(1620) Geographos
|
Asteroid (1620) Geographos |
|
|---|---|
|
|
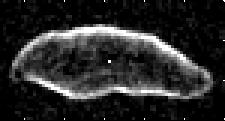
| Radar image | |
| Properties of the orbit ( animation ) | |
| Orbit type | Apollo type |
| Major semi-axis | 1.2454 AU |
| eccentricity | 0.3355 |
| Perihelion - aphelion | 0.8276 AU - 1.6633 AU |
| Inclination of the orbit plane | 13.341 ° |
| Sidereal period | 1,390 a |
| Mean orbital velocity | 26.69 km / s |
| Physical Properties | |
| Medium diameter | 5 × 2 × 1.5 km |
| Albedo | 0.19 |
| Rotation period | 5 h 13 m |
| Absolute brightness | 15.6 mag |
| Spectral class | S type |
| history | |
| Explorer | A. Wilson , R. Minkowski |
| Date of discovery | September 14, 1951 |
| Another name | 1951 RA, 1983 CY 3 |
| Source: Unless otherwise stated, the data comes from JPL Small-Body Database Browser . The affiliation to an asteroid family is automatically determined from the AstDyS-2 database . Please also note the note on asteroid items. | |
(1620) Geographos is a near-Earth asteroid (planetoid) from the group of the Apollo asteroids . These are heavenly bodies whose orbits can cross the earth's orbit.
The asteroid was on 14 September 1951 at the Mount Palomar - Observatory discovered. The name means geographer and the naming was in honor of the National Geographic Society .
Geographos moves between 0.8276 AU ( perihelion ) and 1.6633 AU ( aphelion ) in around 508 days around the sun . The orbit eccentricity is 0.3355, the orbit is inclined by 13.341 ° to the ecliptic .
Radar observations carried out in 1994 showed that Geographos is an elongated object measuring 5 × 2 × 1.5 km. The asteroid rotates around its own axis in around 5 hours and 13 minutes.
The American space probe Clementine was supposed to visit Geographos after its stay on the moon. However, due to an engine malfunction, the asteroid was not reached.