Invention of radio: Difference between revisions
Nonsense about tuned circuits removed from header. See talk page please. |
Undid revision 233129042 by Martin Hogbin (talk) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
: ''"Great Radio Controversy" redirects here. For the album by the band Tesla, see'' [[The Great Radio Controversy]] |
: ''"Great Radio Controversy" redirects here. For the album by the band Tesla, see'' [[The Great Radio Controversy]] |
||
{{TOCright}} |
{{TOCright}} |
||
Within the [[timeline of radio]], many people were involved in the '''invention of radio''' transmission of information as we know it today. Despite this, during its early development and long after wide use of the technology, disputes persisted as to who could claim sole credit for this obvious boon to mankind. Closely related, radio was developed after two other key inventions, the [[telegraph]] and the [[telephone]].<ref name="inventorsaboutcom">[http://inventors.about.com/od/rstartinventions/a/radio.htm The Invention of Radio] inventors.about.com/od/rstartinventions/a/radio.htm </ref> Radio development began as "[[wireless telegraphy]]". <ref name="inventorsaboutcom" /> |
Within the [[timeline of radio]], many people were involved in the '''invention of radio''' transmission of information as we know it today. Despite this, during its early development and long after wide use of the technology, disputes persisted as to who could claim sole credit for this obvious boon to mankind. Closely related, radio was developed after two other key inventions, the [[telegraph]] and the [[telephone]].<ref name="inventorsaboutcom">[http://inventors.about.com/od/rstartinventions/a/radio.htm The Invention of Radio] inventors.about.com/od/rstartinventions/a/radio.htm </ref> Radio development began as "[[wireless telegraphy]]". <ref name="inventorsaboutcom" /> A [[radio communication system]] requires two tuned circuits each at the transmitter and receiver, all four tuned to the same frequency.<ref>320 U.S. 1. Marconi Wireless Telegraph co. of America v. United States</ref><ref>Cheney, M., Uth, R., & Glenn, J. (1999). Tesla, master of lightning. New York: Barnes & Noble Books. Page 71.</ref> |
||
==Wireless work and engineering== |
==Wireless work and engineering== |
||
===Scientific theory and verification=== |
===Scientific theory and verification=== |
||
| Line 335: | Line 336: | ||
;People: [[Edwin Howard Armstrong]], [[John Stone Stone]], [[Ernst Alexanderson]], [[Reginald Fessenden]], [[Oliver Lodge]], |
;People: [[Edwin Howard Armstrong]], [[John Stone Stone]], [[Ernst Alexanderson]], [[Reginald Fessenden]], [[Oliver Lodge]], |
||
;Radio: [[Timeline of radio]], [[list of oldest radio stations|Oldest radio station]], [[Birth of public radio broadcasting]] |
;Radio: [[[Radio communication system]], [[Timeline of radio]], [[list of oldest radio stations|Oldest radio station]], [[Birth of public radio broadcasting]] |
||
; Categories: [[:Category:Radio people|Radio People]], [[:Category:Radio pioneers|Radio Pioneers]], [[:Category:Discovery and invention controversies|Discovery and invention controversies]] |
; Categories: [[:Category:Radio people|Radio People]], [[:Category:Radio pioneers|Radio Pioneers]], [[:Category:Discovery and invention controversies|Discovery and invention controversies]] |
||
;Other: [[Radiotelegraph]] and [[Spark-Gap Transmitter]]s, [[The Great Radio Controversy]], [[Induction coil]], [[Ruhmkorff coil]], [[Poldhu]], [[Alexanderson alternator]], [[De Forest tube]] |
;Other: [[Radiotelegraph]] and [[Spark-Gap Transmitter]]s, [[The Great Radio Controversy]], [[Induction coil]], [[Ruhmkorff coil]], [[Poldhu]], [[Alexanderson alternator]], [[De Forest tube]] |
||
{{Morse code}} |
{{Morse code}} |
||
Revision as of 15:37, 20 August 2008
- This article covers the main arguments about who had what part in the early development of radio.
- For the general history of radio, see History of radio.
- "Great Radio Controversy" redirects here. For the album by the band Tesla, see The Great Radio Controversy
Within the timeline of radio, many people were involved in the invention of radio transmission of information as we know it today. Despite this, during its early development and long after wide use of the technology, disputes persisted as to who could claim sole credit for this obvious boon to mankind. Closely related, radio was developed after two other key inventions, the telegraph and the telephone.[1] Radio development began as "wireless telegraphy". [1] A radio communication system requires two tuned circuits each at the transmitter and receiver, all four tuned to the same frequency.[2][3]
Wireless work and engineering
Scientific theory and verification
James Clerk Maxwell performed the theoretical physical research that correctly predicted the existence of radio (and all other electromagnetic) waves. Heinrich Rudolf Hertz was the experimental physicist who confirmed Maxwell's work.[4] He transmitted and received radio waves in a controlled laboratory manner. Neither Maxwell nor Hertz, though, devised systems for actual general use or described the application of the technology.
Developments, parallel to these individuals and after, are engineering investigations that lead to the 'invention of radio': the objects, processes, or techniques of information transception. Many individuals contributed to the art of wireless, in the air, earth, and water; this includes the precursory work in wireless telephony and wireless telegraphy
SLF and UHF experimentation
David E. Hughes, years before Hertz's experiments and nearly two decades before Guglielmo Marconi's demonstrations, induced electromagnetic waves in a signalling system. Hughes transmitted Morse code by an induction apparatus. In 1879, Hughes's induction transmission method utilized a "clockwork transmitter" to transmit signals. In 1885, T. A. Edison used a vibrator magnet for induction transmission. In 1888, Edison deployed a system of signalling on the Lehigh Valley Railroad. In 1892, Edison attained the wireless patent for this method using inductance (U.S. patent 465,971).
From 1886 to 1888 inclusive in his classic UHF experiments, Heinrich Hertz had proved that the properties of radio waves were consistent with Maxwell’s electromagnetic theory. He demonstrated that radio radiation had all the properties of waves (now called Hertzian waves), and discovered that the electromagnetic equations could be reformulated into a partial differential equation called the wave equation.
