Amidosulfonic acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
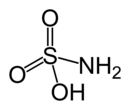
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Amidosulfonic acid | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | H 2 NSO 3 H | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless and odorless, orthorhombic crystals or powder |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 97.09 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
2.13 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
205 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
0.78 Pa (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
~ 1 |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility | ||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Amidosulphonic acid is a colorless crystalline substance which, analogous to sulphamide - the diamide of sulfuric acid - can be understood as the monoamide of sulfuric acid . The salts of amidosulfonic acid are called amidosulfonates or sulfamates.
Manufacturing
Amidosulfonic acid is produced from urea , sulfuric acid and disulfuric acid :
properties
Amidosulfonic acid forms colorless to whitish yellow crystals , which melt at 205 ° C with the onset of decomposition and violent smoke development and dissolve well in water . The solution is acidic. Due to its acidic properties, direct contact is irritating and corrosive to the eyes and skin . Amidosulfonic acid is not hygroscopic and can therefore be used as a base substance .
The structure of the sulfamic acid can be described by the formula + H 3 N-SO 3 - . It is therefore present as a zwitterion . The tautomeric form H 2 N-SO 2 (OH) does not exist in the solid state.
use
Amidosulfonic acid in concentrations of 10–15%, often 14%, is (mostly in addition to phosphoric acid or citric acid ) a component of decalcifying agents and sanitary cleaners, in the laboratory it is used as a basic substance and to destroy nitrite :
In electroplating technology , sulfamic acid is used to adjust the pH of nickel sulfamate baths to pH 3.9 to 4.2. A solution of amidosulfonic acid with sodium lauryl sulfate at 35 to 40 ° C is also used to activate a nickel layer.
By reaction of sulfamic acid with cyclohexylamine is sodium cyclamate , an artificial sweetener made.
The ammonium sulfamate is an important flame retardants .
determination
The content of an aqueous sulfamic acid solution can be determined by means of titration analysis. The reaction equation for this acid-base titration is:
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Georg Brauer (Ed.), With the collaboration of Marianne Baudler u a .: Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 3rd, revised edition. Volume I, Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1975, ISBN 3-432-02328-6 , p. 487.
- ↑ a b c d Entry on sulfamic acid. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on May 30, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d Entry on sulphamic acid in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 10, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d Data sheet amidosulfonic acid (PDF) from Merck , accessed on January 19, 2011.
- ↑ Entry on Sulphamidic acid in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .




