Macmillan, 1979.
- Langbaum, Robert. "Thomas Hardy in Our Time." New York: St. Martin's Press, 1995, London: Macmillan, 1997.
- Marroni, Francesco, "The Negation of Eros in 'Barbara of the House of Grebe' ", in "Thomas Hardy Journal", 10, 1 (February 1994) pp. 33–41
- Marroni, Francesco and Norman Page (eds.), Thomas Hardy. Pescara: Edizioni Tracce, 1995.
- Marroni, Francesco, La poesia di Thomas Hardy. Bari: Adriatica Editrice, 1997.
- Marroni, Francesco, "The Poetry of Ornithology in Keats, Leopardi, and Hardy: A Dialogic Analysis", in "Thomas Hardy Journal", 14, 2 (May 1998) pp. 35–44
- Millgate, Michael (ed.). The Life and Work of Thomas Hardy by Thomas Hardy. London: Macmillan, 1984.
- Millgate, Michael. Thomas Hardy: A Biography. New York: Random House, 1982.
- Millgate, Michael. Thomas Hardy: A Biography Revisited. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2004.
- Morgan, Rosemarie, (ed) The Ashgate Research Companion to Thomas Hardy, (Ashgate publishing), 2010.
- Morgan, Rosemarie, (ed) The Hardy Review,(Maney Publishing), 1999–.
- Morgan, Rosemarie, Student Companion to Thomas Hardy (Greenwood Press), 2006.
- Morgan, Rosemarie, Cancelled Words: Rediscovering Thomas Hardy (Routledge, Chapman & Hall),1992
- Morgan, Rosemarie, Women and Sexuality in the Novels of Thomas Hardy (Routledge & Kegan Paul), 1988; paperback: 1990.
- Musselwhite, David, Social Transformations in Hardy's Tragic Novels: Megamachines and Phantasms, Palgrave Macmillan, 2003.
- Norman, Andrew. Behind the Mask, History Press, 2011. ISBN 978-0-7524-5630-0
- O'Sullivan, Timothy. Thomas Hardy: An Illustrated Biography. London: Macmillan, 1975.
- Orel, Harold. The Final Years of Thomas Hardy, 1912–1928. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas, 1976.
- Orel, Harold. The Unknown Thomas Hardy. New York: St. Martin's, 1987.
- Page, Norman, ed. Thomas Hardy Annual. No.1: 1982; No.2: 1984; No.3: 1985; No.4:1986; No.5; 1987. London: Macmillan, 1982–1987.
- Phelps, Kenneth. The Wormwood Cup: Thomas Hardy in Cornwall. Padstow: Lodenek Press, 1975.
- Pinion, F. B. Thomas Hardy: His Life and Friends. London: Palgrave, 1992.
- Pite, Ralph. Thomas Hardy: The Guarded Life. London: Picador, 2006.
- Saxelby, F. Outwin. A Thomas Hardy dictionary : the characters and scenes of the novels and poems alphabetically arranged and described (London: G. Routledge, 1911).
- Seymour-Smith, Martin. Hardy. London: Bloomsbury, 1994.
- Stevens-Cox, J. Thomas Hardy: Materials for a Study of his Life, Times, and Works. St. Peter Port, Guernsey: Toucan Press, 1968.
- Stevens-Cox, J. Thomas Hardy: More Materials for a Study of his Life, Times, and Works. St. Peter Port, Guernsey: Toucan Press, 1971.
- Stewart, J. I. M. Thomas Hardy: A Critical Biography. New York: Dodd, Mead & Co., 1971.
- Taylor, Richard H. The Neglected Hardy: Thomas Hardy's Lesser Novels. London: Macmillan; New York: St Martin's Press, 1982.
- Taylor, Richard H., ed. The Personal Notebooks of Thomas Hardy. London: Macmillan, 1979.
- Tomalin, Claire. Thomas Hardy. New York: Penguin Press, 2006.
- Turner, Paul. The Life of Thomas Hardy: A Critical Biography. Oxford: Blackwell, 1998.
- Weber, Carl J. Hardy of Wessex, His Life and Literary Career. New York: Columbia University Press, 1940.
- Wilson, Keith. Thomas Hardy on Stage. London: Macmillan, 1995.
- Wilson, Keith, ed. Thomas Hardy Reappraised: Essays in Honour of Michael Millgate. Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 2006.
- Wilson, Keith, ed. A Companion to Thomas Hardy. Wiley-Blackwell, 2009.
- Wotton, George. Thomas Hardy: Towards A Materialist Criticism. Lanham: Rowman & Littlefield, 1985.
External links[edit]
- Digital collections
- Works by Thomas Hardy in eBook form at Standard Ebooks
- Works by Thomas Hardy at Project Gutenberg
- Works by or about Thomas Hardy at Internet Archive
- Works by Thomas Hardy at LibriVox (public domain audiobooks)

- Thomas Hardy at the Poetry Foundation
- A Hyper-Concordance to the Works of Thomas Hardy at the Victorian Literary Studies Archive, Nagoya University, Japan
- Physical collections
- Dorset Museum, Dorchester, Dorset, contains the largest Hardy collections in the world, donated directly to the Museum by the Hardy family and inscribed on the UNESCO Memory of the World register for the United Kingdom.
- Thomas Hardy Collection at the Harry Ransom Center at the University of Texas at Austin
- Thomas Hardy at the British Library
- Letter from Hardy to Bertram Windle, transcribed by Birgit Plietzsch, from Collected Letters, vol 2, pp.131–133. Retrieved 25 May 2015.
- Biographical information
- Geographic information
- Hardy's Cottage National Trust visitor information for Hardy's birthplace.
- Hardy Country A visitor guide for 'Hardy Country' in Dorset (sites of interest).
- Max Gate National Trust visitor information for Max Gate (the home Hardy designed, lived and died in).
- Other links
- The Thomas Hardy Association (TTHA)
- The Thomas Hardy Society
- The New Hardy Players Theatrical group specialising in the works of Thomas Hardy.
- Newspaper clippings about Thomas Hardy in the 20th Century Press Archives of the ZBW
- Thomas Hardy at Curlie
- The Dynasts on Great War Theatre
- Thomas Hardy
- 1840 births
- 1928 deaths
- 19th-century British short story writers
- 19th-century English novelists
- 19th-century English poets
- 20th-century English writers
- Alumni of King's College London
- Anti-vivisectionists
- British male poets
- Burials at Westminster Abbey
- English male novelists
- English male short story writers
- English short story writers
- Fellows of the Royal Society of Literature
- Members of the Order of Merit
- Pantheists
- People from Dorchester, Dorset
- Philosophers of pessimism
- Victorian novelists
- Victorian poets
- Presidents of the Society of Authors