Of the three basic forms of wireless aerial launching structures, the Hertz antenna was a center-fed half-wavelength dipole (with the other forms being the Marconi antenna and Tesla antenna). Hertz’s setup for a source and detector of radio waves (archaically called Hertzian waves[5] or Hertz waves in his honor), comprised a primitive radio system capable of transmitting and receiving space waves through free space.[6] His transmitter was not at all efficient and was severely limited in power output. Its dipole antenna differed from the vertical quarter-wavelength antenna that was subsequently adopted by Marconi and others in that it was not grounded.[7]
Hertz used the damped oscillating currents in a dipole antenna, triggered by a high-voltage electrical capacitive spark discharge, as his source of radio waves. His detector in some experiments was another dipole antenna connected to a narrow spark gap. A small spark in this gap signified detection of the radio wave. When he added cylindrical reflectors behind his dipole antennas, Hertz could detect radio waves about 20 metres from the transmitter in his laboratory. He did not try to transmit further because he wanted to prove electromagnetic theory, not to develop wireless communications.
Hertz seemed uninterested in the practical importance of his experiments. He stated that "It's of no use whatsoever ... this is just an experiment that proves Maestro Maxwell was right - we just have these mysterious electromagnetic waves that we cannot see with the naked eye. But they are there."[8] Asked about the ramifications of his discoveries, Hertz replied, "Nothing, I guess." Hertz also stated, "I do not think that the wireless waves I have discovered will have any practical application."[8] Hertz died in 1894, so the art of radio was left to others to implement into a practical useful form. His discoveries would later be taken up by entrepreneurs looking to make their fortunes. Marconi's 1895 experiments followed Hertz's work (among others') by using a spark source in what became known as a spark-gap transmitter.
Tesla's work

Radio frequency generation
The electromechanical engineer Nikola Tesla, called the father of wireless telegraphy,[10] was one of the first to patent a means to reliably produce radio frequency waves. Tesla's U.S. patent 447,920, "Method of Operating Arc-Lamps" (March 10, 1891), describes an alternator that produced high-frequency (for that time period) current of around 10,000 cycles per second. (The term cycles-per-second was later changed to "hertz.") His patentable innovation was suppression of the sound produced by arc lamps that were operated on alternating or pulsating current by using frequencies beyond the range of human hearing. The alternator produced frequencies in the Very Low Frequency (VLF) band.
Continued research and patents
Around July 1891, he established his New York laboratory and constructed various apparatuses that produced between 15,000 to 18,000 cycles per second. At this location, he also lit vacuum tubes wirelessly (thus providing hard evidence for the potential of wireless transmissions). Transmission and radiation of radio frequency energy was a feature exhibited in the experiments by Tesla and was noted early on to be used for the telecommunication of information.[11][12]
After 1892, Tesla delivered a widely reported presentation before the Institution of Electrical Engineers of London in which he noted, among other things, that intelligible messages could be transmitted without wires. Later, a variety of Tesla's radio frequency systems were demonstrated during another widely known lecture, presented to meetings of the National Electric Light Association in St. Louis, Missouri and the Franklin Institute in Philadelphia. According to the IEEE, "the apparatus that he employed contained all the elements of spark and continuous wave that were incorporated into radio transmitters before the advent of the vacuum tube".[13] However, "he almost perversely rejected the notion of transmission by Hertzian waves, which he considered to be wasteful of energy."[13][14][15] Wireless transmissions could be done by "Hertzian" waves with his devices acting as a radiator, but Tesla claimed to be using longitudinal waves as more desirable (setting up standing surface waves through resonance).
Between 1895 and 1899, Tesla received wireless signals transmitted from actions at long distances.[16][17] After 1896, the transmitter consisted of an RF alternator and produced undamped (or continuous) waves in the neighborhood of 50,000 cycles per second.[18] The receiver consisted of a powerful electromagnet, two large condensers, and a taut steel wire. The wire was placed within the magnetic field, and in conjunction with the condensers formed a tuned circuit.[19][20] In 1899 Tesla established an "Experimental Station" in Colorado Springs where he continued his research into wireless transmission principles often using a form of electrical oscillator known as the magnifying transmitter.

An early Tesla transmitter consisting of a flat-spiral quarter-wave resonator and an elevated terminal. This image is from one of Tesla's patents.
Early on in his research Tesla used his high voltage resonance transformer — the Tesla coil[21] — in radio-wave propagation experiments. The aerial consisted of a top-loaded electrical conductor that was connected to a high-voltage terminal of the transformer. The opposing high-voltage terminal was grounded. The secondary winding was driven by a primary circuit consisting of a few turns of heavy wire, a capacitor bank, a circuit controller, and a power supply transformer. The launching structure radiated as a common "Hertz wave" antenna. In Tesla's own words,
"The popular impression is that my wireless work was begun in 1893, but as a matter of fact I spent the two preceding years in investigations, employing forms of apparatus, some of which were almost like those of today. . . ."[22]
After a while he began to favor another technique that he called the “disturbed charge of ground and air method.” Tesla's wireless system used the same basic apparatus, however instead of using electromagnetic space waves the energy is carried by the conduction of electrical currents through the earth and along with accompanying surface waves. In one form of the system the ‘return’ path closing the circuit is an electrical current flow established between two elevated terminals, one belonging to the transmitter and the other the receiver. These consist of conduction currents flowing through plasma and also electrostatic induction. Once again in Tesla's own words,
"... It was clear to me from the very start that the successful consummation could only be brought about by a number of radical improvements. Suitable high frequency generators and electrical oscillators had first to be produced. The energy of these had to be transformed in effective transmitters and collected at a distance in proper receivers. Such a system would be manifestly circumscribed in its usefulness if all extraneous interference were not prevented and exclusiveness secured. In time, however, I recognized that devices of this kind, to be most effective and efficient, should be designed with due regard to the physical properties of this planet and the electrical conditions obtaining on the same ..."[23]
In other words, Tesla’s structure injected a large alternating current into the earth via the ground terminal. Tesla's discovery of importance was the "Surface wave" method. The production of surface waves as described by Arnold Sommerfeld and Jonathan Zenneck was partially the consequence of adding a deep ground connection to the transmitter. Tesla said in 1893 that "One of the terminals of the source would be connected to Earth [as a electric ground connection ...] the other to an insulated body of large surface.[24]
A shallow buried ground plane or an elevated insulated counterpoise is commonly used in the construction of low and medium frequency 1/4-wavelength radio antennas. These lend to the development of the Norton Surface Wave. This method led to longer transmission ranges. Many AM stations use this same principle to boost reception of their signals.[25] This also allows modern grounded AM 1/4 wavelength monopole antennas to be more practical in order to overcome the restrictions imposed upon designers by the large physical dimensions required for these structures.
