Hematoma
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| T14.0 | Superficial injury to an unspecified part of the body |
| T00.9 | Multiple superficial injuries, unspecified |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
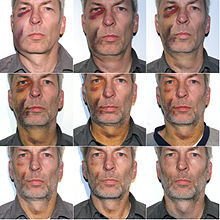
A hematoma (from ancient Greek αἷμα haima , German ' blood ' and ancient Greek τομή tome , German 'cut, cut' ) is a blood leak from injured blood vessels in body tissue or an accumulation of blood in a pre-existing body cavity . A hematoma is depending on the location and extent, bruising , suffusion , Suggilation , bruise or (eye) Violet called.
The suffusion or bruise is a two-dimensional skin or mucosal bleeding after injury or bleeding disorders.
The term sugillation , which is usually the same to a lesser extent, is also defined as an extensive and up to 30 mm large leakage of blood from the capillary vessels ( diapedesis ) into the skin ( skin bleeding ). It occurs mainly in coagulopathy (clotting disorders).
A so-called hickey is a hypobaric (created by negative pressure) sugillation.
Cause and course
Hematomas are mostly bleeding events in the subcutaneous area that result from external force, e.g. B. impact, blow, fall or after an operation . They can swell a lot and be very painful. However, they can also occur in the case of hemophilia without direct trauma . As a rule, a bruise heals on its own within two to three weeks. Different colors appear as the healing process progresses as the blood is broken down by the body. The phases can be explained as follows:
- Red: the small vessels ( capillaries ) burst and the blood (red due to hemoglobin ) enters the tissue
- Dark red-blue: the blood coagulates
- Brown-black: enzymatic breakdown of hemoglobin to choleglobin / verdoglobin (bile pigment)
- Dark green: enzymatic breakdown of hemoglobin to biliverdin (bile pigment) by hemoxygenase ( NADPH / H -dependent).
- Yellow-brown: enzymatic breakdown of hemoglobin to bilirubin (bile pigment) by biliverdin reductase ( NADP / H -dependent).
By immediately cooling the injured area, the pain and its spread can be contained because the blood vessels contract and therefore less blood escapes.
Heavily swelling hematomas require rapid medical, usually surgical, treatment in order to avoid necrosis and loss of skin.
Hematomas can be differentiated according to their location:
- just under the skin (subcutaneous bruise)
- in muscle tissue (intramuscular bruise)
- in or under the periosteum (periosteal bruise)
- in certain parts of the body (such as joints or the brain)
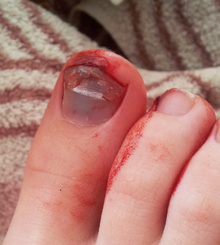
- under a fingernail or toenail ( subungual hematoma )
A hematoma under the periosteum is accompanied by severe pain; In the medium term, pressure-sensitive, u. U. permanent, palpable indurations come. For first aid, the PECH rule ( break - ice - compression - elevation ) must be observed; an anti-coagulant ointment may have to be used. It often occurs in the shin because the bone is hardly protected by tissue or muscles in between in the event of a bruise , such as a blow with an angular object or a fall against a stair nosing.
Haematomas in the brain area (see cerebral haemorrhage ) and internal hematomas, as well as hemophilia or the use of anticoagulant ("blood-thinning") drugs (e.g. Marcumar ) are dangerous . In the latter case, hematomas can already be triggered by a minor trauma or a lesion . Also in the (supporting) joints such as the knee , ankle , hip can bloody effusions are formed and the formation of a repeated occurrence in osteoarthritis favor. Hematomas in muscle boxes , caused e.g. B. by a " horse kiss " can lead to a compartment syndrome and in extreme cases make a fasciotomy necessary.
In the course of the myelodysplastic syndrome , more and more hematomas appear all over the body.
Forensic medicine
In forensic medicine, suffusions are important for three reasons:
Age determination
The blood underflow changes color over time and takes on the following colors: dark blue-violet (1st – 5th day), greenish (6th – 8th day), yellowish (from 8th day).
Vital or post-mortem development
Suffusions can also arise post-mortem, but are usually in areas with a loose cell structure and extremely rarely in firm muscle tissue. Color changes as described above always indicate a vital reaction.
Conclusion about the instrument of the crime
Sometimes blood shifts into the surrounding tissue can lead to imprints of the instrument of the crime , e.g. B. with stick lashes (light recess between the parallel stripes).
See also
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ A. Hirner et al. a .: surgery . Thieme Verlag, 2004, ISBN 3-13-130841-9 , p. 388 ( limited preview in the Google book search).
- ^ Pschyrembel. Clinical Dictionary. 255th edition. De Gruyter, Berlin / New York 1986, ISBN 3-11-007916-X , p. 1621.
- ↑ a b H. S. Füeßl, M. Middeke: Anamnesis and clinical examination. Georg Thieme Verlag, 2010, ISBN 3-131-26884-0 , p. 369. Limited preview in the Google book search.
- ^ F. Horn: Biochemistry of humans, textbook for medical students . 3. Edition. Thieme, Stuttgart 2005.
- ^ Rolf Haaker: Sports injuries - what to do? Prophylaxis and sports physiotherapy treatment . Springer, 1998, ISBN 978-3-642-58917-1 , p. 39 ( limited preview in the Google book search).
- ^ Emergency operation on national player Christian Ziege . In: FAZ , December 29, 2002, Sport.