1,4-dichlorobenzene
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 1,4-dichlorobenzene | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 4 Cl 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white crystalline solid with a camphor-like odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 147.00 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.248 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
53 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
174 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water (49 mg / l at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
Switzerland: 20 ml m −3 or 122 mg m −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
1,4-dichlorobenzene , also called paradichlorobenzene ( PDCB , p-DCB ), is an aromatic chemical compound consisting of a benzene ring with two chlorine atoms (–Cl) as substituents . It is a by-product of the production of monochlorobenzene and is a solid with a strong odor. With its two constitutional isomers 1,2-dichlorobenzene and 1,3-dichlorobenzene , it belongs to the group of dichlorobenzenes with the empirical formula C 6 H 4 Cl 2 . The substance is found in the air and in water worldwide and is difficult to biodegrade .
presentation
If benzene is used directly with chlorine in the presence of a Lewis acid such as. B. iron (III) chloride or aluminum chloride reacted, the main product is chlorobenzene in 80-90% yield . The 1,2- and 1,4-dichlorobenzenes are only obtained in small amounts as by-products in this reaction.
If the amount of chlorinating agent used is increased significantly, larger amounts of 1,4-dichlorobenzene can be obtained in addition to 1,2-dichlorobenzene and a little 1,3-dichlorobenzene. The more highly chlorinated benzenes (e.g. trichlorobenzenes ) are also formed.
properties
Physical Properties
1,4-Dichlorobenzene crystallizes at room temperature in the monoclinic crystal system in the space group P 2 1 / a (space group no. 14, position 3) with the lattice parameters a = 1480 pm , b = 399 pm, c = 578 pm and β = 113 °. In the unit cell contains two formula units . The crystals are isomorphic to 1,4-dibromobenzene . Two other solid phases exist, the phase transitions take place at 271.77 K and at 304.35 K.
The enthalpy of fusion of 1,4-dichlorobenzene is 17907 J mol −1 . The coefficients of the Antoine equation for 1,4-dichlorobenzene are A = 4.12290, B = 1575.110 and C = −64.637.
Chemical properties
The nitration of 1,4-dichlorobenzene with nitric acid and sulfuric acid initially leads to 2-nitro-1,4-dichlorobenzene, then a mixture of 2,6-dinitro-1,4-dichlorobenzene and 2,5-dinitro- 1,4-dichlorobenzene in a ratio of 7: 1.
use
For 1,4-dichlorobenzene, which is a by-product, some very controversial areas of application have been found in the past. In many toilet stones , the substance has now been replaced by alternative substances such as sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate or sodium carbonate . It is still used today in stones for urinals in gastronomy because it has a strong, raspberry-like smell. However, the substance has no germicidal effect. In urinals, odor neutralization with certain cyclodextrins or terpenes using an evaporator or atomizer would therefore be a biologically acceptable and more effective solution than with 1,4-dichlorobenzene. 1,4-Dichlorobenzene is also still used in mothballs ( globules ) and pesticides as well as in coffin hygiene.
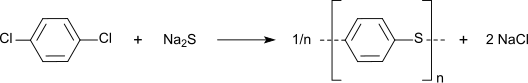
1,4-dichlorobenzene is the starting material for the synthesis of polyphenylene sulfide (PPS), a highly temperature-resistant thermoplastic plastic . The reaction is the polycondensation of 1,4-dichlorobenzene with sodium sulfide , which is carried out in aprotic solvents such as N-methylpyrrolidone .
1,4-Dichlorobenzene ( Globol ) used to be used frequently (and in some cases still on a small scale) to disinfect collections of insects .
hazards
1,4-dichlorobenzene is poorly degradable in the environment. It is very toxic to aquatic organisms (WGK 2) and can therefore have long-term harmful effects. It has a harmful effect in the animal organism by primarily attacking the liver, kidneys and lungs. It is also irritating to the skin and eyes. In more recent studies, the suspicion arose that 1,4-dichlorobenzene could be carcinogenic (carcinogenic / carcinogenic). 1,4-dichlorobenzene depolarizes the nerve cells and thus induces an over-excitability that is comparable to that caused by organochlorine insecticides.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on 1,4-dichlorobenzene in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on 1,4-dichlorobenzene in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 106-46-7 or 1,4-dichlorobenzene ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ a b c Petroleum Derivatives - Ruminants , accessed on July 13, 2011.
- ↑ U. Croatto, S. Bezzi, E. Bua: "The Crystal Structure of p -Dichlorobenzene", in: Acta Cryst. , 1952 , 5 , pp. 825-829; doi : 10.1107 / S0365110X52002203 .
- ^ A. Dworkin, P. Figuière, M. Ghelfenstein, H. Szwarc: "Heat capacities, enthalpies of transition, and thermodynamic properties of the three solid phases of p -dichlorobenzene from 20 to 330 K", in: The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics , 1976 , 8 (9), pp. 835-844; doi : 10.1016 / 0021-9614 (76) 90161-0 .
- ^ PR van der Linde, JC van Miltenburg, GJK van den Berg, HAJ Oonk: "Low-Temperature Heat Capacities and Derived Thermodynamic Functions of 1,4-Dichlorobenzene, 1,4-Dibromobenzene, 1,3,5-Trichlorobenzene, and 1,3,5-Tribromobenzene ", in: J. Chem. Eng. Data , 2005 , 50 (1), pp. 164-172; doi : 10.1021 / je049762q .
- ↑ Entry on 1,4-dichlorobenzene . In: P. J. Linstrom, W. G. Mallard (Eds.): NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69 . National Institute of Standards and Technology , Gaithersburg MD, accessed July 19, 2011.
- ^ PN Walsh, NO Smith: "Sublimation Pressure of α- p -Dichloro-, β- p -Dichloro, p -Dibromo-, and p -Bromochlorobenzene", in: J. Chem. Eng. Data , 1961 , 6 (1), pp. 33-35; doi : 10.1021 / je60009a010 .
- ↑ HJ Page, BR Heasman "nitration of p-Dichlorobenzene", in: J. Chem Soc Trans... , 1923 , 123 , pp 3247 to 3255; doi : 10.1039 / CT9232303247 .
- ↑ P. Hartley, JB Cohen: "The Nitration Products of the Isomeric Dichlorobenzenes", in: J. Chem. Soc., Trans. , 1904 , 85 , pp. 865-870; doi : 10.1039 / CT9048500865 ; Full text .
- ↑ a b Abwasserlexikon: Paradichlorbenzol
- ↑ Patent US3354129 : Production of polymers from aromatic compounds. Published November 21, 1967 , inventor: JT Edmonds, HW Hill.
- ↑ Gerfried Deschka: The disinfection of small insect collections according to more recent points of view , Steyrer Entomologenrunde 21, Steyr 1987; Table of contents .