Radio antennas radiate electromagnetic waves that can reach the receiver either by ground-wave propagation or by refraction from the ionosphere, known as sky-wave propagation. The ground-wave component is the portion of the radiated electromagnetic wave that propagates close to the earth's surface. It has both direct-wave and ground-reflected components, and under certain conditions a tropospheric ducting component. The direct-wave is limited only by the distance from the transmitter to the horizon plus a small distance added by atmospheric diffraction around the curvature of the earth. The ground-reflected portion of the radiated wave reaches the receiving antenna after being reflected from the earth's surface. A portion of the ground-wave energy radiated by the antenna may also be guided by the earth's surface as a ground-hugging surface wave.
Nikola Tesla's rights to radio were based upon these patents:
- Division of U.S. patent 645,576 "System of Transmission of Electrical Energy", March 20, 1900 (March 20, 1900; filed Sept. 2, 1897). In US645576, Tesla cited the well-known radiant energy phenomena and corrected previous errors in theory of behavior. Within this specification, Tesla declared, "The apparatus which I have shown will obviously have many other valuable uses - as, for instance, when it is desired to transmit intelligible messages to great distances [...]".
- U.S. patent 649,621, "Apparatus for Transmission of Electrical Energy" (May 15, 1900; filed February 19, 1900). In US649621, Tesla established a system which was composed of a transmitting coil (or conductor) arranged and excited to cause oscillations (or currents) to propagate via conduction through the natural medium from one point to another remote point therefrom and a receiver coil, or conductor, of the transmitted signals.
Popov's work
Beginning in the early 1890s, Alexander Stepanovich Popov conducted experiments along the lines of Hertz's research. In 1894 he built his first radio receiver, which contained a coherer. Further refined as a lightning detector, he presented it to the Russian Physical and Chemical Society on May 7, 1895 — the day has been celebrated in the Russian Federation as "Radio Day". The paper on his findings was published the same year (December 15 1895). Popov had recorded, at the end of 1895, that he was hoping for distant signaling with radio waves.[26] In 1900, Popov stated (in front of the Congress of Russian Electrical Engineers),
- "[...] the emission and reception of signals by Marconi by means of electric oscillations [was] nothing new. In America, the famous engineer Nikola Tesla carried the same experiments in 1893."[27]
Bose's work

In November 1894, the Bengali Indian physicist, Jagdish Chandra Bose, demonstrated publicly the use of radio waves in Calcutta, but he was not interested in patenting his work.[28] In 1894, Bose ignited gunpowder and rang a bell at a distance using electromagnetic waves, showing independently that communication signals can be sent without using wires. In 1896, the Daily Chronicle of England reported on his UHF experiments: "The inventor (J.C. Bose) has transmitted signals to a distance of nearly a mile and herein lies the first and obvious and exceedingly valuable application of this new theoretical marvel." The 1895 public demonstration by Bose in Calcutta was before Marconi's wireless signalling experiment on Salisbury Plain in England in May 1897.[29][30] Bose did his demonstration shortly after Tesla had performed radio communication earlier in 1892 and 1893.
Bose was not interested in the commercial applications of the experiment's transmitter. He did not try to file patent protection for sending signals. In 1899, Bose announced the development of a "iron-mercury-iron coherer with telephone detector" in a paper presented at the Royal Society, London.[31] Later he received U.S. patent 755,840, "Detector for electrical disturbances" (1904), for a specific electromagnetic receiver. Though he did not file any patents for transmission, he is recognized for contributing to the development of radio.
Guglielmo Marconi's work
Early years

Guglielmo Marconi's proponents say that while he was on vacation in 1894 he read about the experiments that Hertz did in the 1880s, and about Nikola Tesla's work in the just-published book Inventions, Researches and Writings of Nikola Tesla. It was at this time that Marconi began to understand that radio waves could be used for wireless communications.[32] It is impossible, though, that Marconi was unaware of Tesla's work.[33][34][35]
Marconi's early apparatus was a development of Hertz’s laboratory apparatus into a system designed for communications purposes. At first Marconi used a transmitter to ring a bell in a receiver in his attic laboratory. He then moved his experiments out-of-doors on the family estate near Bologna, Italy, to communicate further. He replaced Hertz’s vertical dipole with a vertical wire topped by a metal sheet, with an opposing terminal connected to the ground. On the receiver side, Marconi replaced the spark gap with a metal powder coherer, a detector developed by Edouard Branly and other experimenters. Marconi transmitted radio signals for about a mile at the end of 1895.[36]
By 1895, Marconi introduced to the public a device in London, asserting it was his invention. Despite Marconi's statements to the contrary, though, the apparatus resembles Tesla's descriptions in the widely translated articles.[37] Marconi's later practical four-tuned system was pre-dated by N. Tesla, Oliver Lodge, and J. S. Stone.[38] Marconi’s late-1895 transmission of signals was for around a mile.[39]
Marconi's reputation is largely based on these accomplishments in radio communications and commercializing a practical system. His demonstrations of the use of radio for wireless communications, equipping ships with life saving wireless communications, establishing the first transatlantic radio service, and building the first stations for the British short wave service, have marked his place in history. Marconi and his company were not alone in the field; his principal competition came from German scientists whose work would become the basis for the Telefunken company (which Nikola Tesla assisted in building).
Marconi's U.S. patent 586,193 (July 13, 1897) (and the reissued U.S. patent RE11913) disclosed a two-circuit system for the transmission and reception of "Hertzian waves" (though he would later acknowledge that in the early wireless systems the "waves do not propagate in the same manner as free radiation from a classical Hertzian oscillator, but glide along the surface of the Earth"[40]). The transmitter was an antenna circuit, with an aerial plate and a ground plate, and a spark gap. Induced signals in the circuit were caused to discharge through a spark gap, producing oscillations which were radiated. The receiver contained an antenna circuit, an aerial plate and a ground plate, and a coherer. Marconi's apparatus was to be resonant (commonly called by various researcheres at the time syntonic). This was done by the careful determination of the size of the aerial plates.
The Poldhu experiment
In 1901, Marconi claimed to have received daytime transatlantic radio frequency signals at a wavelength of 366 metres (820 kHz).[41][42][43] The early spark transmitters may have been broadly tuned and the Poldhu transmitter may have radiated sufficient energy in that part of the spectrum for a transatlantic transmission, if Marconi was using an untuned receiver when he claimed to have received the transatlantic signal at Newfoundland in 1901. When he used a tuned receiver aboard the SS Philadelphia in 1902, he could only receive a daytime signal from Poldhu, a distance of 700 miles, less than half the distance from Poldhu to Newfoundland. At night the signals were reported to have been received several times further, and his successful transatlantic transmissions from Glace Bay, Nova Scotia in 1902 were made at night. Marconi would later found the Marconi Company and would jointly receive the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics with Karl Ferdinand Braun.
