Armoracia
| Armoracia | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Horseradish ( Armoracia rusticana ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Armoracia | ||||||||||||
| G. Gaertn. & B.Mey. & Scherb. |
Armoracia is a genus of plants in the cruciferous family (Brassicaceae). The genus includes two to three species worldwide. The best-known type, the horseradish, is often cultivated due to its distinctive, pungent smell and served with many dishes.
description
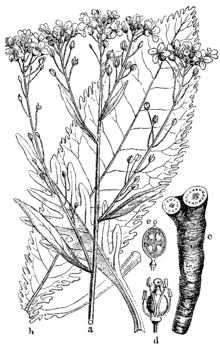
Vegetative characteristics
The Armoracia species grow as perennial , herbaceous plants . They form tap roots as persistence organs. No parts of the plant have trichomes (plant hair). The upright stems are branched towards the tip.
The leaves are both in basal rosettes and distributed on the stem ( phyllotaxis ). The basal leaves are long-stalked, simply with notched or smooth leaf margins . The stem leaves, on the other hand, have petioles in the lower area and the upper ones are sessile. Their leaf blades are pinnate with notched to slit leaf margins .
Generative characteristics
The racemose partial inflorescences are grouped in paniculate or often umbrella-shaped overall inflorescences and contain many flowers , but no bracts. The inflorescences lengthen until the fruit is ripe. The slender flower stalks are rising, sparse or slightly bent back when the fruit ripe.
The hermaphroditic flowers are fourfold with double perianth . The four expanded or emerging sepals are ovate or oblong in shape. The four white-colored petals are longer than the sepals, ascending and show an inverted egg-shaped or inverted-lanceolate shape . In two circles (diplostemon) there are a total of six stamens , slightly spreading , with four somewhat longer stamens in the inner circle and two shorter stamens in the outer circle. The stamens are slightly widened at the base. The anthers show an egg-shaped to oblong linear shape with blunt tips. The nectar glands are at the base of all stamens, with the middle glands also being present. The ovary contains 8 to 20 ovules . The stylus is either absent or short and measures a maximum of 2 millimeters. The scar is heady or sometimes bilobed.
Stalked, elongated, egg-shaped, elliptical or spherical pods are formed. The bare and smooth valves have no veins. The replum is rounded and the septum perforated or reduced to a wreath. The seeds , laid out in two rows, are wingless, plump and ovate-elongated. The seed coat is spotted and does not become sticky or slimy when wet.
Spread, endangerment and protection
One species of the genus Armoracia was originally thought to have been native to Eastern Europe , the second species is known from Asia in Siberia and East Asia, and the third species inhabits the eastern half of the North American continent. The cultivation of the originally Eastern European species, the horseradish, meant that this species found new habitats through naturalization. They colonize wet or damp habitats.
The International Union for Conservation of Nature IUCN does not have any Armoracia species on the Red List of Threatened Species - they are therefore viewed globally as not endangered.
Systematics
The genus Armoracia was set up in 1800 by Philipp Gottfried Gaertner , Bernhard Meyer and Johannes Scherbius in Oekonomisch-Technische Flora der Wetterau , 2, pp. 426-428. They published the species name Armoracia rusticana P.Gaertn for the horseradish . , B.Mey. & Scherb. , which was first published as Cochlearia armoracia L. in 1753. A synonym for Armoracia P.Gaertn. , B.Mey. & Scherb. is Raphanis Moench . The genus Armoracia belongs to the tribe Cardamineae within the cruciferous family (Brassicaceae).
The genus Armoracia contains two or three species:
- Horseradish ( Armoracia rusticana ) G.Gaertn. , B.Mey. & Scherb. : With the presumed original distribution in Eastern Europe and through cultivation and subsequent naturalization, now very widespread and also on other continents.
- Armoracia sisymbroides ( DC. ) Cajander : The home is in Siberia and in Russian East Asia.
In some sources, a third species Armoracia lacustris ( A.Gray ) Al-Shehbaz & VMBates is mentioned, but according to the Brassicaceae specialist Ihsan Ali Al-Shehbaz and other sources, it is included in the genus Rorippa as Rorippa aquatica .
swell
- Ihsan Ali Al-Shehbaz: Armoracia in the Flora of North America , Volume 7, 2010, p. 459: Online.
- Tai-yien Cheo, Lianli Lu, Guang Yang, Ihsan Al-Shehbaz & Vladimir Dorofeev: Brassicaceae in der Flora of China , Volume 8, 2001, p. 86: Armoracia - Online.
Individual evidence
- ^ A b Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN): Taxon: Armoracia G.Gaertn. et al. In: GRIN Taxonomy for Plants. United States Department of Agriculture Agricultural Research Service, accessed June 30, 2010 .
- ^ Ihsan A. Al-Shehbaz: Armoracia in the Flora of North America , Volume 7, 2010, p. 455: Armoracia rusticana - Online.
- ^ Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN): Taxon: Armoracia sisymbroides. In: GRIN Taxonomy for Plants. United States Department of Agriculture Agricultural Research Service, accessed June 30, 2010 .