W.
W or w (spoken: [ veː ]) is the 23rd letter of the modern Latin alphabet and is a consonant in most of the languages in which it is used . The W originally emerged as a ligature in the Middle Ages , i. H. as a doubling of the "V" or "U". The letter W has a relative frequency of 1.89% in German texts. It is the 17th most common letter in German texts .
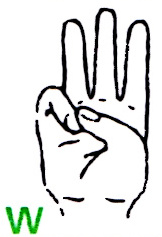
The finger alphabet for the deaf or hard of hearing represents the letter W , with the flat hand pointing away from the body and the index , middle and ring fingers pointing upwards. The thumb rests on the fingernail of the little finger .
origin
|
|
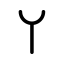
|

|
|
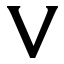
|

|
| Waw sign (Protosinaitic) | Phoenician vaw | Greek Ypsilon | Etruscan V | Latin V / U | Latin W |
The W shares a large part of its history with the U and V , besides the Y and the F are related to it.
Nothing is known about the sound value and meaning of the letter in the Protosinaitic script , the corresponding symbol represents a hook or a club with a round head. In the Phoenician alphabet , the letter opened this head and looked like a rounded Y. The letter was named Vaw and was used to represent the phonetic value [w] (a non-syllable [u]).
The letter was added to the Greek alphabet as Ypsilon . In early Greek the sound value of the Ypsilon was the vowel [u] corresponding to the [w ].
The Etruscans adopted the early Greek Ypsilon and its sound value. Over time, the lower point disappeared among the Etruscans, the letter took the form V. The meaning of the letter also changed: Etruscan also knew the half-vowel [w] corresponding to the [u] and the letter was used to denote both sounds write.
The Romans adopted the letter with both sound values. Originally the letter was written in the pointed form adopted by the Etruscans. In late antiquity , a rounded variant was also developed that corresponds to the U in appearance.
Also in late antiquity the unsyllabic [w] developed into a [v]. When, towards the end of the first millennium AD, scripts were created in the Germanic languages that still had the sound [w], the character V was already felt to be unsuitable for its rendering and therefore the ligature VV or UU was created from the the W developed.
This origin is from the name of the letter W in English , double u ('double u') or double-u ('double u'), in French and Italian , double vé or doppia vu ('double vau') still recognizable (it should be noted that at that time no distinction was made between the consonant letter V and the vowel letter U).
The German sound [w] (an unsyllabic [u]) underwent the same development in the Middle Ages that the Latin w sound had already made in late antiquity. He became a [v]. However, some phoneticians are of the opinion that the German w-sound is not a voiced labiodental fricative [v], but a voiced labiodental approximant [ʋ].
The English language , on the other hand, has retained the original pronunciation [w] (unsyllabic [u] or labiovelar approximant , similar to the German word Ba u er ) to this day.
Others
In Sweden , the letter W was only included in the 13th edition of its dictionary by the Swedish Academy in 2006 , making it a separate letter. Before, the W, now the 23rd letter of the Swedish alphabet between V and X, was considered a variation of the letter V (double V) (one reason for this is the same pronunciation of both letters in Swedish). Words beginning with the letter W are words like “whiskey”, “wok” or “webb” borrowed from foreign languages. In addition, W occurs in Swedish proper names (e.g. “ Wasa ”, “ Wilhelmina ”, Woxna ), whereby the W was often used instead of the V and the spelling with V has largely replaced the W in the meantime.
In Welsh , the W is used both as a consonant (before vowels and at the beginning of a word) and as a vowel and can therefore also be provided with a circumflex (ˆ) in accordance with the vowel extension rules .
The rapper / hip-hop the US West Coast use a formed from the fingers of the hand "W" as the recognition symbol for the " West Coast ", said middle and ring fingers are superimposed and form the central top of the W and the outer leg through the small and index finger.
Quote
“In mhd. Zeit, b for w and vice versa w for b is written in Bavarian very often, s. WEINHOLD bair. gram. § 124. 136, which can only be explained by approximation, not by the total coincidence of the sounds. "
swell
- ^ DTV-Brockhaus-Lexikon, Mannheim and Munich 1989, XIX, s. 240
- ^ The "W" becomes the official letter in Sweden. In: news.ch. April 21, 2005, accessed August 11, 2015 .
- ↑ Vhat, no W in Swedish dictionary? Now there is. (No longer available online.) In: sweden.se. April 21, 2006, archived from the original on June 29, 2006 ; accessed on August 11, 2015 .
See also
- ₩
- Abbreviation, acronym, starting with the letter W or w :
- Questioning technique # Open W-questions in practice