Marconi’s 1901 Poldhu to Newfoundland transmission claim has been criticized.[44] Critics have claimed that it is more likely that Marconi received stray atmospheric noise from atmospheric electricity in the 1901 experiment.[45] The transmitting station in Poldhu, Cornwall used a spark-gap transmitter that could produce a signal just below the medium frequency and with high power levels (a maximum time-averaged power of 35 kilowatts, but with a peak pulse power of megawatts). The message received was the morse letter 'S' - three dots. Dr Jack Belrose has recently contested this, however, based on theoretical work as well as a reenactment of the experiment; he believes that Marconi heard only random atmospheric noise and mistook it for the signal. There are various science historians who agree with Jack Belrose (in addition to being bolstered by Tesla supporters) that the Atlantic was not bridged in 1901, but other science historians have taken the position that this was the first trans-atlantic radio transmission.
20th century patents
Shortly after the turn of the 20th century, the US Patent Office reawarded Marconi a patent for radio. The U.S. patent RE11913 was granted on June 4, 1901. Marconi's U.S. patent 676,332 was awarded on June 11, 1901, also. This system was more advanced than his previous works.
Individual "inventors of radio"
Tesla and Marconi
| Name | Pro | Con | Earliest transmission |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Tesla developed means to reliably produce radio frequency currents.[46] In 1891 and afterwards, lectured about high-frequency devices and demonstrated devices using power without the use of wires.[47][48][49][50][51][52] Referring to a demonstration of his wireless equipment in 1893 the IEE said "the apparatus that he employed contained all the elements of spark and continuous wave that were incorporated into radio transmitters before the advent of the vacuum tube".[53] By 1895, stated that he had the ability to transmit signals under 50 miles.[54][17][55][56][57] In 1897, Tesla applied for patent protection for the radio arts.[58] In 1900 Tesla was granted U.S. patent 645,576[59] and U.S. patent 649,621[60]. In 1898, demonstrated a radio controlled boat in Madison Square Garden that allowed secure communication between transmitter and receiver.[61] After 1915, assisted the Telefunken engineers in constructing the Telefunken Wireless Station (the "Arco-Slaby system"[62]) in Sayville, Long Island. |
Primarily because of financial difficulties, Tesla never completed his "worldwide wireless system".[63] The Wardenclyffe Tower transceiver that he began at Shoreham on Long Island, New York was eventually torn down. | 1891 [64][65] | |
| Marconi | In summer 1895, Marconi sent signals 1.5 km.[66]
In 1896, applied for British patent protection for a radio system. In 1900, he was granted British patent No. 12,039. Transmission over 6 km in March and May 1897.[67] Transatlantic transmission on 12 December 1901.[68] Transmission over 3,378 km in February 1902.[69] Transatlantic message on 17 December 1902.[70] In 1897 Marconi founded "Wireless Telegraph and Signal Company"[71] and exploited the "Marconi System"[62][72][73][74] of radio commercially. |
His 1901 transatlantic transmission is disputed.[44]
Most of Marconi's system components were developed by others.[75] Oliver Lodge claimed British patent of 1900 to contain his own ideas which he failed to patent. Marconi's more advanced U.S. patent 676,332[76] was filed after contributions made by other investigators.[77] |
1895 |
Other inventors and researchers
| Name | Pro | Con | Earliest transmission |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bose | Researched coherers.[78][79]
Transmitted microwaves over distance of 75 feet in 1895.[80][81] Had transmitted microwaves nearly a mile by 1896.[82][83][84] |
Did not pursue commercialization. [85][86] | 1895 |
| Deforest | The triode amplifier and the Audion tube. | Late date upon beginning research into space telegraphy. | n/a[citation needed] |
| Henry | Henry detected electromagnetic effects at a distance of two hundred feet.[87][88][89] | He was focused on wired telegraphy and researched self-inductance.[90][91] | 1829[92] |
| Hertz | By 1888, Hertz had studied and understood the work of Maxwell and, by design, produced the first clear and undisputed experimental evidence for the transmission and reception of radio waves.[8] | Hertz took this work no further, did not exploit it commercially, and famously did not consider it useful.[8] | 1888 |
| Hughes | In 1879, Hughes began research into radio waves. He noticed electrical interference in an induction balance he was working with.[93][94] The observed effect was due to radio waves and he discovered and improved the coherer.[95] | Hughes was not trying to design equipment for wireless communication. His discovery was taken no further.[95] | 1879[95][96] |
| Loomis | In 1872, received a patent for a "wireless telegraph". Patent utilizes atmospheric electricity to eliminate the overhead wire used by the existing telegraph systems. | His patent U.S. patent 129,971 was for the purpose of receiving and imparting atmospheric electricity. | None (n/a) |
| Lodge | On 14 August 1894 Lodge sent a radio message in Morse code.[97] | Did not pursue further.[98] | 1894 |
| Maxwell | By 1864 Maxwell had become the first person to demonstrate theoretically the existence of radio (electromagnetic) waves, which are used by all radio equipment.[99][100] | Maxwell did not generate or receive radio waves.[101] | None (n/a) |
| Popov | Confirmed laboratory demonstration of radio on 17 May 1895. In March 1896 publicly demonstrated the sending of a signal 550 m between two campus buildings.[102] By 1900 he had reliable communications over 25 miles.[103] | Was not the first to send signals significant distances.[104] | 1895 |
| Ward | Ward was the first person to be granted a US patent relating to wireless telegraphy.[105][106] | His patent U.S. patent 126,356 was for the purpose of receiving and imparting natural electricity.[107] | None (n/a) |
Tesla vs. Marconi
- United States Patent Dispute
| Marconi v. United States | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Argued April 9-12, 1943 Decided June 21, 1943 | |
| Full case name | Marconi Wireless Telegraph co. of America v. United States, United States v. Marconi Wireless Telegraph co. of America |
| Citations | 320 U.S. 1 (more) |
| Holding | |
| The broad claims of the Marconi Patent No. 763,772, for improvements in apparatus for wireless telegraphy — briefly, for a structure and arrangement of four high-frequency circuits with means of independently adjusting each so that all four may be brought into electrical resonance with one another — held invalid because anticipated. P. 320 U. S. 38. | |
| Court membership | |
| |
| Case opinions | |
| Majority | Stone, joined by Roberts, Black, Reed, Douglas, Jackson, Rutledge |
| Dissent | Rutledge |
| Dissent | Frankfurter |
Radio patent decision
In 1943 a lawsuit regarding Marconi's radio patents was resolved by the United States Supreme Court, who overturned most of these. The Marconi Company brought this suit in the Court of Claims to recover damages for infringement of four United States patents. Two, U.S. patent 763,772 and U.S. patent RE11913, were issued to Marconi, a third, U.S. patent 609,154, to Lodge, and a fourth, U.S. patent 803,684, to Fleming. The court held that the Marconi reissue patent was not infringed. The court found Marconi showed no invention over Stone (U.S. patent 714,756) by making the tuning of his antenna circuit adjustable, or by using Lodge's variable inductance for that purpose. At the time, the United States Army was involved in a patent infringement lawsuit with Marconi's company regarding radio, leading various observers to posit that the government nullified Marconi's other patents in order to moot any claims for compensation (as, it is speculated, the government's initial reversal to grant Marconi the patent right in order to nullify any claims Tesla had for compensation).
The court decision was based on the proven prior work conducted by others, such as by Tesla, Oliver Lodge, and John Stone Stone, from which some of Marconi patents stemmed. The U. S. Supreme Court stated that,
- "The Tesla patent No. 645,576, applied for September 2, 1897 and allowed March 20, 1900, disclosed a four-circuit system, having two circuits each at transmitter and receiver, and recommended that all four circuits be tuned to the same frequency. [... He] recognized that his apparatus could, without change, be used for wireless communication, which is dependent upon the transmission of electrical energy."[108]
In making their decision, the court noted,
- "Marconi's reputation as the man who first achieved successful radio transmission rests on his original patent, which became reissue No. 11,913, and which is not here [320 U.S. 1, 38] in question. That reputation, however well-deserved, does not entitle him to a patent for every later improvement which he claims in the radio field. Patent cases, like others, must be decided not by weighing the reputations of the litigations, but by careful study of the merits of their respective contentions and proofs."[109]
The court also stated that,
- "It is well established that as between two inventors priority of invention will be awarded to the one who by satisfying proof can show that he first conceived of the invention."[110]
Priority of Patents
|
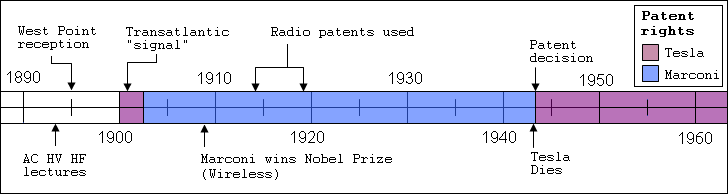
Timeline
The identity of the original inventor of radio, at the time called wireless telegraphy, is contentious. The key invention for the beginning of "wireless transmission of data using the entire frequency spectrum" has been attributed to various inventors and researchers. Below is a selection of pertinent events and individuals related to the development of radio.

References and citation
Notes
- ^ a b The Invention of Radio inventors.about.com/od/rstartinventions/a/radio.htm
- ^ 320 U.S. 1. Marconi Wireless Telegraph co. of America v. United States
- ^ Cheney, M., Uth, R., & Glenn, J. (1999). Tesla, master of lightning. New York: Barnes & Noble Books. Page 71.
- ^ Massie, W. W., & Underhill, C. R. (1911). Wireless telegraphy and telephony popularly explained. New York: D. Van Nostrand.
- ^ Hertzian Waves (1901) Accessed 2008-08-11
- ^ Hertz wave
- ^ Peterson, Gary, "Comparing the Hertz-wave and Tesla wireless systems". Feed Line No. 9 Article
- ^ a b c d Eugenii Katz, "Heinrich Rudolf Hertz". Biographies of Famous Electrochemists and Physicists Contributed to Understanding of Electricity, Biosensors & Bioelectronics.
- ^ tesla2006
- ^ Johnson, R., & Brown, J. H. (1904). "Nikola Tesla", The twentieth century biographical dictionary of notable Americans. Boston: Biographical Society. (cf., He was called the father of wireless telegraphy, which theory he first described in a lecture before the National Electric Light association at St. Louis, Mo., March, 1893; his ideas being given practical demonstration by Marconi in 1902.)
- ^ "On Light and Other High Frequency Phenomena". Delivered before the Franklin Institute, Philadelphia, February 1893, and before the National Electric Light Association, St. Louis, March 1893.
- ^ "Experiments with Alternating Currents of High Potential and High Frequency". Delivered before the Institution of Electrical Engineers, London, February 1892.
- ^ a b "Nikola Tesla, 1856 - 1943". IEEE History Center, IEEE, 2003.
- ^ Martin, T. C., & Tesla, N. (1894). The inventions, researches and writings of Nikola Tesla, with special reference to his work in polyphase currents and high potential lighting. New York: The Electrical Engineer.
- ^ The True Wireless, Electrical Experimenter, May 1919, pages 28-30, 61-63, 87.
- ^ One such location was his Houston street lab in New York City to West Point.
- ^ a b Tesla, N., & Childress, D. H. (2000). The Tesla papers. Kempton, Ill: Adventures Unlimited. Page 136.
- ^ Nikola Tesla On His Work With Alternating Currents and Their Application to Wireless Telegraphy, Telephony and Transmission of Power : An Extended Interview. Chapter IV ISBN 1-893817-01-6 (cf., [Counsel] What do you mean by high frequencies?
[Tesla] I mean frequencies of 30,000, 40,000, 50,000, or something like that.
[Counsel] And by means of that machine, you put undamped waves of frequency about 50,000 into that antenna at Houston Street in 1895?
[Tesla] No [with that machine], not in 1895. Late in 1895 the machine was furnished and I began to operate in early 1896. That is when I began to operate.
[Counsel] Then you did this, that I speak of, in 1896?
[Tesla] Yes, from 1896 to 1899, right along.) - ^ "Nikola Tesla On His Work with Alternating Currents and Their Application to wireless Telegraphy, Telephony, and Transmission of Power", Leland I. Anderson, Twenty First Century Books, 2002, pp. 26-27.]
- ^ PBS: Marconi and Tesla: Who invented radio?
- ^ U.S. patent 454,622, June 23, 1891 (ed., This patent is cited in Maver's Wireless Telegraphy by William Maver on Page 165.)
- ^ "The True Wireless"
- ^ "ibid"
- ^ "On Light and Other High Frequency Phenomena". Delivered before the Franklin Institute, Philadelphia, February 1893, and before the National Electric Light Association, St. Louis, March 1893.
- ^ Why AM Radio Stations Must Reduce Power, Change Operations, or Cease Operations at Night fcc.gov
- ^ D.T. Emerson, "The work of Jagadis Chandra Bose: 100 years of mm-wave research". National Radio Astronomy Observatory, February 1998.
- ^ "The Guglielmo Marconi Case; Who is the True Inventor of Radio".
- ^ "Jagadish Chandra Bose". ieee-virtual-museum.org.
- ^ "The Work of Jagdish Chandra Bose: 100 years of mm-wave research". tuc.nrao.edu.
- ^ "Jagadish Chandra Bose", ieee-virtual-museum.org.
- ^ Bondyopadhyay, Probir K., "Sir J. C. Bose's Diode Detector Received Marconi's First Transatlantic Wireless Signal Of December 1901 (The "Italian Navy Coherer" Scandal Revisited)". Proc. IEEE, Vol. 86, No. 1, January 1988.
- ^ Henry M. Bradford, "Marconi's Three; Transatlantic Radio Stations In Cape Breton". Read before the Royal Nova Scotia Historical Society, 31 January 1996. (ed. the site is reproduced with permission from the Royal Nova Scotia Historical Society Journal, Volume 1, 1998.)
- ^ In a US patent U.S. patent 676,332 in 1901 (page 2, line 69) Marconi uses the words "Tesla coil" for a high frequency oscillator
- ^ Tesla's 1893 presentation at the Franklin Institute was reported across America (such as in The Century Magazine) and throughout Europe.
- ^ Ljubo Vujovi, "Tesla Biography; Nikola Tesla, The genius who lit the world". Teslasociety.com.
- ^ Marconi's Three; Transatlantic Radio Stations In Cape Breton.
- ^ P.J.Papadopoulos, "Nikola Tesla; The Guglielmo Marconi Case, Who is the True Inventor of Radio?" Originally at http://www.mercury.gr/tesla/marcen.html
- ^ Tesla was the first, though, to expound the principles of the four-tuned system. The earlier two-tuned systems were not practical for commercial activity (as found in the United States court case). In addition, other prior work was conducted by others (such as by Hertz and Braun, but not excluding others) from which many of Marconi's devices and methods were derived. Marconi's U.S. patent 676,332 Apparatus for wireless telegraphy [1901], in which a more intricate system was disclosed than in his earlier patents, was filed after contributions made by other investigators.
- ^ This was small when put against Tesla's transmissions below 50 miles.
- ^ Marconi, "Wireless Telegraphic Communication: Nobel Lecture, December 11, 1909." Nobel Lectures. Physics 1901–1921. Amsterdam: Elsevier Publishing Company, 1967: 196–222.
- ^ Henry M. Bradford, "Marconi in Newfoundland: The 1901 Transatlantic Radio Experiment".
- ^ Henry M. Bradford, "Did Marconi Receive Transatlantic Radio Signals in 1901? - Part 1". Wolfville, N.S..
- ^ Henry M. Bradford, "Did Marconi Receive Transatlantic Radio Signals in 1901? Part 2, Conclusion: The Trans-Atlantic Experiments". Wolfville, N.S..
- ^ a b John S. Belrose, "Fessenden and Marconi; Their Differing Technologies and Transatlantic Experiments During the First Decade of this Century" International Conference on 100 Years of Radio, 5-7 September, 1995. Accessed 2008-08-09
- ^ "Marconi's Error: The First Transatlantic Wireless Telegraphy in 1901"
- ^ U.S. patent 447,920
- ^ Tesla's presentation at the Franklin Institute was reported across America (such as in The Century Magazine) and throughout Europe.
- ^ "Nikola Tesla, 1856 - 1943". IEEE History Center, IEEE, 2003. (cf., In 1891 he lectured on his high-frequency devices to the American Institute of Electrical Engineers, and this lecture, coupled with a spectacular demonstration of these apparatuses, made him famous. He [later in 1892] repeated his performance in Europe, to great acclaim, and enjoyed international celebrity.)
- ^ "On Light and Other High Frequency Phenomena". Delivered before the Franklin Institute, Philadelphia, February 1893, and before the National Electric Light Association, St. Louis, March 1893.
- ^ "Experiments with Alternating Currents of High Potential and High Frequency". Delivered before the Institution of Electrical Engineers, London, February 1892.
- ^ Tesla; Man Out of Time By Margaret Cheney. Page 144.
- ^ Ljubo Vujovi, "Tesla Biography; Nikola Tesla, The genius who lit the world". Teslasociety.com.
- ^ "Nikola Tesla, 1856 - 1943". IEEE History Center, IEEE, 2003. (cf., In a lecture-demonstration given in St. Louis in [1893] - two years before Marconi's first experiments - Tesla also predicted wireless communication; the apparatus that he employed contained all the elements of spark and continuous wave that were incorporated into radio transmitters before the advent of the vacuum tube.)
- ^ Nikola Tesla On His Work With Alternating Currents and Their Application to Wireless Telegraphy, Telephony and Transmission of Power : An Extended Interview. Chapter IV ISBN 1-893817-01-6 (cf., [Counsel] What form of device did you use, and where did you use it, for noting the generation of these oscillations or waves in the antenna?
[Tesla] [...] With such an instrument, I operated, for instance, in West Point — I received signals from my laboratory on Houston Street in West Point.
[Counsel] This was then the machine that you used when working with West Point?
[Tesla] I operated once or twice with it at that distance, but usually as I was investigating in the city. [...]") - ^ Who Invented Radio? (cf., By early 1895, Tesla was ready to transmit a signal 50 miles to West Point, New York ... But in that same year, disaster struck. A building fire consumed Tesla's lab, destroying his work.)
- ^ Leland I. Anderson (ed.), "John Stone Stone, Nikola Tesla's Priority in Radio and Continuous-Wave Radiofrequency Apparatus". The Antique Wireless Review, Vol. 1. 1986. 24 pages, illustrated. (ed., available at Twenty First Century Books)
- ^ Marshall Cavendish Corporation. (2008). Inventors and inventions. New York: Marshall Cavendish. Page 1395
- ^ U.S. Supreme Court, "Marconi Wireless Telegraph co. of America v. United States". 320 U.S. 1. Nos. 369, 373. Argued April 9-12, 1943. Decided June 21, 1943. (cf. The Tesla patent No. 645,576, applied for September 2, 1897, [...] disclosed a four-circuit system, having two circuits each at transmitter and receiver, and recommended that all four circuits be tuned to the same frequency. [... the apparatus could be] used for wireless communication, which is dependent upon the transmission of electrical energy.)
- ^ "System of Transmission of Electrical Energy", (March 20, 1900; filed Sept. 2, 1897)
- ^ "Apparatus for Transmission of Electrical Energy" (May 15, 1900; filed February 19, 1900)
- ^ The schematics are illustrated in U.S. patent 613,809 and describes "rotating coherers".
- ^ a b Collins, A. F. (1913). Manual of wireless telegraphy and telephony. New York: J. Wiley. Page 177 - 209
- ^ Wardenclyffe - A Forfeited Dream
- ^ Tesla, Nikola (1891). "Experiments with Alternate Currents of Very High Frequency and Their Application to Methods of Artificial Illumination".
- ^ The True Wireless. Electrical Experimenter, May 1919, pages 28-30, 61-63, 87. (cf., The popular impression is that my wireless work was begun in 1893, but as a matter of fact I spent the two preceding years in investigations, employing forms of apparatus, some of which were almost like those of today.)
- ^ Guglielmo Marconi -- Britannica Online Encyclopedia
- ^ BBC Wales, "Marconi's Waves"
- ^ Marconi's Achievement (1902)
- ^ http://www.ieee.ca/millennium/radio/radio_differences.html
- ^ Marconi's Wellfleet (Cape Cod) Wireless. Stormfax.
- ^ "Wireless Telegraph and Signal Company" was formed on 20 July 1897 after granting of a British patent
- ^ http://home.luna.nl/~arjan-muil/radio/marconi/marconi-system.html
- ^ Beauchamp, K. G. (2001). History of telegraphy. London: Institution of Electrical Engineers. Page 206
- ^ American Institute of Electrical Engineers. (1884). Transactions of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers. New York: American Institute of Electrical Engineers. Page 120
- ^ "Marconi Wireless Tel. Co. v. United States, 320 U.S. 1 (U.S. 1943)", 320 U.S. 1, 63 S. Ct. 1393, 87 L. Ed. 1731 Argued April 9,12, 1943. Decided June 21, 1943. http://caselaw.lp.findlaw.com/scripts/printer_friendly.pl?page=us/320/1.html (cf., But it is now held that in the important advance upon his basic patent Marconi did nothing that had not already been seen and disclosed.)
- ^ Apparatus for wireless telegraphy [1901]
- ^ Intellectual Property Law for Engineers and Scientists By Howard B. Rockman, IEEE. Page 196 - 199.
- ^ Fleming, J. A. (1908). The principles of electric wave telegraphy. London: New York and. (cf., [...] researches of Professor J. C. Bose are of particular interest. He states that the sensitiveness of any form of contact cymoscope consisting of conducting particles depends upon the proper adjustment of the pressure between the particles and the value of the external electromotive force which is in waiting, so to speak, to send or increase the current through the contacts.) See J. C. Bose, Proc. Soy. Soc. Land., 1899, vol. G5, p. 166 ; or Science Abstracts, vol. ii. No. 1716.
- ^ Institution of Electrical Engineers, Physical Society (Great Britain), American Physical Society, American Institute of Electrical Engineers, Electrochemical Society, & Associazione elettrotecnica italiana. (1898). Science abstracts. [London]: Institution of Electrical Engineers. Page 963
- ^ Prof Rajesh Kochhar, J.C. BOSE: The Inventor Who Wouldn’t Patent. Science Reporter, Feb 2000
- ^ The life and work of Sir Jagadis C. Bose on page 62
- ^ In 1896, the Daily Chronicle of England reported on his UHF experiments: "The inventor (J.C. Bose) has transmitted signals to a distance of nearly a mile and herein lies the first and obvious and exceedingly valuable application of this new theoretical marvel."
- ^ Jagadis Chandra Bose and His Pioneering Research on Microwave
- ^ jcbose, calcuttaweb.com
- ^ "Jagadish Chandra Bose", ieee-virtual-museum.org
- ^ Geddes, P. (1920). The life and work of Sir Jagadis C. Bose. London: Longmans, Green.
- ^ Fleming, J. A. (1908). The principles of electric wave telegraphy. London: New York and Co. (cf., Joseph Henry, in the United States, between 1842 and 1850, explored many of the puzzling facts connected with this subject, and only obtained a clue to the anomalies when he realized that the discharge of a condenser through a low resistance circuit is oscillatory in nature. Amongst other things, Henry noticed the power of condenser discharges to induce secondary currents which could magnetize steel needles even when a great distance separated the primary and secondary circuits.)
- ^ See "The Scientific Writings" of Joseph Henry, vol. i. pp. 203, 20:-i ; also Proceedings of tltc American Assoc. fur Advancement of Science, 1850, vol. iv. pp. 877, 378, Joseph Henry, "On the Phenomena of the Leyden Jar." The effect of the oscillatory discharge on a magnetized needle is clearly described in this paper.
- ^ Ames, J. S., Henry, J., & Faraday, M. (1900). The discovery of induced electric currents. New York: American book. (cf. On moving to Princeton, in 1832, [...] investigated also the discharge of a Leyden jar, proved that it was oscillatory in character, and showed that its inductive effects could be detected at a distance of two hundred feet, thus clearly establishing the existence of electro-magnetic waves.)
- ^ Eugenii Katz, "Joseph Henry". Biographies of Famous Electrochemists and Physicists Contributed to Understanding of Electricity, Biosensors & Bioelectronics.
- ^ Timeline of the First Thirty Years of Radio
- ^ Ames, J. S., Henry, J., & Faraday, M. (1900). The discovery of induced electric currents. New York: American book (cf., [...] experiment was performed in August 1829.)
- ^ Researches of Prof. D. E. Hughes (1899)
- ^ http://tenwatts.blogspot.com/2006/03/bio-david-e-hughes.html
- ^ a b c Darrel T. Emerson, The Stage Is Set: Developments before 1900 Leading to Practical Wireless Communication
- ^ Eugenii Katz, "David Edward Hughes". Biographies of Famous Electrochemists and Physicists Contributed to Understanding of Electricity, Biosensors & Bioelectronics.
- ^ Peter Rowlands (ed.) and J. Patrick Wilson (ed.) "Oliver Lodge and the Invention of Radio" ISBN 1-873694-02-4
- ^ OTB - Oliver Lodge: Almost the Father of Radio. antiquewireless.org.
- ^ "Electromagnetism, Maxwell’s Equations, and Microwaves". IEEE Virtual Museum (2008). Retrieved on 2008-06-02.
- ^ James Clerk Maxwell, A Dynamical Theory of the Electromagnetic Field, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London 155, 459-512 (1865).
- ^ Estabrooks, M. (1995). Electronic technology, corporate strategy, and world transformation. Westport, Conn: Quorum Books. Page 27. (cf., [...] Maxwell did not prove that these waves actually existed [...])
- ^ "Early Radio Transmission Recognized as Milestone". IEEE. Retrieved on July 16, 2006.
- ^ Eugenii Katz, "Alexander Stepanovich Popov ". Biographies of Famous Electrochemists and Physicists Contributed to Understanding of Electricity, Biosensors & Bioelectronics.
- ^ By 1895, Tesla stated that he had the ability to transmit signals under 50 miles
- ^ earlyradiohistory Fakes, Frauds, and Cranks (1866-1922)
- ^ The patent called for construction so as to collect, hold, distribute, and utilize aerial currents of natural electricity for telegraphic and other purposes.
- ^ Specification forming part of Letters Patent No. 126,356, dated April 30, 1872.
- ^ U.S. Supreme Court, "Marconi Wireless Telegraph co. of America v. United States". 320 U.S. 1. Nos. 369, 373. Argued April 9-12, 1943. Decided June 21, 1943.
- ^ Wireless Telegraph co. of America v. United States.
- ^ Wireless Telegraph co. of America v. United States.
General Information
- Offline
- Anderson, L.I., "Priority in the Invention of Radio: Tesla vs. Marconi", Antique Wireless Association Monograph No. 4, March, 1980.
- Anderson, L.I., "John Stone Stone on Nikola Tesla's Priority in Radio and Continuous-Wave Radiofrequency Apparatus", The A.W.A. (Antique Wireless Association) Review, Vol. 1, 1986, pp. 18-41.
- Weblinks
- "Marconi Wireless Tel. Co. v. United States, 320 U.S. 1 (U.S. 1943)", 320 U.S. 1, 63 S. Ct. 1393, 87 L. Ed. 1731 Argued April 9,12, 1943. Decided June 21, 1943.
- Howeth, Captian H.S. History of Communications – Electronics in the United States Navy, published 1963, GPO, 657 pages. Free online public domain US government published book.
- Wunsch, A.D., "Misreading the Supreme Court,” Antenna, Volume 11 No. 1, November 1998, Society for the History of Technology
- Brand, W.E., "Rereading the Supreme Court: Tesla's Invention of Radio", Antenna, Volume 11 No. 2, May 1998, Society for the History of Technology
- "Wireless telegraphy", The Encyclopaedia Britannica. (1922). London: Encyclopaedia Britannica.
- Mazzotto, D., & Bottone, S. R. (1906). Wireless telegraphy and telephony. London: Whittaker & Co.
- Fleming, J. A. (1908). The principles of electric wave telegraphy. London: New York and Co.
- Murray, J. E. (1907). A handbook of wireless telegraphy. New York: D. Van Nostrand Co.; [etc.].
- Twining, H. L. V., & Dubilier, W. (1909). Wireless telegraphy and high frequency electricity; a manual containing detailed information for the construction of transformers, wireless telegraph and high frequency apparatus, with chapters on their theory and operation. Los Angeles, Cal: The author.
- Massie, W. W., & Underhill, C. R. (1911). Wireless telegraphy and telephony popularly explained. New York: D. Van Nostrand.
- Sewall, C. H. (1904). Wireless telegraphy: its origins, development, inventions, and apparatus. New York: D. Van Nostrand.
- Collins, A. F. (1905). Wireless telegraphy; its history, theory and practice. New York: McGraw Pub.
- Fahie, J. J. (1900). A history of wireless telegraphy, 1838-1899: including some bare-wire proposals for subaqueous telegraphs. Edinburgh: W. Blackwood and Sons.
- Colby, F. M., Williams, T., & Wade, H. T. (1930). "Wireless Telegraphy", The New international encyclopaedia. New York: Dodd, Mead and Co.
- Trevert, E. (1904). The A.B.C. of wireless telegraphy; a plain treatise on Hertzian wave signaling; embracing theory, methods of operation, and how to build various pieces of the apparatus employed. Lynn, Mass: Bubier Pub.
- Stanley, R. (1919). Text-book on wireless telegraphy. London: Longmans, Green.
- Thompson, S. P. (1915). Elementary lessons in electricity and magnetism. New York: Macmillan
- Telegraphing across space, Electric wave method. The Electrical engineer. (1884). London: Biggs & Co.
- Simmons, H. H. (1908). "Wireless telegraphy", Outlines of electrical engineering. London: Cassell and Co.
- Bottone, S. R. (1910). Wireless telegraphy and Hertzian waves. London: Whittaker & Co.
- Erskine-Murray, J. (1909). A handbook of wireless telegraphy: its theory and practice, for the use of electrical engineers, students, and operators. New York: Van Nostrand.
- American Institute of Electrical Engineers. (1884). "Wireless Telephony — By R. A. Fessenden (Illustrated.)", Transactions of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers. New York: American Institute of Electrical Engineers.
- The New Physics and Its Evolution. Chapter VII : A Chapter in the History of Science: Wireless telegraphy by Lucien Poincare, eBook #15207, released February 28, 2005.
- Stanley, R. (1914). Text book on wireless telegraphy. London: Longmans, Green.
- Comparative Study of the Hertz, Marconi and Tesla Low-Frequency Wireless Systems
- Timeline: First Thirty Years of Radio, 1895-1925

See also
- People
- Edwin Howard Armstrong, John Stone Stone, Ernst Alexanderson, Reginald Fessenden, Oliver Lodge,
- Radio
- [[[Radio communication system]], Timeline of radio, Oldest radio station, Birth of public radio broadcasting
- Categories
- Radio People, Radio Pioneers, Discovery and invention controversies
- Other
- Radiotelegraph and Spark-Gap Transmitters, The Great Radio Controversy, Induction coil, Ruhmkorff coil, Poldhu, Alexanderson alternator, De Forest tube